Abstract
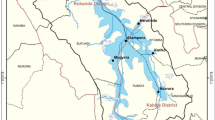
Poyang Lake Migratory Bird Sanctuary includes Bang Lake, Sha Lake, Dahu Lake, and estuaries of the Xiu and Gan Rivers in the Migratory Bird Natural Reserve. Water samples were collected and analyzed to study spatial and temporal water quality variation. Strong seasonal variation of water quality was found. The water quality of Bang Lake was relatively poor compared to Sha and Dahu Lakes in the wet season, but better in the normal season. During the dry season, the water quality of Bang Lake is negatively affected by the activity of migratory birds. According to the correlation analysis of monthly concentrations of each parameter, the concentrations of COD, NH4 +–N, and NO3 −–N were highly correlated. The correlation index was 0.829 and significance index was 0.042 < 0.05. From north to south within Bang Lake, the concentration of TN decreased; however, the concentration of Chl-a increased. From east to west within Bang Lake, concentrations of COD, NH4 +–N, NO3 −–N, and Chl-a increased. The Xiu and Gan Rivers influence the water quality of Bang Lake, especially in the northeast area of the lake. The water quality of Bang Lake only reached Chinese water quality standard level IV or V according to a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. The evaluation factors impacting Bang Lake are TN>TP>NH4 +–N>COD, in order of decreasing importance. The waters of Poyang Lake Migratory Bird Sanctuary have been polluted; one of the important contributing factors was migratory birds’ disturbance and feces.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng X, Zhao Y, Wu F, Lin Y, Lu Q, Dai J (2011) Analysis of the trade-off between economic growth and the reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus emissions in the Poyang Lake Watershed, China [J]. Ecol Model 222:330–336
Guo H, Hu Q, Jiang T (2008) Annual and seasonal streamflow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin, China [J]. J Hydrol 355:106–122
Hadas O, Altabet MA, Agnihotri R (2009) Seasonally varying nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry of particulate organic matter in Lake Kinneret, Israel [J]. Limnol Oceanogr 54(1):75–85
Hu C, Lou Q, Ding W, Zhou W (2012) Study on the retention effect of nitrogen and phosphate nutrients in Poyang Lake [J]. Environ Pollut Control 34(9):1–4 (In Chinese)
Kolada A (2014) The effect of lake morphology on aquatic vegetation development and changes under the influence of eutrophication [J]. Ecol Ind 38:282–293
Kundzewicz ZW, Mata LJ, Arnell NW, Döll P, Kabat P, Jiménez B, Miller KA, Oki T, Sen Z, Shiklomanov IA (2007) Freshwater resources and their management. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 73–210
Lehmann MF, Bernasconi SM, McKenzie JA (2004) Seasonal variation of the δ13 C and δ15 N of particulate and dissolved carbon and nitrogen in Lake Lugano: constraints on biogeochemical cycling in a Eutrophic lake [J]. Limnol Oceanogr 49(2):415–429
Liou Y, Lo S (2005) A fuzzy index model for trophic status evaluation of reservoir waters [J]. Water Res 39:1415–1423
Liou S, Lo S, Hu C (2003) Application of two-stage fuzzy set theory to river quality evaluation in Taiwan [J]. Water Res 37:1406–1416
Liu C, Liu X (2012) Research on Poyang Lake wetland information extraction and change monitoring based on spatial data mining [J]. Phys Procedia 33:1412–1419
Lu M, Zeng D, Liao Y, Tong B (2012) Distribution and characterization of organochlorine pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediment from Poyang Lake, China [J]. Sci Total Environ 433:491–497
Minghui L, Wen Z, Yu X, Yongsheng G (2011) Study on removal efficiencies of pollutant from constructed wetland in aquiculture waste water around Poyang Lake [J]. Procedia Environ Sci 10:2444–2448
Mvungi EF, Lyimo TJ, BjÖrk M (2012) When Zostera marina is intermixed with Ulva, its photosynthesis is reduced by increased pH and lower light, but not by changes in light quality [J]. Aquat Bot 102:44–49
Ocampo-Duque W, Osorio C, Piamba C, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2013) Water quality analysis in rivers with non-parametric probability distributions and fuzzy inference systems: application to the Cauca River, Colombia [J]. Environ Int 52:17–28
Schiemer F, Hein T, Peduzzi P (2006) Hydrological control of system characteristics of floodplain lakes [J]. Ecohydrol hydrol 6(1–4):7–18
SEPA, Editorial Board of water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring analysis method (fourth edition) [M]. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 210–281
Vatn A (2010) An institutional analysis of payments for environmental services [J]. Ecol Econ 69(6):1245–1252
Wang S, Jin X, Zhao H, Wu F (2006) Phosphorus fractions and its release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River area in China. Coll Surf A 273:109–116
Wang M, Zhou W, Hu C (2008) Status of nitrogen and phosphorus in waters of Lake Poyang Basin. J Lake Sci 20(3):334 –338 In Chinese
Wang X, Gong P, Zhao Y, Xu Y, Cheng X, Niu Z, Luo Z, Huang H, Sun F, Li X (2013a) Water-level changes in China’s large lakes determined from ICESat/GLAS data [J]. Remote Sens Environ 132:131–144
Wang Y, Yu X, Zhang L, Lei G (2013b) Seasonal variability in baseline δ15 N and usage as a nutrient indicator in Lake Poyang, China [J]. J Freshw Ecol 28(3):365–373
Wu L, Li M, Guo Y, Yang X (2011) Influence of Three Gorges project on water quality of Poyang Lake [J]. Procedia Environ Sci 10:1496–1501
Wu HY, Chen KL, Chen ZH, Chen QH, Qiu YP, Wu JC, Zhang JF (2012) Evaluation for the ecological quality status of coastal waters in East China Sea using fuzzy integrated assessment method [J]. Mar Pollut Bull 64:546–555
Zhang B, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Tang C, Yu Y, Ma Y (2012) Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China [J]. Water Res 46:2737–2748
Zhen L, Li F, Huang H, Dilly O, Liu J, Wei Y, Yang L, Cao X (2011) Households’ willingness to reduce pollution threats in the Poyang Lake region, southern China [J]. J Geochem Explor 110:15–22
Zhou Z, Zhang X, Dong W (2013) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for safety guarantee system of reclaimed water quality [J]. Procedia Environ Sci 18:227–235
Zhu H, Zhang B (1997) Poyang Lake hydrology, biology, sediment, wetlands, and development [M]. China University of Science and Technology Press, Hefei, pp 125–128
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 20123BBG70192), Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GJJ13074), and by the Key Laboratory of Poyang Lake environment and resource utilization, Ministry of Education, Nanchang University (No.13006462).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Xiao, H., Liu, X. et al. Spatial and temporal water quality characteristics of Poyang Lake Migratory Bird Sanctuary in China. Chin. J. Geochem. 34, 38–46 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0017-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0017-3