Abstract
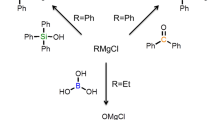
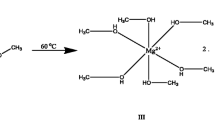
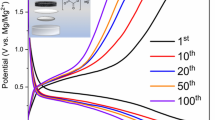
Magnesium bis(oxalate)borate salt (Mg(B(C2O4)2)2 or Mg(BOB)2) was prepared by a solid-state reaction solvent-free process, and is potentially viable to be used as an electrolytic material for magnesium ion batteries (MIBs). The synthesis was achieved by mixing oxalic acid, boric acid, and magnesium hydroxide using a molar ratio of 4:2:1, respectively. The resulting powders were dried under vacuum at 60°C, then pressed into pellets, and heated at 110 °C for 3 h, with a final heating at 150 °C for 12 h. The crystalline structure and particle morphology of the reaction product were characterized by x-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy results confirmed the presence of functional groups in the final product, identified by the absorption bands C = O, C-O-B-O-C, O-B-O, and B-O. In order to evaluate the electrochemical properties, pure crystalline Mg(BOB)2 powders were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (THF) and evaluated within a three-electrode electrolytic cell and in half-cells through cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liang, C.-Z. Zhao, H. Yuan, Y. Chen, W. Zhang, J.-Q. Huang, Yu. Dingshan, Y. Liu, M.-M. Titirici, Y.-L. Chueh, Yu. Haijun, and Q. Zhang, A review of rechargeable batteries for portable electronic devices. InfoMat 1, 6 (2019).
D. Gielen, F. Boshell, D. Saygin, M.D. Bazilian, N. Wagner, and R. Gorini, The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 24, 38 (2019).
B. John, Goodenough, How we made the Li-ion rechargeable battery. Nat. Electron. 1, 204 (2018).
A. Ramar and F.-M. Wang, Advances in polymer electrode materials for alkali metals (lithium, sodium and potassium)-ion rechargeable batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. 31, 21832 (2020).
A. Watanabe, K. Yamamoto, Y. Orikasa, T. Masese, T. Mori, T. Uchiyama, T. Matsunaga, and Y. Uchimoto, Reaction mechanism of electrochemical insertion/extraction of magnesium ions in olivine-type FePO4. Solid State Ion. 349, 115311 (2020).
X. Lei, Y. Zheng, F. Zhang, Y. Wang, and Y. Tang, Highly stable magnesium-ion-based dual-ion batteries based on insoluble small-molecule organic anode material. Energy Storage Mater. 30, 34 (2020).
Z. Zhang, S. Dong, Z. Cui, Du. Aobing, G. Li, and G. Cui, Rechargeable magnesium batteries using conversion-type cathodes: a perspective and minireview. Small Methods 2, 1800020 (2018).
T. Placke, R. Kloepsch, S. Dühnen, and M. Winter, Lithium ion, lithium metal, and alternative rechargeable battery technologies: the odyssey for high energy density. J. Solid State Electrochem. 21, 1939 (2017).
R. Attias, M. Salama, B. Hirsch, Y. Goffer, and D. Aurbach, Anode-electrolyte interfaces in secondary magnesium batteries. Joule 3, 1 (2019).
R. Deivanayagam, B.J. Ingram, and R. Shahbazian-Yassar, Progress in development of electrolytes for magnesium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 21, 136 (2019).
R. Dominko, J. Bitenc, R. Berthelot, M. Gauthier, G. Pagot, and V. Di Noto, Magnesium batteries: current picture and missing pieces of the puzzle. J. Power Sour. 478, 229027 (2020).
M. Rashad, M. Asif, Y. Wang, Z. He, and I. Ahmed, Recent advances in electrolytes and cathode materials for magnesium and hybrid-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 25, 342 (2020).
Z. Zhang, Z. Cui, L. Qiao, J. Guan, Xu. Huimin, PuHu. Xiaogang Wang, Du. Huiping, S. Li, X. Zhou, S. Dong, Z. Liu, G. Cui, and L. Chen, Novel design concepts of efficient Mg-ion Electrolytes Toward High-Performance Magnesium-Selenium And Magnesium-Sulfur Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602055 (2017).
A. Le Bail, Monte carlo indexing with McMaille. Powder Diffr. 19, 249 (2004).
K. He, N. Chen, C. Wang, L. Wei, and J. Chen, Method for determining crystal grain size by X-Ray diffraction. Cryst. Res. Technol. 53, 1700157 (2018).
E.M. Wigayati, C.R. Ratri, I. Purawiardi, F. Rohman, T. Lestariningsih, Microstructure analysis of synthesized LiBOB. Indones. J. Chem. 15, 242 (2015).
C. Ge, L. Wang, L. Xue, Wu. Zhong-Shuai, H. Li, Z. Gong, and X.-D. Zhang, Synthesis of novel organic-ligand-doped sodium bis(oxalate)-borate complexes with tailored thermal stability and enhanced ion conductivity for sodium ion batteries. J. Power Sour. 248, 77 (2014).
L. Wang, W. Han, C. Ge, R. Zhang, Y. Bai, and X. Zhang, Functionalized carboxyl carbon/NaBOB composite as highly conductive electrolyte for sodium ion batteries. ChemistrySelect 3, 9293 (2018).
T. Lestariningsih, Christin Rina Ratri, Etty Marty Wigayati, and Qolby Sabrina, Characterization of pore and crystal structure of synthesized LiBOB with varying quality of raw materials as electrolyte for lithium-ion battery. AIP Conf. Proc. 1711, 060005–060011 (2016).
Etty Marti Wigayati, Titik Lestariningsih, Achmad Subhan, Christin Rina Ratri, and Ibrahim Purawiardi, Synthesis and characterization of LiBOB as electrolyte for lithium-ion battery. Ionics 22, 43 (2016).
Etty Marti Wigayati, Titik Lestariningsih, Christin Rina Ratri, Ibrahim Purawiardi, and Bambang Prihandoko, Synthesis of LiBOB fine powder to increase solubility. Makara J. Technol. 21, 26 (2017).
C. Zor, Yaprak Subası̧, Durata Haciu, Mehmet Somer, and Semih Afyon, guide to water free lithium Bis(oxalate) borate (LiBOB). J. Phys. Chem. C. 125, 11310 (2021).
F. Cheng, X. Zhang, Y. Qiu, J. Zhang, Yi. Liu, P. Wei, Ou. Mingyang, S. Sun, Xu. Yue, Q. Li, C. Fang, J. Han, and Y. Huang, Tailoring electrolyte to enable high-rate and super-stable Ni-rich NCM cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Nano Energy 88, 106301 (2021).
A.A. Kamnev, A.V. Tugarova, Y.A. Dyatlova, P.A. Tarantilis, O.P. Grigoryeva, A.M. Fainleib, and S. De Luca, Methodological effects in Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy: Implications for structural analyses of biomacromolecular samples. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 193, 558 (2018).
E.F. Medvedev and ASh. Komarevskaya, IR Spectroscopic study of the phase composition of boric acid as a component of glass batch. Glass Ceram. 64, 42 (2007).
K. Nakamoto, Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds: Theory and Applications in Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed., (New York: Wiley, 1997).
A. Tsurumaki, M. Branchi, A. Rigano, R. Poiana, and S. Panero, and Maria Assunta Navarra, Bis(oxalato)borate and difluoro(oxalato)borate-based ionic liquids as electrolyte additives to improve the capacity retention in high voltage lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 315, 17 (2019).
T. Lestariningsih, Q. Sabrina, I. Nuroniah, B. Prihandoko, E. Marti Wigayati, and C. Rina Ratri, Study the synthesis of LiBOB compounds using lithium sources from sea water. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1282, 012044 (2019).
L. Shiyou, L. Wenbo, C. Xiaoling, L. Chunlei, H. Yamin, Y. Li, W. Peng, W. Jie, W. Yuan. Patent number: CN 110305151 A (2019)
J. Shi, J. Zhang, J. Guo, and Lu. Jun, Interfaces in rechargeable magnesium batteries. Nanoscale Horiz. 5, 1467 (2020).
Y. Yamada, J. Wang, S. Ko, E. Watanabe, and A. Yamada, Advances and issues in developing saltconcentrated battery electrolytes. Nat. Energy 4, 269 (2019).
T. Ichitsubo, T. Adachi, S. Yagi, and T. Doi, Potential positive electrodes for high-voltage magnesium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 11764 (2011).
T.T. Tran, W.M. Lamanna, and M.N. Obrovac, Evaluation of Mg[N(SO2CF3)2]2/acetonitrile electrolyte for use in Mg-Ion cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, A2005 (2012).
J. Muldoon, C.B. Bucur, A.G. Oliver, T. Sugimoto, M. Matsui, H.S. Kim, G.D. Allred, J. Zajicek, and Y. Kotani, Electrolyte roadblocks to a magnesium rechargeable battery. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 5941 (2012).
P. Saha, M.K. Datta, O.I. Velikokhatnyi, A. Manivannan, D. Alman, and P.N. Kumta, Rechargeable magnesium battery: current status and key challenges for the future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 66, 1 (2014).
R. Mohtadi and F. Mizuno, Magnesium batteries: current state of the art, issues and future perspectives. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 5, 1291 (2014).
K. S. Han, N. T. Hahn, K. R. Zavadil, N. R. Jaegers, Y. Chen, J. Z. Hu, V. Murugesan, and K. T. Mueller (2021). Factors influencing preferential anion interactions during solvation of multivalent cations in ethereal solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C. 125 6005
Z. Ma, D.R. MacFarlane, and M. Kar, Mg cathode materials and electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries: a review. Batter. Supercaps 2, 1 (2019).
Z. Zhao-Karger and M. Fichtner, Beyond intercalation chemistry for rechargeable Mg batteries: a short review and perspective. Front. Chem. 6, 656 (2019).
L. Kong, C. Yan, J.-Q. Huang, M.-Q. Zhao, M.-M. Titirici, R. Xiang, and Q. Zhang, A review of advanced energy materials for magnesium– sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 1, 100 (2018).
H. Shuai, Xu. Jing, and K. Huang, Progress in retrospect of electrolytes for secondary magnesium batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 422, 213478 (2020).
A. Chernyaev, J. Partinen, L. Klemettinen, B.P. Wilson, A. Jokilaakso, and M. Lundstrom, The efficiency of scrap Cu and Al current collector materials as reductants in LIB waste leaching. Hydrometallurgy 203, 105608 (2021).
Y. Youssef, W. El Bestawy, M. Ghazy, M. Shehadeh, and I. Hassan, Investigation of the corrosion behaviour of welded area of austenitic stainless steels under stress. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 9, 135 (2018).
Y. Zhang, H. Geng, W. Wei, J. Ma, and L. Chen, and Cheng Chao Li, challenges and recent progress in the design of advanced electrode materials for rechargeable Mg batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 20, 118 (2018).
O. Tutusaus, R. Mohtadi, T.S. Arthur, F. Mizuno, E.G. Nelson, and Y.V. Sevryugina, An efficient halogen-free electrolyte for use in rechargeable magnesium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 7900 (2015).
S. M. de la Parraarciniega, E. Gonzálezjuárez, R. A. Hernándezcarrillo, R. Brionesmartínez, R. M. Jiménezbarrera, N. A. Garciagómez, E. M. Sánchez. A Mg2+/Li+ hybrid‑ion battery based on MoS2 prepared by solvothermal synthesis with ionic liquid assistance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31 14702 (2020)
V. Duffort, X. Sun, and L.F. Nazar, Screening for positive electrodes for magnesium batteries: a protocol for studies at elevated temperatures. Chem. Commun. 52, 12458 (2016).
A.C. Kucuk, T. Minato, T. Yamanaka, and T. Abe, Effects of LiBOB on salt solubility and BiF3 electrode electrochemical properties in fluoride shuttle batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 8559–8567 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA10396H.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to Facultad de Ciencias Químicas, Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León for financial support and the laboratory equipment used in this project (Materials Laboratory 2) at División de Estudios de Posgrado. Jesús Guzmán-Torres also thanks to CONACYT for the scholarship awarded to continue the PhD studies.
Funding
Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología,888794,Jesus Guzman-Torres,Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León,1940246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JG-T: Investigation, validation, software, formal analysis, and writing-original draft. DLO-G: Helped with electrolytes preparation. LLG-T: XRD testing participation. LCT-G: Electrochemical testing participation. SM de la P-A: FTIR testing participation. EG-J: Battery assembly supervision. IG: Conceptualization and writing comments. EMS: Conceptualization, supervision, writing-review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guzmán-Torres, J., Ochoa-Gamboa, D.L., Garza-Tovar, L.L. et al. Magnesium Bis(Oxalate)Borate as a Potential Electrolyte for Rechargeable Magnesium Ion Batteries. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 1250–1257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10073-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10073-3