Abstract
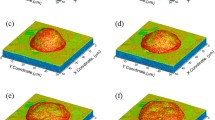
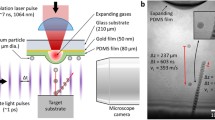
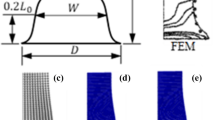
Impact of spherical particles onto a flat sapphire surface was investigated in 50-950 m/s impact speed range experimentally and theoretically. Material parameters of the bilinear Johnson–Cook model were determined based on comparison of deformed particle shapes from experiment and simulation. Effects of high-strain-rate plastic flow, heat generation due to plasticity, material damage, interfacial friction and heat transfer were modeled. Four distinct regions were identified inside the particle by analyzing temporal variation of material flow. A relatively small volume of material near the impact zone becomes unstable due to plasticity-induced heating, accompanied by severe drop in the flow stress for impact velocity that exceeds ~ 500 m/s. Outside of this region, flow stress is reduced due to temperature effects without the instability. Load carrying capacity of the material degrades and the material expands horizontally leading to jetting. The increase in overall plastic and frictional dissipation with impact velocity was found to be inherently lower than the increase in the kinetic energy at high speeds, leading to the instability. This work introduces a novel method to characterize HSR (109 s−1) material properties and also explains coupling between HSR material behavior and mechanics that lead to extreme deformation.













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 March 2018
An acknowledgement was omitted by the authors. The following should have been included with the published article.
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Static yield stress, MPa
- A c :
-
Contact area, m2
- B :
-
Coefficient of strain hardening, MPa
- c :
-
Specific heat, J/kg K
- C :
-
Bilinear strain rate coefficient
- D1 :
-
Height of deformed particle, m
- D2 :
-
Diameter of deformed particle, m
- D p :
-
Diameter of particle, m
- e :
-
Coefficient of restitution
- E :
-
Elastic modulus, error between experiment and simulation aspect ratios
- E k :
-
Kinetic energy of particle, J
- E r :
-
Recovered strain energy, J
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity, W/m K
- m :
-
Index of thermal softening
- m p :
-
Mass of particle, kg
- n :
-
Index of strain-rate hardening
- R e :
-
Experimental aspect ratio
- R s :
-
Simulated aspect ratio
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- T * :
-
Homologous temperature
- T m :
-
Melting temperature, K
- T R :
-
Reference temperature, K
- U p :
-
Energy dissipated due to plastic action, J
- v i :
-
Impact velocity, m/s
- v r :
-
Rebound velocity, m/s
- W f :
-
Work done against friction, J
- x :
-
Optimization variable vector
- α :
-
Thermal expansion ratio, K−1
- β :
-
Inelastic heat fraction
- \(\varepsilon_{f}\) :
-
Failure shear strain
- \(\varepsilon_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Equivalent plastic strain
- \(\dot{\varepsilon }_{ 0}\) :
-
Reference strain rate, s−1
- \(\dot{\varepsilon }_{\text{c}}\) :
-
Critical reference strain rate, s−1
- \(\dot{\varepsilon }_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Equivalent plastic strain rate, s−1
- µ :
-
Kinetic friction coefficient
- ν :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- ρ :
-
Mass density, kg/m3
- σ Y :
-
Yield (flow) stress, MPa
- r :
-
Material properties at room temperature
- CS:
-
Cold spray
- FEA:
-
Finite element analysis
- GZ:
-
Gao-Zhang
- HSR:
-
High strain rate
- JC:
-
Johnson–Cook
- KHL:
-
Khan–Huang–Liang
- LIPIT:
-
Laser-induced projectile impact test
- PDMS:
-
Polydimethylsiloxane
- PTW:
-
Preston–Tonk–Wallace
- VA:
-
Voyiadjis–Abed
- ZA:
-
Zerilli–Armstrong
References
S.V. Klinkov, V.F. Kosarev, and M. Rein, Cold Spray Deposition: Significance of Particle Impact Phenomena, Aerosp. Sci. Technol., 2005, 9(7), p 582-591
M.A. Meyers, Dynamic Behavior of Materials, Wiley, New York, 1994
G.T. Gray, Classic Split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar Testing, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000, p 462-476
H. Kolsky, An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Materials at Very High Rates of Loading, Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. B, 1949, 62(11), p 676
J. Harding, E. Wood, and J. Campbell, Tensile Testing of Materials at Impact Rates of Strain, J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 1960, 2(2), p 88-96
F.E. Hauser, Techniques for Measuring Stress-Strain Relations at High Strain Rates, Exp. Mech., 1966, 6(8), p 395-402
U. Lindholm and L. Yeakley, High Strain-Rate Testing: Tension and Compression, Exp. Mech., 1968, 8(1), p 1-9
D. Rittel, S. Lee, and G. Ravichandran, A Shear-Compression Specimen for Large Strain Testing, Exp. Mech., 2002, 42(1), p 58-64
J. Zhao, H. Li, and Y. Zhao, Dynamic Strength Tests of the Bukit Timah Granite, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 1998
S. Huang, X. Feng, and K. Xia, A Dynamic Punch Method to Quantify the Dynamic Shear Strength of Brittle Solids, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2011, 82(5), p 053901
J. Zhao, An Overview of Some Recent Progress in Rock Dynamics Research, Advances in Rock Dynamics and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011, p 5-33
R. Armstrong and F. Zerilli, Dislocation Mechanics Aspects of Plastic Instability and Shear Banding, Mech. Mater., 1994, 17(2-3), p 319-327
C. Gao and L. Zhang, Constitutive Modelling of Plasticity of FCC Metals Under Extremely High Strain Rates, Int. J. Plast., 2012, 32, p 121-133
G.R. Johnson, and W.H. Cook, A Constitutive Model and Data for Metals Subjected to Large Strains, High Strain Rates and High Temperatures, Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983
A.S. Khan and R. Liang, Behaviors of Three BCC Metal Over a Wide Range of Strain Rates and Temperatures: Experiments and Modeling, Int. J. Plast., 1999, 15(10), p 1089-1109
A.S. Khan and R. Liang, Behaviors of Three BCC Metals During Non-proportional Multi-axial Loadings: Experiments and Modeling, Int. J. Plast., 2000, 16(12), p 1443-1458
D.L. Preston, D.L. Tonks, and D.C. Wallace, Model of Plastic Deformation for Extreme Loading Conditions, J. Appl. Phys., 2003, 93(1), p 211-220
G.Z. Voyiadjis and F.H. Abed, Microstructural Based Models for BCC and FCC Metals with Temperature and Strain Rate Dependency, Mech. Mater., 2005, 37(2), p 355-378
M. Grujicic, C. Zhao, W. DeRosset, and D. Helfritch, Adiabatic Shear Instability Based Mechanism for Particles/Substrate Bonding in the Cold-Gas Dynamic-Spray Process, Mater. Des., 2004, 25(8), p 681-688
T. Hu, S. Zhalehpour, A. Gouldstone, S. Muftu, and T. Ando, A Method for the Estimation of the Interface Temperature in Ultrasonic Joining, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45(5), p 2545-2552
V.K. Champagne, Jr., D. Helfritch, P. Leyman, S. Grendahl, and B. Klotz, Interface Material Mixing Formed by the Deposition of Copper on Aluminum by Means of the Cold Spray Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14(3), p 330-334
M. Grujicic, J. Saylor, D. Beasley, W. DeRosset, and D. Helfritch, Computational Analysis of the Interfacial Bonding Between Feed-Powder Particles and the Substrate in the Cold-Gas Dynamic-Spray Process, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2003, 219(3), p 211-227
S. Guetta, M.-H. Berger, F. Borit, V. Guipont, M. Jeandin, M. Boustie, Y. Ichikawa, K. Sakaguchi, and K. Ogawa, Influence of Particle Velocity on Adhesion of Cold-Sprayed Splats, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(3), p 331-342
T. Hussain, D. McCartney, P. Shipway, and D. Zhang, Bonding Mechanisms in Cold Spraying: The Contributions of Metallurgical and Mechanical Components, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(3), p 364-379
H. Assadi, F. Gärtner, T. Stoltenhoff, and H. Kreye, Bonding Mechanism in Cold Gas Spraying, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(15), p 4379-4394
W.-Y. Li, H. Liao, C.-J. Li, G. Li, C. Coddet, and X. Wang, On High Velocity Impact of Micro-sized Metallic Particles in Cold Spraying, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 253(5), p 2852-2862
T. Schmidt, H. Assadi, F. Gärtner, H. Richter, T. Stoltenhoff, H. Kreye, and T. Klassen, From Particle Acceleration to Impact and Bonding in Cold Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(5-6), p 794
T. Schmidt, F. Gärtner, H. Assadi, and H. Kreye, Development of a Generalized Parameter Window for Cold Spray Deposition, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(3), p 729-742
W. Li, D. Zhang, C. Huang, S. Yin, M. Yu, F. Wang, and H. Liao, Modelling of Impact Behaviour of Cold Spray Particles: Review, Surf. Eng., 2014, 30(5), p 299-308
G. Bae, Y. Xiong, S. Kumar, K. Kang, and C. Lee, General Aspects of Interface Bonding in Kinetic Sprayed Coatings, Acta Mater., 2008, 56(17), p 4858-4868
B. Yildirim, H. Fukanuma, T. Ando, A. Gouldstone, and S. Müftü, A Numerical Investigation into Cold Spray Bonding Processes, J. Tribol., 2015, 137(1), p 011102
S. Müftü, S. Zhalehpour, A. Gouldstone, and T. Ando, Assessment of Interface Energy in High Velocity Particle Impacts, 38th Annual Meeting of The Adhesion Society. Savannah, GA, 2015
B. Yildirim, S. Müftü, and A. Gouldstone, On Cohesion of Micron Scale Metal Particles in High Velocity Impact with a Metal Substrate, ASME/STLE 2011 International Joint Tribology Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2011
W.-Y. Li, C. Zhang, X. Guo, C.-J. Li, H. Liao, and C. Coddet, Study on Impact Fusion at Particle Interfaces and Its Effect on Coating Microstructure in Cold Spraying, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 254(2), p 517-526
A. Alkhimov, A. Gudilov, V. Kosarev, and N. Nesterovich, Specific Features of Microparticle Deformation Upon Impact on a Rigid Barrier, J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys., 2000, 41(1), p 188-192
G. Bae, S. Kumar, S. Yoon, K. Kang, H. Na, H.-J. Kim, and C. Lee, Bonding Features and Associated Mechanisms in Kinetic Sprayed Titanium Coatings, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(19), p 5654-5666
S. Schoenfeld and T. Wright, A Failure Criterion Based on Material Instability, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2003, 40(12), p 3021-3037
T.W. Wright and J.W. Walter, On Stress Collapse in Adiabatic Shear Bands, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1987, 35(6), p 701-720
T. Wright and H. Ockendon, A Scaling Law for the Effect of Inertia on the Formation of Adiabatic Shear Bands, Int. J. Plast., 1996, 12(7), p 927-934
T. Wright, Shear Band Susceptibility: Work Hardening Materials, Int. J. Plast., 1992, 8(5), p 583-602
B. Yildirim, S. Muftu, and A. Gouldstone, Modeling of High Velocity Impact of Spherical Particles, Wear, 2011, 270(9-10), p 703-713
W. Xie, A. Alizadeh-Dehkharghani, Q. Chen, V.K. Champagne, X. Wang, A.T. Nardi, S. Kooi, S. Müftü, and J.-H. Lee, Dynamics and Extreme Plasticity of Metallic Microparticles in Supersonic Collisions, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, p 5073
J.-H. Lee, P.E. Loya, J. Lou, and E.L. Thomas, Dynamic Mechanical Behavior of Multilayer Graphene Via Supersonic Projectile Penetration, Science, 2014, 346(6213), p 1092-1096
J.-H. Lee, D. Veysset, J.P. Singer, M. Retsch, G. Saini, T. Pezeril, K.A. Nelson, and E.L. Thomas, High Strain Rate Deformation of Layered Nanocomposites, Nature communications, 2012, 3, p 1164
S. Barradas, V. Guipont, R. Molins, M. Jeandin, M. Arrigoni, M. Boustie, C. Bolis, L. Berthe, and M. Ducos, Laser Shock Flier Impact Simulation of Particle-Substrate Interactions in Cold Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2007, 16(4), p 548-556
M. Arrigoni, M. Boustie, C. Bolis, S. Barradas, L. Berthe, and M. Jeandin, Shock Mechanics and Interfaces, Mechanics of Solid Interfaces, M. Braccini and M. Dupeux, Eds., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118561669.ch7
M. Jeandin, D.K. Christoulis, F. Borit, M.-H. Berger, S. Guetta, G. Rolland, V. Guipont, F. N’Guyen, D. Jeulin, and E. Irissou, A Socratic Approach to Surface Modification: The Example of Thermal Spray, 24th International Conference on Surface Modification Technologies, SMT 24, 2010
M. Hassani-Gangaraj, D. Veysset, K.A. Nelson, and C.A. Schuh, In-situ Observations of Single Micro-particle Impact Bonding, Scripta Mater., 2018, 145, p 9-13
Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp., P., RI, USA, ABAQUS/Explicit 6.13 User Manual. 2013
Dehkharghani, A.A., Tuning Johnson–Cook Material Model Parameters for Impact of High Velocity, Micron Scale Aluminum Particles, Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering. 2016, MS Thesis, Northeastern University.
Yildirim, B., Mechanistic Modeling of High Velocity Micro-particle Impacts: Application to Material Deposition by Cold Spray Process, in Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering. 2013, PhD Thesis, Northeastern University
T. Belytschko, J.S.-J. Ong, W.K. Liu, and J.M. Kennedy, Hourglass Control in Linear and Nonlinear Problems, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 1984, 43(3), p 251-276
JAHM Software Inc., I., MPDB Material Database Software, 1998
A. Manes, D. Lumassi, L. Giudici, and M. Giglio, An Experimental–Numerical Investigation on Aluminium Tubes Subjected to Ballistic Impact with Soft Core 7.62 Ball Projectiles, Thin-Walled Structures, 2013, 73, p 68-80
A. Manes, L. Peroni, M. Scapin, and M. Giglio, Analysis of Strain Rate Behavior of an Al 6061 T6 Alloy, Procedia Engineering, 2011, 10, p 3477-3482
R.G. Munro, Evaluated Material Properties for a Sintered alpha-Alumina, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, 80(8), p 1919-1928
S.P. Keeler and W.A. Backofen, Plastic Instability and Fracture in Sheets Stretched Over Rigid Punches, Asm. Trans. Q., 1963, 56(1), p 25-48
Z. Marciniak and K. Kuczyński, Limit Strains in the Processes of Stretch-Forming Sheet Metal, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 1967, 9(9), p 609IN1613-612IN2620
G.R. Johnson and W.H. Cook, Fracture Characteristics of Three Metals Subjected to Various Strains, Strain Rates, Temperatures and Pressures, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1985, 21(1), p 31-48
F.J. Zerilli and R.W. Armstrong, Dislocation-Mechanics-Based Constitutive Relations for Material Dynamics Calculations, J. Appl. Phys., 1987, 61(5), p 1816-1825
R. Liang and A.S. Khan, A Critical Review of Experimental Results and Constitutive Models for BCC and FCC Metals Over a Wide Range of Strain Rates and Temperatures, Int. J. Plast., 1999, 15(9), p 963-980
S. Rahmati and A. Ghaei, The Use of Particle/Substrate Material Models in Simulation of Cold-Gas Dynamic-Spray Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2014, 23(3), p 530-540
D.R. Lesuer, G. Kay, and M. LeBlanc, Modeling Large-Strain, High-Rate Deformation in Metals, Third Biennial Tri-Laboratory Engineering Conference on Modeling and Simulation, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Pleasanton, CA (US), 2001
L. Pun, Introduction to Optimization Practice, Wiley, New York, 1969
L.R. Grace and M. Altan, Characterization of Anisotropic Moisture Absorption in Polymeric Composites Using Hindered Diffusion Model, Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2012, 43(8), p 1187-1196
K.L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge Cambridgeshire; New York, 1985, p 452
B. Yildirim, H. Yang, A. Gouldstone, and S. Müftü, Rebound Mechanics of Micrometre-Scale, Spherical Particles in High-Velocity Impacts, Proc. R. Soc. A., 2017, 473, p 20160936
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Alizadeh, A., Xie, W. et al. High-Strain-Rate Material Behavior and Adiabatic Material Instability in Impact of Micron-Scale Al-6061 Particles. J Therm Spray Tech 27, 641–653 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-018-0712-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-018-0712-4