Abstract
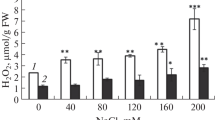
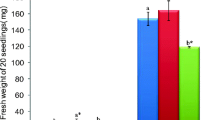
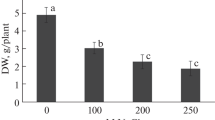
Comparative study about the salt-induced oxidative stress and lipid composition has been realised in primary root tissues for two varieties of maize (Zea mays L.) in order to evaluate their responses to salt stress. The root growth, root water content (WC), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) generation, lipid peroxidation, membrane stability index and the changes in the profile of fatty acids composition were investigated. Salinity impacts in term of root growth, water content, H2O2 generation, lipid peroxidation and membrane destabilisation were more pronounced in primary roots of Aristo than in those of Arper indicating more sensitivity of the first variety. It was confirmed by gas chromatography that the composition of fatty acids in roots of both varieties was constituted mainly by 16:0 and 18:0 as major saturated fatty acids and 18:1ω9, 18:2ω6 and 18:3ω3 as major unsaturated fatty acids. Total lipid extracts from the roots of both varieties showed that the lipid saturation level increased under salt stress, notwithstanding the increased proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The changes in lipid saturation being predominantly due to decreases in oleic acid (18:1ω9) and increases in palmitic acid (16:0). However, Arper root extracts contained a lower proportion of saturated lipids than Aristo. The enhanced proportion of highly polyunsaturated fatty acids especially linolenic and eicosapentaenoic acids was considered to be the characteristic of the relatively salt tolerance in Arper roots.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FM:
-
Fresh mass
- DM:
-
Dry mass
- WC:
-
Root water content
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- TiCl4 :
-
Titanium chloride
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TBARS:
-
Total 2-thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- FA:
-
Fatty acids
- U/S:
-
Ratio of unsaturated to saturated fatty acids
- MSI:
-
Membrane stability index
References
Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Eneas-Filho J, de Abreu CEB, Gomes-Filho E (2006) Effect of salt stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive maize genotypes. Environ Exp Bot 56:87–94
Cachorro P, Ortiz A, Cerda A (1993) Effects of saline stress and calcium on lipid composition in bean roots. Phytochemistry 32:1131–1136. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)95077-5
Cakmak I, Horst J (1991) Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Physiol Plant 83:463–468. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1991.tb00121.x
Cassells AC, Curry RF (2001) Oxidative stress and physiological, epigenetic and genetic variability in plant tissue culture: implications for micropropagators and genetic engineers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64:145–157. doi:10.1023/A:1010692104861
Chen S, Li J, Fritz E, Wang S, Hütermann A (2002) Sodium and chloride distribution in roots and transport in three poplar genotypes under increasing NaCl stress. For Ecol Manage 168:217–230. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00743-5
das Neves JPC, Ferreira LFP, Vaz MM, Gazarini LC (2008) Gas exchange in the salt marsh species Atriplex portulacoides L. and Limoniastrum monopetalum L. in southern Portugal. Acta Physiol Plant 30:91–97
de Lacerda CF, Cambraia J, Oliva MA, Ruiz HA (2005) Changes in growth and in solute concentrations in sorghum leaves and roots during salt stress recovery. Environ Exp Bot 54:69–76
Demiral T, Türkan I (2006) Exogenous glycinebetaine affects growth and proline accumulation and retards senescence in two rice cultivars under NaCl stress. Environ Exp Bot 56:72–79
Elenkov I, Stefanov K, Dimitrova-Konaklieva S, Popov S (1996) Effect of salinity on lipid composition of Cladophora vagabunda. Phytochemistry 42:39–44
Eraslan F, Inal A, Gunes A, Alpaslan A (2007) Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on the growth, antioxidant activity and physiology of carrot plants subjected to combined salinity and boron toxicity. Sci Hortic 113:120–128
Fujii S, Uenaka M, Nakayama S, Yamamoto R, Mantani S (2001) Effects of sodium chloride on the fatty acids composition in Boekelovia hooglandii (Ochromonadales, Chrysophyceae). Phycol Res 49:73–77
Hajlaoui H, Denden M, Bouslama M (2006) Effet du chlorure de sodium sur les critères morpho-physiologiques et productifs du pois chiche (Cicer arietinum L.). Ann INRGREF 8:171–187
Hajlaoui H, Denden M, Bouslama M (2007) Etude de la variabilité intraspécifique de tolérance au stress salin du pois chiche (Cicer arietinum L.) au stade germination. Tropicultura 25(3):168–173
Halliwell B (2006) Reactive species and antioxidants. Redox biology is a fundamental theme of aerobic life. Plant Physiol 141:312–322
Hung SH, Yu CW, Lin CH (2005) Hydrogen peroxide function as a stress signal in plants. Bot Bull Acad Sin 46:1–10
Imlay JA (2003) Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:395–418
Jbir N, Chaïbi W, Ammar S, Jemmali A, Ayadi A (2001) Root growth and lignification of two wheat species differing in their sensitivity to NaCl, in response to salt stress. C R Acad Sci III 324:863–868
Khan MH, Panda SK (2008) Alterations in root lipid peroxidation and antioxidative responses in two rice cultivars under NaCl-salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 30:81–89
Khan MH, Singha Ksh LB, Panda SK (2002) Changes in antioxidant levels in Oryza sativa L. roots subjected to NaCl-salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 24:145–148
Konieczny R, Libik M, Tuleja M, Niewiadomska E, Miszalski Z (2008) Oxidative events during in vitro regeneration of sunflower. Acta Physiol Plant 30:71–79
Kuiper PJC (1984) Functioning of plant cell membrane under saline conditions: membrane lipid composition and ATPase. In: Staples RC, Toenniessen GH (eds) Salinity tolerance in plants. Wiley, New York, pp 77–91
Liang Y, Zhang W, Chen Q, Ding R (2005) Effects of silicon on H+-ATPase and H+-PPase activity, fatty acid composition and fluidity of tonoplast vesicles from roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ Exp Bot 53:29–37
Lin H, Wu L (1996) Effects of salt stress on root plasma membrane characteristics of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive Buffalograss clones. Environ Exp Bot 36:239–254
Loggini B, Scartazza A, Brugnoli E, Navari-Izzo F (1999) Antioxidative defense system, pigment composition, and photosynthetic efficiency in two wheat cultivars subjected to drought. Plant Physiol 119:1091–1100
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann Bot 78:389–398
Malkit A, Sadka A, Fisher M, Goldshlag P, Gokhman I, Zamir A (2002) Salt induction of fatty acid elongase and membrane lipid modifications in the extreme halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol 129:1320–1329
Mansour MMF (1995) Changes in cell permeability and lipid content in wheat roots induced by NaCl. Biol Plant 37:143–145
Mansour MMF, Lee-Stadelmann OY, Stadelmann EJ (1993) Salinity stress and cytoplasmic factors. A comparison of cell permeability and lipid partiality in salt sensitive and salt resistant cultivars and lines of Triticum aestivum and Hordeum vulgare. Physiol Plant 88:141–148
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Termaat A (1986) Whole plant responses to salinity. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:143–160
Neill SJ, Desikan R, Clarke A, Hurst RD, Hancock JT (2002) Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide as signalling molecules in plants. J Exp Bot 53:1237–1247
Panou-Filotheou H, Bosabalidis AM (2004) Root structural aspects associated with copper toxicity in oregano (Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum). Plant Sci 166:1497–1504
Patterson BD, Mackae EA, Ferguson IB (1984) Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium (IV). Anal Biochem 139:487–492
Qiujie D, Bin Y, Shaobai H (1997) Response of oxidative stress defense systems in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves with supplemental UV B radiation. Physiol Plant 101:301–308
Schutter ME, Dick RP (2000) Comparison of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) methods for characterizing microbial communities. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:1659–1668
Ślesak I, Libik M, Karpinska B, Karpinski S, Miszalski Z (2007) The role of hydrogen peroxide in regulation of plant metabolism and cellular signalling in response to environmental stresses. Acta Biochim Pol 54:39–50
Surjus A, Durand M (1996) Lipid changes in soybean root membranes in response to salt treatment. J Exp Bot 47:17–23
Upchurch RG (2008) Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization, and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol Lett 30:967–977
Vaidyanathan H, Sivakumar P, Chakrabarty R, Thomas G (2003) Scavenging of reactive oxygen species in NaCl-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.)-differential response in salt-tolerant and sensitive varieties. Plant Sci 165:1411–1418
Verslues PE, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu J, Zhu JK (2006) Methods and concepts in quantifying resistance to drought, salt and freezing, abiotic stresses that affect plant water status. Plant J 45:523–539
Wu J, Seliskar DM, Gallagher JL (1998) Stress tolerance in the marsh plant Spartina patens: impact of NaCl on growth and root plasma membrane lipid composition. Physiol Plant 102:307–317
Zhang W, Chen Q, Liu Y (2002) Relationship between H+-ATPase activity and fluidity of tonoplast in barley roots under NaCl stress. Acta Bot Sin 44:292–296
Zhang M, Barg R, Yin M, Gueta-Dahan Y, Leikin-Frenkel A, Salts Y, Shabtai S, Ben-Hayyim G (2005) Modulated fatty acid desaturation via overexpression of two distinct ω-3 desaturases differentially alters tolerance to various abiotic stresses in transgenic tobacco cells and plants. Plant J 44:361–371
Zhao FG, Qin P (2005) Protective effects of exogenous fatty acids on root tonoplast function against salt stress in barley seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 53:215–223
Zhong H, Läuchli A (1994) Spatial distribution of solutes K+, Na+, Ca++ and their deposition rates in the growth zone of primary cotton roots: effects of NaCl and CaCl2. Planta 194:31–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Weidner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajlaoui, H., Denden, M. & Ayeb, N.E. Changes in fatty acids composition, hydrogen peroxide generation and lipid peroxidation of salt-stressed corn (Zea mays L.) roots. Acta Physiol Plant 31, 787–796 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0293-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0293-4