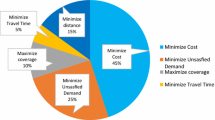
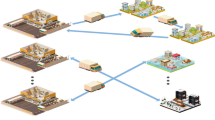
Abstract
Each year people affected by disasters, either natural or human-made, can be counted by millions. When a major disaster strikes a country, local and international communities usually respond with an outpouring of assistance, which has to be efficiently managed in order to arrive where it is needed as soon as possible and under adverse conditions. Despite its importance, not until recently has Humanitarian Logistics received much attention as a specific field, and there is a lack of specific tools. In this work, a lexicographical goal programming model for distribution of goods to the affected population of a disaster in a developing country is presented, which sustains a decision support system currently in development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aouni B, Kettani O (2001) Goal programming model: a glorious history and a promising future. Eur J Oper Res 133:225–453
Ariñes-Voets A (2003) An effective humanitarian supply management system for natural and man-made disasters. In: Proc of the 2003 international conference on total disaster risk management, 95–97. (See www.disaster-info.net/SUMA for more information [date accessed Sept-09])
Bakuli DL, Smith JM (1996) Resource allocation in state-dependent emergency evacuation networks. Eur J Oper Res 89(4):543–555
Charnes A, Cooper WW (1961) Management models and industrial applications of linear programming. Wiley, New York
CRED (2009) Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. EMDAT Data Entry Procedures. Louvain: Catholic University of Louvain; www.cred.be [date accessed: Sept-09]
Jones DF, Tamiz M (2002) Goal programming in the period 1990–2000. In: Ehrgott M, Gandibleux X (eds) Multicriteria optimization: state of the art annotated bibliographic survey. Kluwer Academic, Boston, Chapter 3
Kovacs G, Spens KM (2007) Humanitarian logistics in disaster relief operations. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 37:99–114
Miller CA Tucker, Zemlin R (1960) Integer programming formulations and travelling salesman problems. J ACM 7(1960):326–329
Niger (2005) An evidence base for understanding the current crisis. Famine Early Warn Syst Netw 29
Rodríguez JT, Vitoriano B, Montero J, Omaña A (2008) A decision support tool for humanitarian operations in natural disaster relief. In: Computational intelligence in decision and control. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 805–810
Romero C (1991) Handbook of critical issues in goal programming. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Schniederjans MJ (1995) Goal programming: methodology and applications. Kluwer Academic, Norwell
Tamiz M, Jones D, Romero C (1998) Goal programming for decision making: an overview of the current state-of-the-art. Eur J Oper Res 111:569–581
Tzeng GH, Cheng HJ, Huang TD (2007) Multi-objective optimal planning for designing relief delivery systems. Transp Res (E) 43:673–686
World Health Organization (1995) Coping with major emergencies—WHO strategies and approaches to humanitarian action. Geneva (Unpublished document WHO/EHA/95.1, available from Emergency and Humanitarian Action, World Health Organization, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been partially supported by project TIN2009-07901 from DGI and project CONS-C5-0281 from MEC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortuño, M.T., Tirado, G. & Vitoriano, B. A lexicographical goal programming based decision support system for logistics of Humanitarian Aid. TOP 19, 464–479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-010-0138-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-010-0138-8