Abstract
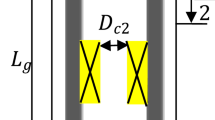
Magnetorheological fluids(MRF) are smart materials consisting of silicon oil and very small soft-magnetic particles. In a magnetic field, the viscosity and the flow behaviour of the fluid are considerably changed. MRF damper is a device to give damping by the shear stress of MR fluids. A MRF damper has the property whose damping changes quickly in response to an external magnetic field strength. The design method of a new MR fluid damper is investigated theoretically and the structure is presented. The equation of the damping by MR fluids within damper is derived to provide the theoretical foundations in the design of the damper. Based on this equation, after mathematical manipulation, the calculations of the volume, thickness and width of the annular MR fluids within the MR fluids damper are yielded and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASHOUR O, CRAIG A, KORDONSKY W I. Magnetorheological fluids: Materials, characterization, and devices [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1996, 7: 123–130.
CARLSON J D, CATANZARITE D M, CLAIR K A S T. Commercial magnetorheological fluid devices [C]//Proceeding of the 5th International Conference on Electrorheological Fluids, Magnetorheological Suspensions and Associated Technology. Sheffield. UK: World Scientific Publishing, Co, Ltd, 1995: 20–28.
KORDONSKY W I. Magnetorheological fluids and their application [J]. Materials Technology, 1993, 8(11): 240–242.
LEE U, KIM D, HUR N. Design analysis and experimental evaluation of an MR fluid clutch [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1999, 10: 701–707.
BOLTER R, JANOCHA H. Design rules for MR fluid actuators in different working modes [C]//Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1997 Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials. Bellingham WA: SPIE, 1997: 148–159.
KORDONSKI W, GORODKIN S, ZHURAVSKI N. Static yield stress in magnetorheological fluid [J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2001, 15(6/7): 1078–1084.
HUANG Jin, DENG Guo-hong, WEI Yu-qing, et al. Application of magnetorheological fluids to variable speed transmission [C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Transmissions. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2001: 296–298.
HUANG Jin, WANG Hua-pei, LIN Jian, et al. Research on chain-model of the transmission mechanical property of the magnetorheological fluids [J]. Machine Design and Manufacturing Engineering, 2001, 30(2): 3–7. (in Chinese)
YANG Chang, GUAN Xin-ping, OU Jin-chun. Theoretical and experimental analysis of MR damper with adjustable hysteretic model [J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2002, 22: 115–120.
HUANG Jin, YANG Yan, WEI Yu-qing, et al. Braking principle and torque analysis of cylindrical magnetorhelogical fluid brake [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2002, 23: 25–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Li, H. & Kang, Bs. Analysis of magnetorheological fluid damper. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 14 (Suppl 1), 263–265 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-007-0260-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-007-0260-4