Abstract
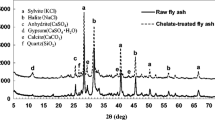
Fly ash is a hazardous byproduct of municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI). An alkali activated blast furnace slag-based cementitious material was used to stabilize/solidify the fly ash at experimental level. The characteristics of the stabilized/solidified fly ash, including metal leachability, mineralogical characteristics and the distributions of metals in matrices, were tested by toxic characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS) respectively. Continuous acid extraction was utilized to extract metal ions and characterize their leaching behavior. The stabilization/ solidification procedure for MSWI fly ash demonstrates a strong fixing capacity for the metals by the formation of CS-H phase, hydrated calcium aluminosilicate and ettringite. The stabilized/solidified fly ash shows a dense and homogeneous microstructure. Cr is mainly solidified in hydrated calcium aluminosilicate, C-S-H and ettringite phase through physical encapsulation, precipitation, adsorption or substitution mechanisms, and Pb is mainly solidified in C-S-H phase and absorbed in the Si-O structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabbas T, Polettini A, Pomi R, Astrup T, Hjelmar O, Mostbauer P, Cappai G, Magel G, Salhofer S, Speiser C, Heuss-Assbichler S, Klein R, Lechner P, 0. Management of municipal solid waste incineration residues. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2003, 23(1): 61–88
Colangelo F, Cioffi R, Montagnaro F, Santoro L. Soluble salt removal from MSWI fly ash and its stabilization for safer disposal and recovery as road basement material. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2012, 32(6): 1179–1185
Diaz-Loya E I, Allouche E N, Eklund S, Joshi A R, Kupwade-Patil K. Toxicity mitigation and solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash using alkaline activated coal ash. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2012, 32(8): 1521–1527
Karagiannidis A, Kontogianni S, Logothetis D. Classification and categorization of treatment methods for ash generated by municipal solid waste incineration: a case for the 2 greater metropolitan regions of Greece. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2013, 33(2): 363–372
Liu W, Hou H, Zhang C, Zhang D. Feasibility study on solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash with circulating fluidized bed combustion coal fly ash. Waste Management & Research, 2009, 27(3): 258–266
Qian G, Yang X, Dong S, Zhou J, Sun Y, Xu Y, Liu Q. Stabilization of chromium-bearing electroplating sludge with MSWI fly ashbased Friedel matrices. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165 (1–3): 955–960
Baricova D, Pribulova A, Demeter P. Utilizing of metallurgical slag for production of cementless concrete mixtures. Metalurgija, 2012, 4 (51): 465–468
Klemm W A, Bhatty J I. Fixation of Heavy Metals as Oxyanionsubstituted Ettringites. Portland Cement Association, 2002
ASTM D6357-00a. Standard Test Methods for Determination of Trace Elements in Coal, Coke, and Combustion Residues from Coal Utilization Processes by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry, Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, and Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry1. American Society for the Testing of Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 2000
US EPA. Test methods for evaluating solid wastes, toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP), Method 1311 SW-846, third edition, Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
Lampris C, Stegemann J A, Pellizon-Birelli M, Fowler G D, Cheeseman C R. Metal leaching from monolithic stabilised/ solidified air pollution control residues. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(2–3): 1115–1123
Junkang L, Meng W, Kai D. Entrapment of CrO 2–4 by C-S-H during C-S-H Formation. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2009, 31(20): 55–57 (in Chinese)
Yan S, Min Z, Weixing W. Identification of chromate binding mechanisms in Friedel’s salt. Construction & Building Materials, 2013, 48: 942–947
Gougar M L D, Scheetz B E, Roy D M. Ettringite and C-S-H Portland cement phases for waste ion immobilization: A review. Waste management, 1996, 16(4): 295–303
Leisinger S M, Lothenbach B, Le Saout G, Kägi R, Wehrli B, Johnson C A. Solid solutions between CrO4- and SO4-ettringite Ca6(Al(OH)6)2[(CrO4)×(SO4)(1−x)]3×26 H2O. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(23): 8983–8988
Zhang D, Liu W, Hou H, He X. Strength, leachability and microstructure characterisation of Na2SiO3-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag solidified MSWI fly ash.Waste Management & Research, 2007, 25(5): 402–407
Yan S, Min Z, Weixing W. Immobilization Mechanisms of Cr and Pb in cement solidified municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Fresenius Environ Bull, 2013, 8(22): 2291–2296
Ojas A C, Joseph J B. Leaching behavior of hazardous heavy metals from lime fly ash cements. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 139(5): 633–641
Aditya K, Gauray S, Cedric P. The influence of sodium and potassium hydroxide on alite hydration: Experiments and simulations. Cement and Concrete Research, 2012, 42(11): 1513–1523
Sanchez H M J, Fernandez J A F, Palomo A. C4A3S hydration in different alkaline media. Cement and Concrete Research, 2013, 46: 41–49
Nicoleau L, Nonat A, Perrey D. The di- and tricalcium silicate dissolutions. Cement and Concrete Research, 2013, 47: 14–30
Junkang L, Yanxin W. Mechanisms of Pb2+ Solidified by Composite Cement. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2005, 4: 10–14 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Hou, H., Wang, G. et al. Characteristics of the stabilized/solidified municipal solid wastes incineration fly ash and the leaching behavior of Cr and Pb. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 10, 192–200 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0719-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0719-0