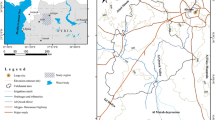
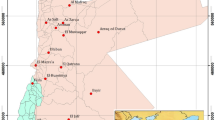
Groundwater is an important water resource in the Helwan area, not only for drinking and agricultural purposes, but also because several famous mineral springs have their origin in the fractured carbonate aquifer of the region. The area is heavily populated with a high density of industrial activities which may pose a risk for groundwater and surface water resources. The groundwater and surface water quality was investigated as a basis for more future investigations. The results revealed highly variable water hydrochemistry. High values of chloride, sulphate, hardness and significant mineralization were detected under the industrial and high-density urban areas. High nitrate contents in the groundwater recorded in the southern part of the study area are probably due to irrigation and sewage infiltrations from the sewage treatment station. The presence of shale and marl intercalation within the fissured and cavernous limestone aquifer promotes the exchange reactions and dissolution processes. The groundwater type is sodium, sulphate, chloride reflecting more mineralized than surface water. The results also showed that water in the study area (except the Nile water) is unsuitable for drinking purposes, but it can be used for irrigation and industrial purposes with some restrictions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla F A 2004 Contaminant transport in fractured chalk aquifer characterised by tracer techniques Sigerslev, Denmark; PhD Thesis, Bonn University, Germany.
Abdel-Daiem A 1971 Hydrogeological studies of springs in the area east of Cairo; MSc Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt.
Abdel-Halim A S, Metwally E and El-Dessouky M 2003 Environmental pollution study around a large industrial area near Cairo, Egypt; J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 257 123–124.
Abdeltawab A 2008 Mokattam Plateau geology and stability; Japan–Egypt joint symposium new horizons in geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering, Geotechnical Engineering Research laboratory, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt September 15–17.
Abdu I 1994 Geology and hydrogeology of Helwan area, Egypt; MSc Thesis, Menofia University, Egypt.
Aboushook M I and Sherif A 2000 Reinforcement of fissured large roof of the Egyptian broadcasting cavern in Mokattam hill; Proceedings of ISRM. Symposium Eurock 2001. Finland, 401–408 Academy of Scientific Research and Technology (ASRT).
Akawy A and Zaky K 2008 Structural analysis of the tectonically inverted Kareim Basin, Eastern Desert, Egypt-Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen 250 9–30.
Akawy A 2009 Structural elements and incremental strain history of the southwestern parts of exposed basement rocks: an example from Um Had area, central Eastern Desert, Egypt; Arabian J. Geosci. 2 285–300.
Awad M and Abdel-Baki A 1993 Water quality and environmental tritium for groundwater of the Quaternary aquifer in Mostorad station, northward Cairo, Egypt; Bull. Faculty of Science, Assiut University 22(2-F) 173–191.
Ayers R S and Westcot D W 1985 Water quality for agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization, FAO irrigation and drainage, paper No. 29, Rev. 1, UN, Rome.
Bäumle R 2003 Geohydraulic characterisation of fractured rock flow regimes. Regional studies in granite (Lindau, Black Forest, Germany) and Dolomite (Tsumeb Aquifers, Northern Namibia); PhD Thesis, Department of Applied Geology, Karlsruhe, Germany.
Bäumle R, Hötzl H and Witthüser K 2000 Flow pattern and transport behaviour of granitic rock intersected by a highly permeable fault zone; In: Tracers and modelling in hydrogeology (ed.) Dassargues A (Wallingford, UK: IAHS Press), 262 283–288.
Bodin J, Delay F and de Marsily G 2003a Solute transport in a single fracture with negligi-ble matrix permeability: 1. Fundamental mechanisms; J. Hydrogeol. 11 418–433.
Bodin J, Delay F and de Marsily G 2003b Solute transport in a single fracture with negligi-ble matrix permeability: 2. Mathematical formalism; J. Hydrogeol. 11 434–454.
Brown S, Sprenger M, Maxemchuk A and Compton A 2005 Ecosystem function in alluvial tailings after biosolids and lime addition; J. Environ. Qual. 34 139–148.
Cartwright I and Weaver T R 2005 Hydrogeochemistry of the Goulburn Valley region of the Murray Basin, Australia: implications for flow paths and resources vulnerability; Hydrogeol. J 13 752–770.
Continental Oil Company (CONOCO) 1989 Geologic map of Egypt, scale 1; 500,000.
Dorsch Gruppe (Dorsch Consult Wasser und Umwelt GmbH) 2008 Extension of Helwan wastewater treatment plant (internal report).
Egyptian Higher Committee for Water (EHCW) 2007 Egyptian standards for drinking water and domestic uses (in arabic).
Elawadi E, El-Qady G, Nigm A, Shaaban F and Ushijima K 2006 Integrated geophysical survey for site investigation at a new dwelling area, Egypt; J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 4 249–259.
El Ghandour M F, Abdel Salam M S, Hindy K T and Kamel M M 1983a Studies on air pollution from construction plants in Helwan industrial area; 1. Total dust deposition over the area; Atmos. Environ. 17 303–309.
El Ghandour M F, Abdel Salam M S, Hindy K T and Kamel M M 1983b Studies onair pollution from construction plants in Helwan industrial area; 2. Water soluble and insoluble deposits; Atmos. Environ. 17 573–579.
Elminir H K, Areed F F and Elsayed T S 2005 Estimation of solar radiation components incident on Helwan site using neural networks; Solar Energy 79 270–279.
El Ramly I M 1969 Recent review of investigations on the thermal and mineral springs; XXIII International Geological Congress 19 201–213.
El-Sayed M H, Shawky H A and Abdel Mottaleb M S 2004 Geochemistry of water resources and pollution problems in Helwan area, Egypt; Bull. Inst. Desert Egypt 54(2) 259–289.
Farag A and Ismail M 1955 On structure of Wadi Hof area north-east of Helwan; Bull. Inst. Desert Egypt 1(5) 179–192.
Fayez M and Shahin R R 2007 Effects of industrial liquid wastes on dinitrogen fixation and microflora of soils and waters. J Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 150(4) 220–227.
Fontes J Ch, Louvat D, Michelot J L and Soreau S 1988 Isotopic content of aqueous sulphate, indicators of the origin of mineralization in crystalline rock groundwaters; In: Proceedings IAH Symposium on the hydrogeology and safety of radioactive and industrial hazardous waste disposal, Doc. BRGM 160, OrleAans, 325–341.
Idris M 2000 Geothermal evaluation for thermal fluids of Helwan springs Egypt; Proceedings World Geothermal Congress, Kyushu-Tohoku, Japan, May 28–June 10 2000.
Han D, Liang X, Jin M, Currell J M, Han Y and Song X 2009 Hydrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu River alluvial fan, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China; Environ. Manag. 44 243–255.
Han D M 2007 Analysis of groundwater flow system and modelling of hydrogeochemical evolution in Xinzhou Basin, China; PhD Thesis, China University of Geosciences, China (in Chinese).
Kahler H I 1944 Once through and recirculation cooling water studies. Proceeding, Engineers Society Western Pcnna, pp. 39–62.
Langelier F 1936 The analytical control of anticorrosion water treatment; J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 28(10) 1500–1521.
Liang X, Han D M, Jin M G et al 2007 Mapping of karst water system round mountainous area and recharge to porous water in the Xinzhou Basin; Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 218(6) 28–32 (in Chinese).
Mahmoodabady H, Mirhosiny A, Hazery F and Morady F 2010 Investigation the effect of industrial development on groundwater pollution in arid zone (case study: Yazd province). The 1st IWA Malaysia Young Water Professionals Conference (IWAYP2010), 1–4 March 2010, Kuala Lumpur, ISBN 983–9805–86–4.
Maya A L and Loucks M D 1995 Solute and isotopic geochemistry and groundwater flow in the Central Wasatch Range, Utah; Hydrol. J 172 31–59.
Moustafa A, Yehia A and Abdel Tawab S 1985 Structural setting in the area east of Cairo; Maadi and Helwan: Middle East Research Centre, Ain Shams University Science Research Series 5 40–64.
National Academy of Science 1972 Water Quality Criteria; Protection Agency, Washington DC, pp. 1–594.
Piper A M 1944 A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 25 914–923.
Reed M H and Spycher N F 2000 User’s Guide for CHILLER: A Program for computing water–rock reactions, boiling, mixing and other reaction processes in aqueous–mineral–gas systems, and minplot guide (3rd edn), Department of Geological Sciences, University of Oregon, Eugene, OR, USA, 69p.
Research Institute for Groundwater (RIGW) 1978 Groundwater safe yield studies, second technical report, El-Kanater, Egypt.
Research Institute for Groundwater (RIGW) 1995 Regional prospective of the fissured carbonate aquifer system in Egypt; First technical report.
Sadek M A and Abd El-Samie S G 2001 Pollution vulnerability of the Quaternary aquifer near Cairo, Egypt, as indicated by isotopes and hydrochemistry. Hydrogeol. J. 9 273–281.
Said R 1954 Remarks on the geomorphology of the area east of Helwan; Bull. Soc. Geogr. Egypt 27 93–100.
Said R 1962 The geology of Egypt (Amesterdam: Elsevier) 348p.
Sawyer G N and McCarthy D L 1967 Chemistry of sanitary engineers; (2nd edition) McGraw Hill, New York, p. 518.
Shahin M A 1990 Impacts of urbanization of the Greater Cairo area on the groundwater in the underlying aquifer. Hydrological processes and water management in urban areas; Proceedings of the Duisberg Symposium, April 1990, IAHS Publ. 198.
Sultan S A, Mansour S A and Santos F A 2008 A hydrogeophysical investigation of the Ain Mousa area, near Cairo, Egypt; Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 67 111–117.
Taha A A, El-Mahmoudi A S and El-Haddad I M 2004 Pollution sources and related environmental impacts in the new communities southeast Nile Delta, Egypt; Emirates J. Eng. Res. 9(1) 35–49.
Tawfik K M 2008 A monitory field study at El Saaf-Helwan faba bean farms irrigated by industrial waste water and polluted water with sewage; J. Appl. Sci. Res. 4(5) 492–499.
Todd D K 1980 Ground water hydrology (2nd edition), John Wiley & Sons, New York.
US Salinity Laboratory Staff USSL 1954 Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils; Agricultural Handbook 60, USDA, US Government printing office, Washington, DC.
Wagdy A, El Adway H and El-Gamal M 2008 Vegetation dynamics assisted hydrological analysis for Wady Degla; UNDP/GEF/Cairo University, Egypt.
Wilkes University Center of Environmental Quality, Geoenvironmental Science and Engineering Department 2002 Corrosion, saturation index, balanced water in drinking water systems–Source and cause of corrosion.
Witthüser K, Reichert B and Hötzl H 2003 Contaminant transport in fractured chalk: Labo-ratory and field experiments; Ground Water 41 806–815.
World Health Organization (WHO) 2008 Guidelines for drinking-water quality (3rd edition) incorporating the first and second Addenda, Volume 1, Geneva.
Zia M, Iqbal M, Nawaz H and Samin G 1999 Langelier calcium carbonate saturometry determination by table values; Int. J. Agri. Biol. 1 353–355.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ABDALLA, F.A., SCHEYTT, T. Hydrochemistry of surface water and groundwater from a fractured carbonate aquifer in the Helwan area, Egypt. J Earth Syst Sci 121, 109–124 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-012-0140-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-012-0140-7