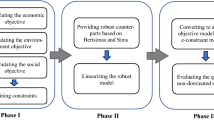
Abstract
The manufacturing industry in India started moving towards multi channel supply chain for delivering products to the customer by his preferred channel of purchasing. But firms are far behind to achieve a goal of omnichannel where there exists better interface between various channels which increases their customer range and customer comfort. Also, today consumer awareness had increased with respect to environmental protection while at the other end the government rules and regulations also force firms to go with adopting sustainability concepts like green and recycling processes in supply chains. This work deals with this major issue faced by the firms in India that how to integrate multiples channels in designing their supply chain network considering economic and environmental sustainability simultaneously. This paper presents a mathematical model for an integrated multi channel closed loop supply chain network problem, the modeling decisions that include the selection of the entity that will fulfill the demands of the omni channel customer during different time periods and the supplier selection process integrated with the production amounts, inventory levels, stock-outs and shipment quantities. The aim of the model is to minimize the total cost incurred to the customer, total cost incurred in running the supply chain and minimize the total pollution emissions from all the transportations of the products between the different stages of the supply chain. It is a mixed integer programming problem considered for a leading kitchenware company in southern part of India and solved using IBM CPLEX optimizer. The result shows that how the dynamics of omni channel customer options affects the optimal supply chain structure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swaminathan J M and Tayur S R 2003 Models for supply chains in e-business. Manag. Sci. 49(10): 1387–1406
Agatz N A, Fleischmann M and Van Nunen J A 2008 E-fulfillment and multi-channel distribution—a review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 187(2): 339–356
Lal R and Sarvary M 1999 When and how is the Internet likely to decrease price competition? Mark. Sci. 18(4): 485–503
King R C, Sen R and Xia M 2004 Impact of web-based e-commerce on channel strategy in retailing. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 8(3): 103–130
Bernstein F, Song J S and Zheng X 2008 “Bricks-and-mortar” vs “clicks-and-mortar”: an equilibrium analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 187(3): 671–690
Farahani R Z and Elahipanah M 2008 A genetic algorithm to optimize the total cost and service level for just-in-time distribution in a supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 111(2): 229–243
Biswas T and Samanta S 2016 A strategic decision support system for logistics and supply chain network design. Sādhanā 41(6): 583–588
Fleischmann M, Van Nunen J A and Gräve B 2003 Integrating closed-loop supply chains and spare-parts management at IBM. Interfaces 33(6): 44–56
Amin S H and Zhang G 2014 Closed-loop supply chain network configuration by a multi-objective mathematical model. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Supply Chain Model. 6(1): 1–5
Keyvanshokooh, E, Sarah M R, and Elnaz K 2016 Hybrid robust and stochastic optimization for closed-loop supply chain network design using accelerated Benders decomposition. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 249(1): 76–92
Gaur J, Amini M and Rao A K 2017 Closed-loop supply chain configuration for new and reconditioned products: an integrated optimization model. Omega 66: 212–223
Elhedhli S and Merrick R 2012 Green supply chain network design to reduce carbon emissions. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 17(5): 370–379
Tao Z G, Guang Z Y, Hao S and Song H J 2015 Multi-period closed-loop supply chain network equilibrium with carbon emission constraints. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 104: 354–365
Lam J S and Gu Y 2016 A market-oriented approach for intermodal network optimization meeting cost, time and environmental requirements. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 171: 266–274
Nouira I, Hammami R, Frein Y and Temponi C 2016 Design of forward supply chains: impact of a carbon emissions-sensitive demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 173: 80–98
Colicchia C, Creazza A, Dallari F and Melacini M 2016 Eco-efficient supply chain networks: development of a design framework and application to a real case study. Prod. Plan. Control 27(3): 157–168
Cummins S, Peltier J W and Dixon A 2016 Omni-channel research framework in the context of personal selling and sales management: a review and research extensions. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 10(1): 2–16
Picot-Coupey K, Huré E and Piveteau L 2016 Channel design to enrich customers’ shopping experiences: Synchronizing clicks with bricks in an omni-channel perspective—the Direct Optic case. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 44(3): 336–368
Hübner A, Kuhn H and Wollenburg J 2016 Last mile fulfilment and distribution in omni-channel grocery retailing: a strategic planning framework. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 44(3): 228–247
Bortolini M, Faccio M, Ferrari E, Gamberi M and Pilati F 2016 Fresh food sustainable distribution: cost, delivery time and carbon footprint three-objective optimization. J. Food Eng. 174:56–67
Mogale D G, Kumar M., Kumar S K and Tiwari M K 2018 Grain silo location-allocation problem with dwell time for optimization of food grain supply chain network. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 111: 40–69
Mogale D G, Lahoti G, Jha S B, Shukla M, Kamath N and Tiwari M K 2018 Dual market facility network design under bounded rationality. Algorithms 11(4): 54
Costantini V, Crespi F, Marin G and Paglialunga E 2017 Eco-innovation, sustainable supply chains and environmental performance in European industries. J. Clean. Prod. 155: 141–154
Arampantzi C and Minis I 2017 A new model for designing sustainable supply chain networks and its application to a global manufacturer. J. Clean. Prod. 156: 276–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niranjan, T., Parthiban, P., Sundaram, K. et al. Designing a omnichannel closed loop green supply chain network adapting preferences of rational customers. Sādhanā 44, 60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-1038-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-1038-0