Abstract
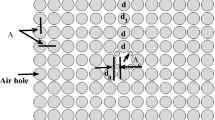
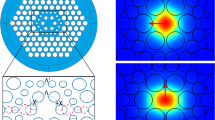
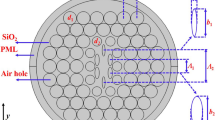
High birefringence with low confinement loss photonic crystal fiber (PCF) has significant advantages in the field of sensing, dispersion compensation devices, nonlinear applications, and polarization filter. In this report, two different models of PCFs are presented and compared. Both the models contain five air holes rings with combination of circular and elliptical air holes arrangement. Moreover, the elliptical shaped air holes polarization and the third ring air holes rotational angle are varied. To examine different guiding characteristics, finite element method (FEM) with perfectly matched layer (PML) absorbing boundary condition is applied from 1.2 to 1.8 μm wavelength range. High birefringence, low confinement loss, high nonlinearity, and moderate dispersion values are successfully achieved in both the PCFs models. Numeric analysis shows that model-1 gives higher birefringence (2.75 × 10–2) and negative dispersion (–540.67 ps/(nm$km)) at 1.55 μm wavelength. However, model-2 gives more small confinement loss than model-1 at the same wavelength. In addition, the proposed design demonstrates the variation of rotation angle has great impact to enhance guiding properties especially the birefringence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knight J C, Russell P S J. New ways to guide light. Science, 2002, 296(5566): 276–277
Knight J C, Birks T A, Russell P S J, Atkin D M. All-silica singlemode optical fiber with photonic crystal cladding. Optics Letters, 1996, 21(19): 1547–1549
Birks T A, Knight J C, Russell P S J. Endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fiber. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(13): 961–963
Knight J C, Broeng J, Birks T A, Russell P S J. Photonic band gap guidance in optical fibers. Science, 1998, 282(5393): 1476–1478
Russell P. Photonic crystal fibers. Science, 2003, 299(5605): 358
Russell P, Dettmer R. A neat idea [photonic crystal fibre]. IEE Review, 2001, 47(5): 19–23
Sinha R K, Kumar A, Saini T S. Analysis and design of single-mode As2Se3-chalcogenide photonic crystal fiber for generation of slow light with tunable features. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2016, 22(2): 287–292
Mishra S, Singh V K. Study of the fundamental propagation properties of a solid core holey photonic crystal fiber in the telecommunication window. Zhongguo Wuli Xuekan, 2010, 48(5): 592
Gangwar R, Mishra S, Singh V K. Designing of endlessly single mode polarization maintaining highly birefringent nonlinear microstructure fiber at telecommunication window by FV-FEM. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2014, 125(5): 1641–1645
Olszewski J, Mergo P, Gasior K, Urba’nczyk W. Highly birefringent microstructured polymer fibers optimized for a preform drilling fabrication method. Journal of Optics, 2013, 15(7): 075713
Ferrando A, Silvestre E, Andres P, Miret J, Andres M. Designing the properties of dispersion-flattened photonic crystal fibers. Optics Express, 2001, 9(13): 687–697
Reeves W, Knight J, Russell P, Roberts P. Demonstration of ultraflattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers. Optics Express, 2002, 10(14): 609–613
Raja G T, Varshney S K. Large mode area modified clad leakage channel fibers with low bending and higher differential losses. Journal of Optics, 2014, 16(1): 015403
Saini T S, Kumar A, Sinha R K. Triangular-core large-mode-area photonic crystal fiber with low bending loss for high power applications. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(31): 7246–7251
Saini T S, Kumar A, Sinha R K. Asymmetric large-mode-area photonic crystal fiber structure with effective single-mode operation: design and analysis. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(9): 2306–2311
Razzak S A, Namihira Y. Proposal for highly nonlinear dispersionflattened octagonal photonic crystal fibers. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2008, 20(4): 249–251
Gangwar R K, Bhardwaj V, Singh V K. Magnetic field sensor based on selectively magnetic fluid infiltrated dual-core photonic crystal fiber. Optical Engineering (Redondo Beach, Calif.), 2016, 55(2): 026111
Dhara P, Singh V K. Effect of MMF stub on the sensitivity of a photonic crystal fiber interferometer sensor at 1550 nm. Optical Fiber Technology, 2015, 21: 154–159
Gangwar R K, Singh V K. Refractive index sensor based on selectively liquid infiltrated dual core photonic crystal fibers. Photonics and Nanostructures-Fundamentals and Applications, 2015, 15: 46
Musin R, Zheltikov A. Designing dispersion-compensating photonic- crystal fibers using a genetic algorithm. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(4): 567–572
Simpson J, Stolen R, Sears F, Pleibel W, MacChesney J, Howard R. A single-polarization fiber. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1983, 1(2): 370–374
Messerly M J, Onstott J R, Mikkelson R C. A broad-band single polarization optical fiber. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1991, 9 (7): 817–820
Okamoto K. Single-polarization operation in highly birefringent optical fibers. Applied Optics, 1984, 23(15): 2638
Yang T J, Shen L F, Chau Y F, Sung M J, Chen D, Tsai D P. High birefringence and low loss circular air-holes photonic crystal fiber using complex unit cells in cladding. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(17): 4334–4338
Chau Y F, Yeh H H, Tsai D P. Significantly enhanced birefringence of photonic crystal fiber using rotational binary unit cell in fiber cladding. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 46(43 11L): L1048–L1051
Chen D, Shen L. Highly birefringent elliptical-hole photonic crystal fibers with double defect. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2007, 25(9): 2700–2705
Sun Y S, Chau Y F, Yeh H H, Shen L F, Yang T J, Tsai D P. High birefringence photonic crystal fiber with a complex unit cell of asymmetric elliptical air hole cladding. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(22): 5276–5281
Islam M A, Alam M S. Design of a polarization-maintaining equiangular spiral photonic crystal fiber for residual dispersion compensation over E + S + C + L + U wavelength bands. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(11): 930–932
Yue Y, Kai G,Wang Z, Sun T, Jin L, Lu Y, Zhang C, Liu J, Li Y, Liu Y, Yuan S, Dong X. Highly birefringent elliptical-hole photonic crystal fiber with squeezed hexagonal lattice. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(5): 469–471
Chaudhuri P R, Paulose V, Zhao C, Lu C. Near-elliptic core polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber: modeling birefringence characteristics and realization. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2004, 16(5): 1301–1303
Samiul Habib M, Selim Habib M, Hasan MI, Razzak SMA. Highly nonlinear polarization maintaining two zero dispersion spiral photonic crystal fiber using artificial defects. Optical Fiber Technology, 2013, 19(6): 539–542
Samiul Habib M, Selim Habib M, Hasan M I, Razzak S M A, Hossain M A, Namihira Y. Polarization maintaining large nonlinear coefficient photonic crystal fibers using rotational hybrid cladding. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2014, 125(3): 1011–1015
Hasan M I, Mahmud R, Morshed M, Hasan M R. Ultraflattened negative dispersion for residual dispersion compensation using soft glass equiangular spiral photonic crystal fiber. Journal of Modern Optics, 2016, 63(17): 1681–1687
Selim Habib M, Samiul Habib M, Razzak S M A, Hossain M A. Proposal for highly birefringent broadband dispersion compensating octagonal photonic crystal fiber. Optical Fiber Technology, 2013, 19(5): 461–467
Suzuki K, Kubota H, Kawanishi S, Tanaka M, Fujita M. Optical properties of a low-loss polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber. Optics Express, 2001, 9(13): 676–680
Hasan M R, Islam MA, Rifat A A, Hasan MI. A singlemode highly birefringent dispersion-compensating photonic crystal fiber using hybrid cladding. Journal of Modern Optics, 2017, 64(3): 218–225
Hasan MI, Selim Habib M, Samiul Habib M, Razzak SMA. Highly nonlinear and highly birefringent dispersion compensating photonic crystal fiber. Optical Fiber Technology, 2014, 20(1): 32–38
Chou Chau Y F, Lim C M, Yoong V N, Syafi’ie Idris MN. A simple structure of all circular-air-holes photonic crystal fiber for achieving high birefringence and low confinement loss. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118(24): 243102
Yang K Y, Chau Y F, Huang Y W, Yeh H Y, Ping Tsai D. Design of high birefringence and low confinement loss photonic crystal fibers with five rings hexagonal and octagonal symmetry airholes in fiber cladding. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(9): 093103
Md A I. Broadband dispersion compensation of single mode fiber by using modified decagonal photonic crystal fiber having high birefringence. Journal of Lasers Optics & Photonics, 2015, 2: 123
Haque M M, Rahman M S, Habib M S, Razzak S. Design and characterization of single mode circular photonic crystal fiber for broadband dispersion compensation. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2014, 125(11): 2608–2611
Gangwar R K, Singh V K. Study of highly birefringence dispersion shifted photonic crystal fiber with asymmetrical cladding. Optik- International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(24): 11854–11859
Koshiba M. Full-vector analysis of photonic crystal fibers using the finite element method. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 2002, 85(4): 881
Lee H, Schmidt M, Tyagi H, Sempere L P, Russell P S J. Polarization-dependent coupling to plasmon modes on submicron gold wire in photonic crystal fiber. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(11): 111102
Malitson I. Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1965, 55(10): 1205
Agrawal G P. Fiber-Optic Communication Systems. vol. 222. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2012
Saitoh K, Koshiba M. Full-vectorial imaginary-distance beam propagation method based on a finite element scheme: application to photonic crystal fibers. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2002, 38(7): 927–933
Caillaud C, Gilles C, Provino L, Brilland L, Jouan T, Ferre S, Carras M, Brun M, Mechin D, Adam J L, Troles J. Highly birefringent chalcogenide optical fiber for polarization-maintaining in the 3–8.5 μm mid-IR window. Optics Express, 2016, 24(8): 7977–7986
Chen D,Wu G. Highly birefringent photonic crystal fiber based on a double-hole unit. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(9): 1682–1686
Begum F, Namihira Y, Razzak S A, Kaijage S, Hai N H, Kinjo T, Miyagi K, Zou N. Novel broadband dispersion compensating photonic crystal fibers: applications in high-speed transmission systems. Optics & Laser Technology, 2009, 41(6): 679–686
Haxha S, Ademgil H. Novel design of photonic crystal fibres with low confinement losses, nearly zero ultra-flatted chromatic dispersion, negative chromatic dispersion and improved effective mode area. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(2): 278–286
Lægsgaard J, Libori S B, Hougaard K, Riishede J, Larsen T, Sørensen T, Hansen T P, Hansen K P, Nielsen M D, Jensen J, Bjarklev A. Dispersion properties of photonic crystal fibers-issues and opportunities. MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, 2003, 797(8): 135–136
Luke S, Sudheer S, Pillai V M. Tellurite based circular photonic crystal fiber with high nonlinearity and low confinement loss. Optik- International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(23): 11138–11142
Liu Z, Wu C, Tse M L V, Lu C, Tam H Y. Ultrahigh birefringence index-guiding photonic crystal fiber and its application for pressure and temperature discrimination. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(9): 1385–1387
Falkenstein P, Merritt C D, Justus B L. Fused preforms for the fabrication of photonic crystal fibers. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(16): 1858–1860
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rekha Saha completed her B.Sc. Engg. and M.Sc. Engg. degrees in Electronics and Communication Engineering Discipline from Khulna University, Khulna-9208, Bangladesh, in the year of 2015 and 2018, respectively. She secured 1st position both in B.Sc. and M.Sc. in her Discipline. Her research interests are nanophotonics, plasmonics, optical biosensor, and photonic crystal fiber.
Md. Mahbub Hossain received his B.Sc. and M.Sc. Engineering degrees from Electronics and Communication Engineering Discipline, Khulna University, Khulna- 9208, Bangladesh, in the year of 2003 and 2014, respectively. Mr. Mahbub is currently a Faculty Member with the Electronics and Communication Engineering Discipline, Khulna University, Bangladesh. His research interests are nanophotonics, plasmonics, optical biosensor, photonic crystal fiber, and wireless communication.
Md. Ekhlasur Rahaman received the B. Sc. Engg. degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering and the M.Sc. Engg. degree also in Electronics and Communication Engineering from Khulna University, Khulna-9208, Bangladesh, in the year of 2015 and 2018, respectively. He was awarded National Science and Technology (NST) Fellowship, Bangladesh for M.Sc. Engg. thesis work. He has published several papers in journals as well as in the proceedings of IEEE flagship/portfolio conferences. His research interests are cloud computing, nanophotonics, plasmonics, optical bio-sensor, photonic crystal fiber, and laser processing of materials.
Himadri Shekhar Mondal received his B. Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Electronics and Communication Engineering from Khulna University, Bangladesh, in 2015 and 2018, respectively. Himadri does research on optics, opto-electronics, distributed computing and cloud computing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, R., Hossain, M.M., Rahaman, M.E. et al. Design and analysis of high birefringence and nonlinearity with small confinement loss photonic crystal fiber. Front. Optoelectron. 12, 165–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0837-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-018-0837-6