Abstract
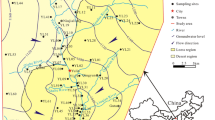
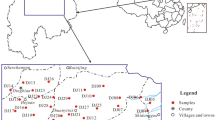
Groundwater is an important source of drinking water in arid areas and groundwater quality can affect human health. In the present study, 42 groundwater samples were collected from the aeolian-sand area of Yulin City, Northwest China, to better understand the groundwater quality for drinking purpose. The water quality index (WQI) was employed to evaluate the groundwater quality, and the associated human health risk was assessed using the assessment models proposed by USEPA for infants, children, and adults. The results showed that the groundwater was slightly alkaline, soft, and fresh water in the study area. The main anion and cation were Ca2+ and HCO3−, respectively, and the main processes controlling the groundwater quality were the dissolution of silicate minerals and cation exchange. NO3− concentration ranged from 0.50 to 98.00 mg/L, with a mean value of 19.13 mg/L. Among the 42 samples, 15 groundwater samples had high NO3− concentration exceeding the acceptable limit (20 mg/L) prescribed by the standard for groundwater quality of China for drinking purpose. In addition, WQI ranged from 5.5 to 132.5, indicating significant variation in water quality in the study area. Most of the groundwater samples (90.5%) were in the categories of excellent to good water for drinking purpose. Moreover, the non-carcinogenic risk of Hazard Quotient (NCHQ) for infants, children, and adults ranged from 0.0136 to 2.6630, 0.0130 to 2.5548, and from 0.0125 to 2.4500, respectively. The order of the NCHQ was infants > children > adults. The areas with high WQI and NCHQ were situated in the agricultural region, where the groundwater was polluted by nitrate due to excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers and large amount of untreated excreta of animals. These results would be helpful to establish reasonable management strategies for sustainable groundwater quality protection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud IA (2018) Geochemistry and quality of groundwater of the Yarmouk basin aquifer, north Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 40(4):1405–1435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0064-x
Adimalla N, Qian H (2019) Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, South India. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 176:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1460579
Adimalla N, Venkatayogi S (2017) Mechanism of fluoride enrichment in groundwater of hard rock aquifers in Medak, Telangana State, South India. Environ Earth Sci 76:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6362-2
Adimalla N, Li P, Qian H (2019) Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: a special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(5):1107–1124. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1460579
Akter T, Jhohura FT, Akter F et al (2016) Water Quality Index for measuring drinking water quality in rural Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. J Health Popul Nutr 35(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-016-0041-5
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H et al (2017) Assessing nitrate and fluoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo Health 9(3):183–195
Chen L, Wang W, Zhang Z et al (2018) Estimation of bare soil evaporation for different depths of water table in the wind-blown sand area of the Ordos Basin. China. Hydrogeol J 26(5):1693–1704
Ghahremanzadeh H, Noori R, Baghvand A et al (2018) Evaluating the main sources of groundwater pollution in the southern Tehran aquifer using principal component factor analysis. Environ Geochem Health 40(4):1317–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0058-8
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection & Quarantine of China, Standardization Administration of China (2017) Standards for groundwater quality (GB/T 14848-2017). Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
He S, Wu J (2019a) Hydrogeochemical characteristics, groundwater quality and health risks from hexavalent chromium and nitrate in groundwater of Huanhe Formation in Wuqi County, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0289-7
He S, Wu J (2019b) Relationships of groundwater quality and associated health risks with land use/land cover patterns: a case study in a loess area, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):354–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.15704
He X, Wu J, He S (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):32–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
Howard GJB, Pedley S, Schmoll O, Chorus I, Berger P (2006) Groundwater and public health. IWA Publishing, London
Khan R, Jhariya DC (2017) Groundwater quality assessment for drinking purpose in Raipur city, Chhattisgarh using water quality index and geographic information system. J Geol Soc India 90(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0665-0
Kumar M, Ramanathan A, Rao MS et al (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50(7):1025–1039
Li P, Wu J (2019a) Sustainable living with risks: meeting the challenges. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1584030
Li P, Wu J (2019b) Drinking Water Quality and Public Health. Expo Health 11(2):73–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00299-8
Li P, Qian H, Wu J et al (2013) Major Ion Chemistry of Shallow Groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin. China. Mine Water Environ 32(3):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015) Building a new and sustainable “Silk Road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li P, Li X, Meng X, Li M, Zhang Y (2016) Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Expo Health 8(3):361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Li P, Qian H, Zhou W (2017) Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: an introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environ Earth Sci 76(3):105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Li P, Wu J, Tian R et al (2018a) Geochemistry, Hydraulic Connectivity and Quality Appraisal of Multilayered Groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine. Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Li P, He S, He X, Tian R (2018b) Seasonal hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality delineation based on matter element extension analysis in a paper wastewater irrigation area, northwest China. Expo Health 10(4):241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-17-0258-6
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2018c) Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1443059
Li P, He X, Li Y, Xiang G (2019a) Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifers in the Chinese Loess Plateau: a case study of Tongchuan, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Li P, Tian R, Liu R (2019b) Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua Phosphorite Mine, Guizhou Province China. Expo Health 11(2):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0277-y
Li P, He X, Guo W (2019c) Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: a case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):11–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1553612
Liu J, Jin D, Wang T et al (2019a) Hydrogeochemical processes and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in Chenqi coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8355-4
Liu J, Gao M, Wang TT et al (2019b) Hydrochemical processes and groundwater quality assessment in Yushenfu mining area, Northwest China. Desalin Water Treat 165:177–187. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24580
Maila YA, EI-Nahal I, Al-Agha MR (2004) Seasonal variations and mechanisms of groundwater nitrate pollution in the Gaza Strip. Environ Geol 47:84–90
Ministry of Environmental Protection of People’s Republic of China (2014) Technical guidance for risk assessment of contaminated sites, (HJ 25.3-2014). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Peng J, Li C, Xiang M et al (2018) Influence of coal mining on phreatic aquifer and its environmental effects in Yulin-Shenmu-Fugu Area. Coal Sci Technol 46(2):156–162 (in Chinese)
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Schoeller H (ed) Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Res Series-33. UNESCO, Delft, pp 54–83
Şener Ş, Şener E, Davraz A (2017) Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci Total Environ 584–585:131–144
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B et al (2010) Quality Assessment of Mine Water in the Raniganj Coalfield Area India. Mine Water Environ 29(4):248–262
Su H, Kang W, Xu Y et al (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality and health risk in the oil and gas field of Dingbian County Northwest China. Expo Health 9(4):224–242
Subba Rao N, Marghade D, Dinakar A et al (2017) Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh India. Environ Earth Sci 76:747
Tiwari AK, Singh AK (2014) Hydrogeochemical investigation and groundwater quality assessment of Pratapgarh district Uttar Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 83(3):329–343
Tiwari AK, Singh AK, Singh MP (2017) Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of surface water quality of Pratapgarh District, Uttar Pradesh India. Appl Water Sci 7(4):1609–1623
USEPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund, vol I., Human health evaluation manual (Part A) Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC
USEPA (2012) Integrated risk information system. United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/index.cfm?fuseaction1/4iris.showSubstanceList. Accessed 3 May 2012
Wang W, Yang Z, Kong J, Cheng D, Duan L (2013) Ecological impacts induced by groundwater and their thresholds in the arid areas in Northwest China. Environ Eng Manage J 12(7):1497–1507
Wang L, Dong Y, Xu Z et al (2017) Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the northeastern Tennger Desert, Northern China. Hydrogeol J 25(8):2363
Wang W, Zhang Z, Duan L et al (2018) Response of the groundwater system in the Guanzhong Basin (central China) to climate change and human activities. Hydrogeol J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1757-7
WHO (2018) Drinking-water. World Health Organization fact sheets. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water. Accessed 27 Dec 2018
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health 8(3):311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Yang Z, Wang W, Huang J et al (2006) Research on buried depth of eco-safety about groundwater table in the blown-sand region of the Northern Shaanxi Province. J Northwest Sci 34(8):67–74 (in Chinese)
Yang Q, Wang L, Ma H et al (2016) Hydrochemical characterization and pollution sources identification of groundwater in Salawusu aquifer system of Ordos Basin, China. Environ Pollut 216:340–349
Yidana SM, Yidana A (2010) Assessing water quality using water quality index and multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 59:1461–1573
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77(7):273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zhao B, Li X, Liu H et al (2011) Results from long-term fertilizer experiments in China: the risk of groundwater pollution by nitrate. NJAS-Wageningen J Life Sci 58:177–183
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Tiandi Science and Technology Co. Ltd. Science and Technology Innovation Venture Capital Special Project (Grant No. 2018-TD-MS073), the State Key Laboratory of Water Resource Protection and Utilization in coal mining (Grant No. SHJT-16-30.10), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41907264). The authors would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their critical comments and suggestions which greatly helped us to the improvement of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Gao, M., Jin, D. et al. Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Human Health Risk in the Aeolian-Sand Area of Yulin City, Northwest China. Expo Health 12, 671–680 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00326-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00326-8