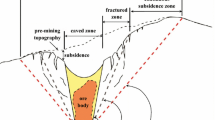
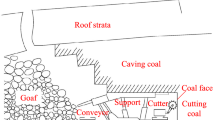
Abstract
The bearing structural characteristics of overlying strata in overlying gobs are the main factor in inducing dynamic disasters in roof in close-distance coal seam group mining. In the present work, the bearing structure and stability characteristics of overlying strata in the shallow-buried interval gob (SBIG) of Yushenfu mining area in north Shaanxi Province, China, have been studied by numerical and physical similarity simulations and theoretical analyses. Research results showed that the instability of gob temporary coal pillars (TCP) led to the rotary instability of basic roof, increasing the stress arch in overlying strata with the expansion of the failure range of overlying rocks giving rise to increases of arch height and superimposition of adjacent stress arches. This way, “trapezoid-semicircular arch” caving of overlying strata was performed. “W-shaped voussoir beam” bearing structure was formed by the fracture of the basic roof of gob and “double arch bridge” bearing structure was created by interval coal pillar (ICP) and fracture rock. In this work, the bearing structure model of interval gob overlying rock “W-shaped voussoir beam + double arch bridge” was established. On the basis of “voussoir beam structure,” the stability of “double arch bridge” type bearing structure formed by the rotation of broken rock block on the top of the basic roof of the interval gob was analyzed. When the support capacity of coal pillar was weakened or the overlying strata were changed, the stability of asymmetrical stress inclined arch equilibrium structure was lost. The stress distribution of “double arch bridge” structure overlying the interval type gob was analyzed by numerical simulation, and the stress transfer law of pier column in floor was obtained. It was found that with the decrease of the width of pier pillar, the “double arch bridge” structure became asymmetric, and the change characteristics of stress inclined arch height were decreased. The arch roof transferring to pier side was divided into prevention and control areas of roof dynamic disaster in the mining of lower coal seams. The purpose of this paper was to provide theoretical guidance for dynamic pressure prevention and control of mining under shallow interval gob.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Du F, Li Z, Jiang G (2017) Types and mechanism of water-sand inrush disaster in west coal mine. J China Coal Soc 42:1846–1853
Ebrahim FS, Majidreza N, Murat K (2017) The effect of rock mass gradual deterioration on the mechanism of post-mining subsidence over shallow abandoned coal mines. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 91:59–71
Feng JF, Zhou Y, Li HG, Liu C (2016) Three kinds of basic structures of working face in near horizontal coal seam. J China Coal Soc 41:2576–2587
Fu EJ. (2010) Study on Reasonable Length of Mining Area and Parameter of Pillar of Nanliang Coal Mine with the Partitional Coal Mining. Master. Thesis. Xi’an University of Science and Technology.
Hou ZJ (1999a) Study on key stratum in shallow seam. J China Coal Soc 04:25–29
Hou ZJ (1999b) Touch measurement of main rock block. J Min Saf Eng Z1:29–31
Hou ZJ (2000) Analysis of combinatorial key strata stability in shallow coal seam with thick loose bed. J China Coal Soc 25:127–131
Hou ZJ, Fu EJ (2009) The study and research on the mining method of longwall interval mining. J Xi’an Univ Sci Technol 29:1–6
Hou ZJ, Xie SH, Zhang J (2003) Simulating test study in shallow seam mining under thick soil of the earth’s surface. J Univ Sci Technol Xi’an 23:357–360
Huang QX (1998) Structural analysis of main roof stability during first weighing in longwall face. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 5:43–48
Huang QX (2000) Study on roof structure and ground control in shallow seam longwall mining. China University of Mining and Technology press. Xuzhou, China
Huang Q, He YP (2019) Research on overburden movement characteristics of large mining height working face in shallow buried thin bedrock. Energies. 12:4208
Huang QX, Qian MG, Shi PW (1999) Structural analysis of main roof stability during periodic weighting in longwall face. J China Coal Soc 06:581–585
Huang QX, Zhang P, Dong AJ (2009) Mathematical model of “arch beam” of thick sandy soil layer movement in shallow seam. Rock Soil Mech 30:2722–2726
Huang Q, He YP, Li F (2020) Research on the roof advanced breaking position and influences of large mining height working face in shallow coal seam. Energies. 13:1685
Hustrulid W.A, Bullock R.L. (1982 ) Underground mining methods handbook[M]. Socioty.
Itasca. UDEC (Universal distinct element code) (2013). Minneapolis, MN, USA: Itasca Consulting Group Inc.
Lai XP, Sun H, Shan PF (2014) Overlying strata ellipsoid-style structure of horizontal section top-coal caving in steeply inclined and extra thick coal seam. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 31:716–720
Li H (1998) The similar simulation testing of ground Pressure. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Li Z, Xu JL, Ju JF, Zhu WB, Xu JM (2018) The effects of the rotational speed of voussoir beam structures formed by key strata on the ground pressure of stopes. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 108:67–79
Lu Z, Sun JM, Pan J, He AM (2002) Application of Wongawili coal mining method in Shendong mining area, Coal Sci. Technol. S1:11–18
Qian MG, Miao XX (1995) Theoretical analysis on the structural and stability of overlying strata in longwall. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 14:97–106
Qian MG, Miao XX (1996) Theoretical study of key stratum in ground control. J China Coal Soc 03:2–7
Qian MG, Miao XX, He FL (1994) Analysis of key block in the structure of voussoir beam in longwall mining. J China Coal Soc 19:557–563
Qian MG, Shi PW, Xu JL (2010) Coal mine pressure and strata control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Wang C, Zhang C, Zhao X, Liao L, Zhang S (2018) Dynamic structural evolution of overlying strata during shallow coal seam longwall mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:20–32
Wang F, Chen SJ, Ren MZ, Xu JL (2019a) Effect of arch structure in unconsolidated layers on failure of the overlying strata. J China Univ Min Technol 48:975–983
Wang F, Xu JL, Xie JL (2019b) Effects of arch structure in unconsolidated layers on fracture and failure of overlying strata. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 114:141–152
Wei DM (2004) Nonlinear theory of arches and its application. Science press, Beijing, China
Wu YP, Xie PS, Ren SG (2010) Analysis of asymmetric structure around coal face of steeply dipping seam mining. J China Coal Soc 35:182–184
Wu YP, Wang HW, Xie PS (2012) Analysis of surrounding rock macro stress arch-shell of longwall face in steeply dipping seam mining. J China Coal Soc 37:559–564
Wu K, Cheng G, Zhou D (2015) Experimental research on dynamic movement in strata overlying coal mines using similar material modeling. Arab J Geosci 8:6521–6534
Xie GX (2005) Study on mechanical characteristics of fully mechanized top-coal caving face and surrounding rock stress shell. J China Coal Soc 30:309–313
Xie GX, Wang L (2013) Lithologic effect on the mechanical characteristics of mining-induced stress shell. J China Coal Soc 38:44–49
Zhang J, Hou ZJ (2005) Study on sand inrush disaster in shallow seam mining. J Univ Sci Technol Hunan 3:15–18
Zhang YL, Wu YP, Luo SH, Xie PS (2020) Study on evolution process and characteristics of overlying strata macro support structure[J]. J China Univ Min Technol 49:280–288
Zhao YH, Wang SR, P. Hagan, Zou ZS. (2017). Instability characteristics analysis of the stress arch in key roof blocks during shallow horizontal thick coal mining. Int. Society Rock Mech. Rock Eng.
Zhao YH, Wang SR, Zou ZS, Ge LL, Cui F (2018) Instability characteristics of the cracked roof rock beam under shallow mining conditions. Int J Min Sci Technol 28:437–444
Zheng BS, Xie WB, Dou LM, Gao MS (2006) 3D simulation on caving of face affected by irregular pillor. J China Coal Soc 31:137–140
Zhu DF. (2018) Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Shallow Insufficient Collapsed Gob and Hazard Induced Mechanism in Lower Seam Mining. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining & Technology, Xuzhou, China.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for its support of this study. We thank academic editors and anonymous reviewers for their kind suggestions and valuable comments.
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51774229), the Innovation Capacity Support Program (Science and Technology Innovation Team) of Shaanxi Province (No.2018TD-038), the Natural Science Fundamental Research Program-Joint Fund Project of Shaanxi Province (2019JLM-41), and Open Fund Project of State Key Laboratory for Water Resources Protection and Utilization in Coal Mining (SHJT-17-42.3)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: J.Z. and B. W.; data curation: B. W.; funding acquisition: J. Z.; project administration: J. Z.; validation: J. Z. and B.W.; writing of original draft: B. W.; writing of review and editing, J: Z. and B.W.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Murat Karakus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, B. Study on the bearing structure and stability of overlying strata: an interval gob in shallow buried coal mining of Northwest China. Arab J Geosci 14, 255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06479-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06479-8