Abstract
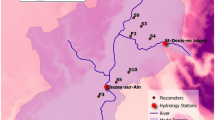
Prediction of groundwater level (GWL) is an important issue for optimal planning and management of groundwater resources. MODFLOW, which is a modular, 3D, finite-difference model, is widely used to simulate GWL. Although MODFLOW is a powerful model for estimating GWLs, it has some unknown parameters, such as specific yield (Sy) and hydraulic conductivity (K). The Dezful-Andimeshk plain, located in the southwest of Iran, was considered as a case study, and its monthly GWLs were simulated. Aquifer boundaries (inflow, outflow, and no-flow), piezometers, operational wells, recharge, drainage, rivers, and evaporation were deemed as the inputs for MODFLOW. Three different algorithms (i.e., shark smell optimization (SSO), particle swarm optimization (PSO), and firefly (FF)) were integrated with MODFLOW (called MODFLOW-SSO, MODFLOW-PSO, and MODFLOW-FF) to find the most accurate values of K, Sy, and GWL of the aquifer. Results revealed that MODFLOW-SSO decreased the root mean square error (RMSE) by 70.2%, 74.9%, and 84.7% at calibration stage and by 68.2%, 73.4%, and 84.2% at validation stage, compared to MODFLOW-PSO, MODFLOW-FF, and MODFLOW, respectively. Other statistical indexes of MODFLOW-SSO (e.g., coefficient of determination (R2) and RMSE) were satisfactory as well. The generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) was applied to calculate the uncertainty of the models with respect to Sy and K. Results indicated that MODFLOW-SSO had the least uncertainty compared to all other models. In general, performance of the MODFLOW was greatly improved by integrating with the SSO algorithm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elmaboud ME, Abdel-Gawad HA, El-Alfy KS, Ezzeldin MM (2021) Estimation of groundwater recharge using simulation-optimization model and cascade forward ANN at East Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 34:100784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100784
Abedinia O, Amjady N, Ghasemi A (2016) A new metaheuristic algorithm based on shark smell optimization. Complexity 21(5):97–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplx.21634
Ahmadisharaf E, Benham BL (2020) Risk-based decision making to evaluate pollutant reduction scenarios. Sci Total Environ 702:135022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135022
Antoniou M, Theodossiou N, Karakatsanis D (2017) Coupling groundwater simulation and optimization models, using MODFLOW and Harmony Search Algorithm. Desalin Water Treat 86:297–304. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20993
Chen J, Yu C, Cai M, Wang H, Zhou P (2020) Multi-objective optimal allocation of urban water resources while considering conflict resolution based on the PSO algorithm: a case study of Kunming, china. Sustainability 12(4):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041337
Chitsazan M, Movahedian A (2015) Evaluation of artificial recharge on groundwater using MODFLOW model (case study: Gotvand Plain-Iran). Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection 3(05):122. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2015.35014
Danandeh Mehr A, Nourani V, Karimi Khosrowshahi V, Ghorbani MA (2019) A hybrid support vector regression–firefly model for monthly rainfall forecasting. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(1):335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1674-2
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, El-Shafie A, Amini Z (2017) Optimizing dam and reservoirs operation-based model utilizing shark algorithm approach. Knowl-Based Syst 122:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.01.026
Farahani N, Karami H, Farzin S, Ehteram M, Kisi O, El-Shafie A (2019) A new method for flood routing utilizing four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum and shark algorithm. Water Resour Manag 33(14):4879–4893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02409-2
Fraga I, Cea L, Puertas J (2019) Effect of rainfall uncertainty on the performance of physically based rainfall–runoff models. Hydrol Process 33(1):160–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13319
Gao H (2011) Groundwater modeling for flow systems with complex geological and hydrogeological conditions. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 3:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2011.09.061
Garousi-Nejad I, Bozorg-Haddad O, Loáiciga HA, Mariño MA (2016) Application of the firefly algorithm to optimal operation of reservoirs with the purpose of irrigation supply and hydropower production. J Irrig Drain Eng 142(10):04016041. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ir.1943-4774.0001064
Gnanasekaran N, Chandramohan S, Kumar PS, Mohamed Imran A (2016) Optimal placement of capacitors in radial distribution system using shark smell optimization algorithm. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 7(2):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2016.01.006
Guzman JA, Moriasi DN, Gowda PH, Steiner JL, Starks PJ, Arnold JG, Srinivasan R (2015) A model integration framework for linking SWAT and MODFLOW. Environ Model Softw 73:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.08.011
Harbaugh AW (2005). MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey modular ground-water model: the ground-water flow process. US Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-A16.
Karimi L, Motagh M, Entezam I (2019) Modeling groundwater level fluctuations in Tehran aquifer: results from a 3D unconfined aquifer model. Groundw Sustain Dev 8:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.01.003
Khadri SFR, Pande C (2016) Groundwater flow modeling for calibrating steady state using MODFLOW software: a case study of Mahesh River basin, India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0049-7
Kisi O, Shiri J, Karimi S, Shamshirband S, Motamedi S, Petković D, Hashim R (2015) A survey of water level fluctuation predicting in Urmia Lake using support vector machine with firefly algorithm. Appl Math Comput 270:731–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2015.08.085
Li L, Qin L, Qu X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Ran B (2019b) Day-ahead traffic flow forecasting based on a deep belief network optimized by the multi-objective particle swarm algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 172:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.01.015
Li Y, Khan MYA, Jiang Y, Tian F, Liao W, Fu S, He C (2019a) CART and PSO+KNN algorithms to estimate the impact of water level change on water quality in Poyang Lake, China. Arab J Geosci 12:287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4350-z
Liu J, Shao W, Xiang C, Mei C, Li Z (2020) Uncertainties of urban flood modeling: influence of parameters for different underlying surfaces. Environ Res 182:108929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108929
Malekinezhad H, Banadkooki FB (2018) Modeling impacts of climate change and human activities on groundwater resources using MODFLOW. Journal of Water and Climate Change 9(1):156–177. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2017.147
Malekzadeh M, Kardar S, Shabanlou S (2019) Simulation of groundwater level using MODFLOW, extreme learning machine and Wavelet-Extreme Learning Machine models. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100279
McDonald MG, Harbaugh AW (1984). A modular three-dimensional finite-difference ground-water flow model. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 83–875, 528 p. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(86)90106-x
Moghaddam HK, Moghaddam HK, Kivi ZR, Bahreinimotlagh M, Alizadeh MJ (2019) Developing comparative mathematic models, BN and ANN for forecasting of groundwater levels. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100237
Mohanty S, Jha MK, Kumar A, Panda DK (2013) Comparative evaluation of numerical model and artificial neural network for simulating groundwater flow in Kathajodi–Surua Inter-basin of Odisha, India. J Hydrol 495:38–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.04.041
Moutsopoulos KN, Papaspyros JNE, Tsihrintzis VA (2017) Management of groundwater resources using surface pumps: optimization using Genetic Algorithms and the Tabu Search method. KSCE J Civ Eng 21:2968–2976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1013-z
Nematolahi M, Jalali V, Hejazi Mehrizi M (2018) Predicting saturated hydraulic conductivity using particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Arab J Geosci 11(16). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3846-2
Peng J, Zhu Y, Yong T (2017) Research on location characteristics and algorithms based on frequency domain for a 2D underwater active electrolocation positioning system. Journal of Bionic Engineering 14(4):759–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60441-9
Rahnama MB, Zamzam A (2013) Quantitative and qualitative simulation of groundwater by mathematical models in Rafsanjan aquifer using MODFLOW and MT3DMS. Arab J Geosci 6(3):901–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0364-x
Sadeghi-Tabas S, Akbarpour A, Pourreza-Bilondi M, Samadi S (2016) Toward reliable calibration of aquifer hydrodynamic parameters: characterizing and optimization of arid groundwater system using swarm intelligence optimization algorithm. Arab J Geosci 9(18). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2751-9
Sadeghi-Tabas S, Samadi V, Akbarpour A, Pourreza-Bilondi M (2017) Sustainable groundwater modeling using single-and multi-objective optimization algorithms. J Hydroinf 19(1):97–114. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2016.006
Sahoo S, Jha MK (2013) Groundwater-level prediction using multiple linear regression and artificial neural network techniques: a comparative assessment. Hydrogeol J 21(8):1865–1887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-013-1029-5
Sheng M, Liu J, Zhu AX, Rossiter DG, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhu L (2019) Comparison of GLUE and DREAM for the estimation of cultivar parameters in the APSIM-maize model. Agric For Meteorol 278:107659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107659
Wang H, Wang W, Cui Z, Zhou X, Zhao J, Li Y (2018) A new dynamic firefly algorithm for demand estimation of water resources. Inf Sci 438:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.01.041
Wei Y, Stanford RJ (2019) Parameter identification of solid oxide fuel cell by Chaotic Binary Shark Smell Optimization method. Energy 188:115770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.07.100
Xu X, Huang G, Qu Z, Pereira LS (2011) Using MODFLOW and GIS to assess changes in groundwater dynamics in response to water saving measures in irrigation districts of the upper Yellow River basin. Water Resour Manag 25(8):2035–2059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9793-2
Xu H, Ma C, Xu K, Lian J, Long Y (2020a) Staged optimization of urban drainage systems considering climate change and hydrological model uncertainty. J Hydrol 587:124959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124959
Xu L, Si Y, Jiang S, Sun Y, Ebrahimian H (2020b) Medical image fusion using a modified shark smell optimization algorithm and hybrid wavelet-homomorphic filter. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 59:101885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101885
Yousefi H, Zahedi S, Niksokhan MH, Momeni M (2019) Ten-year prediction of groundwater level in Karaj plain (Iran) using MODFLOW2005-NWT in MATLAB. Environ Earth Sci 78(12):343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8340-y
Zarei A, Mousavi SF, Eshaghi Gordji M, Karami H (2019) Optimal reservoir operation using bat and particle swarm algorithm and game theory based on optimal water allocation among consumers. Water Resour Manag 33(9):3071–3093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02286-9
Availability of data and material
Data are available by request.
Code availability
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have somehow participated in this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We agree with the COPE principles.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, M., Mousavi, SF., Moridi, A. et al. A new hybrid framework based on integration of optimization algorithms and numerical method for estimating monthly groundwater level. Arab J Geosci 14, 994 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07349-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07349-z