Abstract
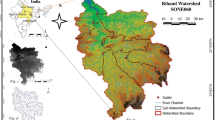
Identification for planning of land and water resource management based on efficient decision-making tool is very important for providing appropriate weightage in stressed site. In the present study, fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (FAHP) with different erosion hazards parameters (EHPs) have been used as a pronouncement for identification of naturally stressed sub-watershed in Nagwan watershed of Hazaribagh district in Jharkhand, India. In fuzzy-AHP, analytical hierarchy process (AHP) builds a hierarchy (ranking) of decision items using comparisons between each pair of items expressed as a matrix with fuzziness. Paired comparisons produce weighting scores that measure how much importance items and criteria have with each other and checking the consistency of the decision. In this study, the Nagwan watershed was divided in 21 sub-watershed which varies from 2.34 to 7 km2 and all EHPs of sub-watersheds have been computed using remote sensing and GIS. From the study, it has been observed that best consistency ratio has been found when using 13 parameters that is 9.44 with narrow trapezoidal shape. Each morphometric parameter was ranked with respect to the value and weightage obtained by deriving the relationships between the morphometric parameters obtained through classification of the SW by associating the strength of fuzzy analytical hierarchy processes (FAHP). By this weight, the results revealed that the priorities in five categories, out of 21 sub-watershed 19 and 24% sub-watersheds qualify for very high and high priority, whereas 57% sub-watersheds fall under medium, low and very low priority.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, P. E. (2005). Watershed hydrology. Hoboken: Wiley.
Buckley, J. J. (1985). Fuzzy herarchical analysis. Journal of Fuzzy Sets and System, 34, 187–195.
Chopra, R., Dhiman, D. R., & Sharma, P. K. (2005). Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in Gurdaspur district, Punjab using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33(4), 532–539.
Chow, V. T. (1964). Handbook of applied hydrology. Section, 8, 61.
Chowdary, V. M., Chakraborthy, D., Jeyaram, A., Krishna Murthy, Y. V. N., Sharma, J. R., & Dadhwal, V. K. (2013). Multi-criteria decision making approach for watershed prioritization using hierarchy process technique and GIS. Journal of Water Resource Management, 27(10), 3555–3571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0364-6.
Deng, H. (1999). Multicriteria analysis with fuzzy pairwise comparisons. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 21, 215–231.
El-Swaify, S. A., Dangler, E. W., & Armstrong, C. L. (1982). Soil erosion by water in the tropics, edit (p. 173). Honolulu: HITAHR, University of Hawai.
Erensal, Y. C., Oncan, T., & Demircan, M. L. (2006). Determining key capabilities in technology management using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: A case study of Turkey. Journal of Information Sciences, 176, 2755–2770.
Essiet, E. (1990). A comparison of soil degradation under small holder farming and large-scale irrigation land use in Kano State, northern Nigeria. Wiley Online Library Land Degradation & Development, 2, 209–214.
Han, W. J., & Tsay, W. D. (1998). Formulation of quality strategy using analytic hierarchy process. In Twenty seven annual meeting of the western decision science institute (pp. 580–583), University of Northern Colorado, USA.
Hansen, H. S. (2005). GIS-based multi-criteria analysis of wind farm development. In H. Hauska and H. Tveite (Eds.), Proceedings of the 10th scandinavian research conference on geographical information science (ScanGIS’2005) (pp. 75–87). Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology.
Hlaing, T. K., Haruyama, S., & Maung, A. M. (2008). Using GIS-based distributed soil loss modeling and morphometric analysis to prioritize watershed for soil conservation in Bago river basin of Lower Myanmar. Journal of Earth Science, 2(4), 465–478.
Jaiswal, R. K., Dehariya, D. K., Nema, A. K., Thomas, T., & Galkate, R. V. (2012). Soil erosion based prioritization and development of CAT plan for catchment of Rangawan reservoir in Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh, India. In National symposium on water resource management in changing environ (pp. 409–420). Roorkee, India, 8–9 February, 2012.
Jaiswal, R. K., Ghosh, N. C., Lohani, A. K., & Thomas, T. (2015). Fuzzy AHP Based Multi Crteria Decision Support for Watershed Prioritization. Water Resources Management, 29(12), 4205–4227
Jaiswal, R. K., Thomas, T., Galkate, R. V., Ghosh, N. C., & Singh, S. (2014). Watershed prioritization using Saaty’s AHP based decision support for soil conservation measures. Journal of Water Resource Management, 28(2), 475–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0494-x.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Ahmed, R. (2009). Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37, 261–274.
Jose, C. S., & Das, D. C. (1982). Geomorphic prediction models for sediment production rate and inter soil erosion properties of watersheds in Mayurakshi catchment. In Proceeding international symposium hydrological aspects of mountainous watersheds (Vol. 1, pp. 15–33). Roorkee.
Khan, M. A., Gupta, V. P., & Moharanam, P. C. (2001). Watershed prioritization using remote sensing and geographical information system: A case study from Guhiya India. Journal of Arid Environment, 49, 465–475.
Kordi, M. (2008). Comparison of fuzzy and crisp analytic hierarchy process (AHP) methods for spatial multicriteria decision analysis in GIS. Master Thesis, Department of Technology and Built Environment, University of Galve, pp. 1–45.
Malczewski, J. (1999). GIS and multicriteria desision analysis. New York: Wiley.
Mikhailov, L., & Tsvetinov, P. (2004). Evaluation of services using a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Journal of Applied Soft Computing, 5, 23–33.
Mishra, S. S., & Nagarajan, R. (2010). Morphometric analysis and prioritization of sub-watersheds using GIS and remote sensing techniques: A case study of Odisha, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geoscience, 1(3), 501–510.
Mishra, N., Satyanarayan, T., & Mukherjee, R. K. (1984). Effect of topo elements on the sediment production rate from sub-watersheds in upper Damodar valley. Journal of the Indian society of Agricultural Engineers (ISAE), 21(3), 65–70.
Nag, S. K., & Chakraborty, S. (2003). Influence of rock types and structures in the development of drainage network in hard rock area. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 1, 25–35.
Oyatoye, E. O., Okpokpo, G. U., & Adekoya, G. A. (2010). An application of analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to investment portfolio selection in the banking sectors of the Nigerian capital market. Journal of Economics International Finance, 2(12), 321–335.
Pandey, A., Chowdary, V. M., & Mal, B. C. (2007). Identification of critical erosion prone areas in the small agricultural watershed using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Journal of Water Resource Management, 21, 729–746.
Patel, D. P., Dholakia, M. B., Naresh, N., & Srivastava, P. K. (2012). Water harvesting structure positioning by using geo-visualization concept and prioritization of mini-watersheds through morphometric analysis in the Lower Tapi Basin. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 40(2), 299–312
Rao, H. S. S., & Mahabaleswara, H. (1990). Prediction of rate of sedimentation of Tungabhadra Reservoir. In Proceeding of symposium on erosion, sedimentation & resource conservation (Vol. 1, pp. 12–20). Dehradun.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). Fundamentals of decision making and priority theory with analytical hierarchical process (Vol. 4, pp. 3–95). Pittusburgh: RWS Publications University of Pittsburgh.
Sharma, J. C., Prasad, J., Saha, S. K., & Pande, L. M. (2001). Watershed prioritization based on sediment yield index in eastern part of Don Valley using RS and GIS. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation, 29(1), 7–13.
Sharma, S. K., Rajput, G. S., Tignath, S., & Pandey, R. P. (2010). Morphometric analysis and prioritization of a watershed using GIS. Journal of Indian Water Resource Society, 30(2), 33–39.
Shrimali, S. S., Aggarwal, S. P., & Samra, J. S. (2001). Prioritizing erosion-prone areas in hills using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of the Sukhna lake catchment, northern India. International Journal Applied Earth Observation Geoinformatics, 3(1), 54–60.
Sidhu, G. S., Das, T. H., Singh, R. S., Sharma, R. K., & Ravishankar, T. (1998). Remote sensing and GIS techniques for prioritization of watershed: A case study in upper Mackkund watershed, Andhra Pradesh. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation, 2(3), 71–75.
Smith, K. G. (1950). Standards for grading textures of erosional topography. American Journal of Science, 248, 655–668.
Tam, C. M., Tong, T. K. L., Leung, A. W. T., & Chiu, G. W. C. (2002). Site layout planning using nonstructural fuzzy decision support system. Journal of Construction Engineering Management, 128(3), 220–228. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2002)128:3(220).
Vittala, S. S., Govindaiah, S., & Gowda, H. H. (2004). Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in the Pavagada area of Tumkar district, south India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society Remote Sensing, 32(4), 351–362.
Wischmeier, W. H., & Smith, D. P. (1978). Predicting rainfall erosion losses-a guide to conservation planning. In Agriculture hand-book No 537 (pp. 58–61). US Department Agriculture, Washington DC.
Yadav, S. K., Singh, S. K., Gupta, M., & Srivastava, P. K. (2014). Morphometric analysis of upper tons basin from northern foreland of peninsular India using CARTOSAT satellite and GIS. Geocarto International J ournal. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.868043.
Yahaya, S., Ahamd, N., & Abdalla, R. F. (2010). Multicriteria analysis for flood vulnerable areas in Hadejia-Jama’are river basin, Nigeria. European Journal of Scientific Research, 42(1), 72–83.
Yoshino, K., & Ishioka, Y. (2005). Guidelines for soil conservation towards integrated basin management for sustainable development: A new approach based on the assessment of soil loss risk using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of Water Environment, 3, 235–247.
Zadeh, L. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8(3), 338–353.
Zimmermann, H. J. (1934). Fuzzy set theory—and its applications (3rd ed.). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, C.D., Jaiswal, R.K., Nema, A.K. et al. Priority Assessment of Sub-watershed Based on Optimum Number of Parameters Using Fuzzy-AHP Decision Support System in the Environment of RS and GIS. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47, 603–617 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0904-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0904-x