Abstract
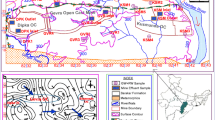
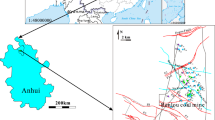
Lack of proper reclamation strategy and indiscriminate mining of various economic resources, particularly coal from Permo-carboniferous Gondwana coalfields affects the groundwater quality of the concerned regions. Leaching from mine-tailings along with seasonal fluctuation of water table caused a significant change in groundwater geochemistry of Raniganj coalfield area. Gondwana sequences, developed in intracratonic rift basin, are characterized by numerous longitudinal and cross faults. This results in the formation of many small aquifer systems which may be interconnected laterally as well as vertically providing the conduit for homogenization of aquifers. Although the predominance of major cations (Ca>Na>Mg>K) and anions (HCO3>Cl>SO4>NO3) remain same irrespective of season, the dominance of Na and SO4 have significantly increased in post-monsoon season. The types of groundwater in pre-monsoon and postmonsoon seasons are CaMgCl and CaHCO3 respectively. Leaching of SO4 from surface sources (mine tailings) has increased TDS in post-monsoon. Base exchange (direct and reverse) reactions have taken place between aquifer materials and groundwater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Appelo, C.A.J. and Postma, D. (1993) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, Balkema, Rotterdam.
Bhattacharya, H.N. and Bhattacharya, B. (2006) A permocarboniferous tide-storm interactive system: Talchir Formation, Raniganj Basin, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.27, pp.303–311.
BIS (1991) Indian standard specification for drinking water. IS: 10500, Bureau of Indian Standards.
Casshyap, S.M. and Tewari, R.C. (1988) Depositional models and tectonic evolution of Gondwana Basins. Palaeobot., v.36, pp.59–66.
Chatterjee, G.C. and Ghosh, P.K. (1970) Tectonic framework of the peninsular Gondwanas of India. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.98(2), pp.1–15.
Choubey, V.D. (1991) Hydrogeological and Environmental Impact of Coal Mining, Jharia Coalfield, India. Environ. Geol. Water Sci., v.17(3), pp.185–194.
Freeze, R.A. and Cherry, J.A. (1979) Ground Water. Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliff, NJ. 605.
Geological Survey of India Bulletin (2003) Series ‘A’, No. 45. Coalfields of India, volume V Coal Resources of West Bengal. Government of India.
Gibbs, R.J. (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, v.17 pp.1088–1090.
Hem, J.D. (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters, Book 2254, 3rd edn. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur.
Johnson, C.C. (1979) Land application of water-an accident waiting to happen groundwater v.17(1) pp.69–72.
Karanth, K.R. (1997) Groundwater assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Mehta, D.R.S. (1957) A revision on the geology and coal resources of the Raniganj Coalfield. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.84, pt. II.
Piper, A.M.A. (1953) Graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Groundwater Note 12. USGS.
Raju, N.J. (2006) Sesonal evalution of hydro-geochemical parameters using correlation and regression analysis, Curr. Sci., v.91(6) pp.820–826.
Raju, N.J. Shukla, U.K. and Ram, P. (2011) Hydrogeochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Varanasi: a fasturbanizing center in Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.173 pp.279–300.
Ruiz, F., Gomis, V. and Blasco, P. (1990) Application of factor analysis to the hydrogeological study of a coastal aquifer. Jour. Hydrology, v.119, pp.169–177.
Schoeller, H. (1967) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Research, Series-33 UNESCO, pp.44–52.
Singh, A.K. Mahato, M.K. Neogi, B. Mondal, G.C. and Singh, T.B. (2011) Hudrogeochemistry, Elemental Flux, and Quality assessment of mine water in the Pootkee-Balihari Mining Area, Jharia coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ. v.30, pp.197–207
Venugopal, T., Giridharan, L., Jayaprakash, M. and Periakali, P. (2009) Environmental impact assessment and seasonal variation study of the groundwater in the vicinity of River Adyar, Chennai, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.149 pp.81–97.
Walton, W.C. (1970) Groundwater resources evaluation. McGraw-Hill, New York.
WHO (1997) Guideline for drinking water quality. Recommendations (Vol. 1, 2nd Edn). Geneva: WHO.
Zaporozec, A. (1972) Graphical interpretation of water quality data. Groundwater, v.10(2), pp.32–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adhikari, K., Sadhu, K., Chakroborty, B. et al. Effect of mining on geochemistry of groundwater in Permo-carboniferous Gondwana coalfields: Raniganj Basin, India. J Geol Soc India 82, 392–402 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0166-8