Abstract
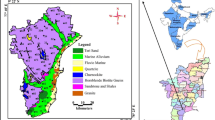
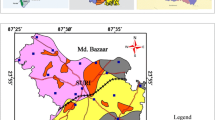
The chemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of Palakkad district, Kerala show the role of slow weathering of rocks rich in ferromagnesian minerals in increasing the residual alkalinity of water, and promoting calcium carbonate precipitation and dissolution of fluoride from minerals like biotite and hornblende. Alkaline clayey soils having high cation exchange capacity have a significant role in the process. Leaching of fluoride from soil and weathered rock in the vadose zone appears to be a major cause for high fluoride in groundwater. No relation is seen between fluoride contents in rocks and soils, and in groundwater, while the degree of weathering is a probable controlling factor. The study indicates that, while alkaline pH promotes dissolution of F−, a further linear increase in pH is not required for more increase in dissolution of F−. Similarly, the correlation of F− with HCO3 −/Ca2+ ratio may be a more reliable indicator than the correlation of F− with Ca2+. Surface water irrigation has influenced groundwater quality in a large tract. Dug well and bore well waters belong to the same chemical type indicating connectivity between the two aquifers. There is evidence for influent flow from streams into the fractured rock aquifer in some areas. The study was conducted between November 2009 and May 2011.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S., Sreedevi, P.D., Sujatha, D., Hashimi, S.A.R., Subrahmanyam, K., Saxena, V.K. and Touchard, F. (2002) Time-variant behavior of fluoride contents in granitic aquifers. Internat. Groundwater Conf., Dindigul, Tamil Nadu, India.
Bench Mark Soils Of Kerala (2007) Soil Survey Organisation, Agriculture (S.C.Unit) Department, Government of Kerala, pp.375–383.
Blom, T. and Cederlund, E. (2006) Fluoride contaminated groundwater in Palakkad and Alappuzha districts of Kerala. South India- Chemical characteristics and mechanisms of mobilization, Stockholm. TRITA-LWR Master Thesis 06–09.
Chae, G.T., Yun, S.T., Mayer, B., Kim, K.H., Kim, S.Y., Kwon, J.S., Kim, K. and Koh, Y.K. (2007) Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Science of the Total Environment. no.385, pp.272–283.
Drever, J.I. (1988) The Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Guo, Q., Wang, Y., Ma, T. and Ma, R. (2007) Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentrations in groundwaters of the Taiyuan Basin, Northern China. Jour. Geochem. Explor., 93, pp.1–12.
Hem, J.D. (1989) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS Water-Supply Paper 22–4.
Jacks, G., Rajagopalan, K., Alveteg, T. and Jonsson, M. (1993) Genesis of high-F groundwaters, southern India. Appld. Geochem., Suppl. issue no.2, pp.241–244.
Kukillaya, J.P. (1995) Hydrogeology of Korayar-Varattar area in Palakkad Gap-An example of induced recharge-need for artificial recharge. Hydrol. Jour. Roorkee, July–Dec.
Kukillaya, J.P., Kunhi, A.M. and Abdul Rahiman, A.K. (1992) Basic and ultrabasic formations as potential aquifers in hard rock terrain-a case study. Bhujal News. v.7(4), pp.14–19.
Langmuir, D. (1997) Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Meenakshi and Maheshwari, R.C. (2006) Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. Jour. Hazard. Mat., B137, pp.456–463.
Nageswara Rao, J. and Srinivasan, R. (year unknown) Some aspects of geomorphology, structure and sedimentation in Palghat Gap area. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ. No.5.
Raja Raja Varma (1992) Presence of fluoride in the groundwater of Palakkad district. Note on Investigation, Planning and Design Sub Division, Kerala Water Authority, Tirur.
Ramesam, V. and Rajagopalan, K. (1985) Fluoride ingestion into the natural waters of hard-rock areas, Peninsular India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.26, pp.125–132.
Saxena, V.K. and Ahmed, S. (2003) Inferring the chemical parameters for the dissolution of fluoride in groundwater. Environ. Geol., v.43, pp.731–736.
Shaji, E., Bindu, Viju J. and Thambi, D.S. (2007) High fluoride in Palghat district of Kerala. Curr. Sci., v.92(2), pp.240–245.
Walther, J.V. (2010) Essentials of Geochemistry. Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukillaya, J.P., Narayanan, T. Role of weathering of ferromagnesian minerals and surface water irrigation in evolving and modifying chemistry of groundwater in Palakkad district, Kerala, with special reference to its fluoride content. J Geol Soc India 84, 579–589 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0165-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0165-4