Abstract
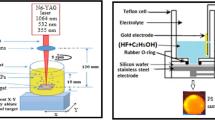
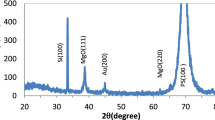
In this study, aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) at 0.3 wt.% was synthesized by a pulsed Nd: YAG laser with a fundamental wavelength (1064 nm). The laser beam is focused on a ZnO-doped target immersed in distilled water at two pulse energies of 200 and 400 mJ. The procedure was applied in two cases: without and with the presence of the magnetic field. AZO nanoparticles were investigated by UV–visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and electron microscopy (SEM). In addition, a mixture of metal oxide nanoparticles was used for gas-sensing application. XRD shows the enhancement of crystallization in the presence of the magnetic field. SEM images show the adoption of AZO thin nanostructures in the high surface region with applying an external magnetic field and with increasing laser power. The AZO-based syngas sensor has greater sensitivity against NO2 gas than H2S gas with an optimal operating temperature of 200 °C. The use of laser energy of 400 mJ with a magnetic field leads to the creation of a nanostructure with a large surface area, which makes it highly sensitive, especially to NO2 gas compared to other samples. The prepared active layer for the gas sensor has an acceptable sensitivity against NO2 gas more than H2S gas with an optimal operating temperature of 200 °C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.-Y. Tsay, K.-S. Fan, S.-H. Chen, C.-H. Tsai, Preparation and characterization of ZnO transparent semiconductor thin films by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 495, 126–130 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.100
C. Klingshirn, R. Hauschild, J. Fallert, H. Kalt, Room-temperature stimulated emission of ZnO: alternatives to excitonic lasing. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 115203 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.115203
C. Li, Y. Li, Y. Wu, B.-S. Ong, R.-O. Loutfy, Fabrication conditions for solution-processed high-mobility ZnO thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 1626 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b812047a
C. Li, X. Fan, L. Yu, L. Cui, M. Yin, Y. Li, N. Nan, N. Liu, A resistive-type UV detector based on ZnO nanowalls decoated by Ag nanowires. Opt. Mater. 103, 109891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109891
X. Zheng, Y. Sun, H. Qin, Z. Ji, H. Chi, Interface engineering on ZnO/Au based Schottky junction for enhanced photoresponse of UV detector with TiO2 inserting layer. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 152537 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152537
A. Wibowo, M.A. Marsudi, M.I. Amal, M.B. Ananda, R. Stephanie, H. Ardy, L.J. Diguna, ZnO nanostructured materials for emerging solar cell applications. RSC Adv. 10, 42838–42859 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA07689A
F. Rahman, Zinc oxide light-emitting diodes: a review. Opt. Eng. 58, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.58.1.010901
S. Nie, D. Dastan, J. Li, W.-D. Zhou, S.-S. Wu, Y.-W. Zhou, X.-T. Yin, Gas-sensing selectivity of n-ZnO/p-Co3O4 sensors for homogeneous reducing gas. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 150, 109864 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109864
H. Zhang, G. Tian, D. Xiong, T. Yang, S. Zhong, L. Jin, B. Lan, L. Deng, S. Wang, Y. Sun, W. Yang, W. Deng, Understanding the enhancement mechanism of ZnO nanorod-based piezoelectric devices through surface engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 14, 29061–29069 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c02371
Z. Zhang, X. Chen, J. Kang, Z. Yu, J. Tian, Z. Gong, A. Jia, R. You, K. Qian, S. He, B. Teng, Y. Cui, Y. Wang, W. Zhang, W. Huang, The active sites of Cu–ZnO catalysts for water gas shift and CO hydrogenation reactions. Nat. Commun. 12, 4331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24621-8
V.H. Nguyen, J. Resende, D.T. Papanastasiou, N. Fontanals, C. Jiménez, D. Muñoz-Rojas, D. Bellet, Low-cost fabrication of flexible transparent electrodes based on Al doped ZnO and silver nanowire nanocomposites: impact of the network density. Nanoscale 11, 12097–12107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR02664A
S.D. Ponja, S. Sathasivam, I.P. Parkin, C.J. Carmalt, Highly conductive and transparent gallium doped zinc oxide thin films via chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Rep. 10, 638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57532-7
A.M. Mostafa, A.A. Menazea, Laser-assisted for preparation ZnO/CdO thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition for catalytic degradation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 176, 109020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.109020
A.F. Abdulrahman, S.M. Ahmed, N.M. Ahmed, M.A. Almessiere, Enhancement of ZnO nanorods properties using modified chemical bath deposition method: effect of precursor concentration. Crystals 10, 386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10050386
D.T. Speaks, Effect of concentration, aging, and annealing on sol gel ZnO and Al-doped ZnO thin films. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 15, 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40712-019-0113-6
A. Patil, C. Dighavkar, R. Borse, Al doped ZnO thick films as CO 2 gas sensors. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 13, 1331–1337 (2011)
M. Özgür, S. Pat, R. Mohammadigharehbagh, C. Musaoğlu, U. Demirkol, S. Elmas, S. Özen, Ş Korkmaz, Al doped ZnO thin film deposition by thermionic vacuum arc. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 624–630 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0329x
D.R.A. El-Hafiz, M.A. Ebiad, A.A.E. Sakr, Ultrasonic-assisted nano-nickel ferrite spinel synthesis for natural gas reforming. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01718-z
M.M. ElFaham, M. Okil, A.M. Mostafa, Effects of post-laser irradiation on the optical and structure properties of Al 2 O 3 nanoparticles produced by laser ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 153104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0022554
F. Taccogna, M. Dell’Aglio, M. Rutigliano, G. Valenza, A. De Giacomo, On the growth mechanism of nanoparticles in plasma during pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26, 045002 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6595/aa595b
A.G. Ardakani, P. Rafieipour, Using ZnO nanosheets grown by electrodeposition in random lasers as scattering centers: the effects of sheet size and presence of mode competition. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B. 35, 1708 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.35.001708
M.A. Kadhim, A.A. Ramadhan, M.O.S. Al-Gburi, G.J. Habi, N.J. Hentawe, Effect of mixing ratio of (SnO2)1–x(In2O3)x thin film on gas sensitivity. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 6, 83–92 (2020). https://doi.org/10.33640/2405-609X.1403
B. Liu, H.C. Zeng, Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods in the diameter regime of 50 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 4430–4431 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0299452
S. Vempati, J. Mitra, P. Dawson, One-step synthesis of ZnO nanosheets: a blue-white fluorophore. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 470 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-470
N. Tripathy, R. Ahmad, H. Kuk, Y.-B. Hahn, G. Khang, Mesoporous ZnO nanoclusters as an ultra-active photocatalyst. Ceram. Int. 42, 9519–9526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.030
P.K. Kannan, R. Saraswathi, J.B.B. Rayappan, CO2gas sensing properties of DC reactive magnetron sputtered ZnO thin film. Ceram. Int. 40, 13115–13122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.05.011
D. Patidar, A. Kaswan, N.S. Saxena, K. Sharma, Monodispersed ZnO nanoparticles and their use in heterojunction solar cell. Sci. World J. 2013, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/260521
I.M. McIntosh, A.R.L. Nichols, K. Tani, E.W. Llewellin, Accounting for the species-dependence of the 3500 cm −1 H 2 O t infrared molar absorptivity coefficient: Implications for hydrated volcanic glasses. Am. Mineral. 102, 1677–1689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2017-5952CCBY
K. Schneider, W. Maziarz, V2O5 thin films as nitrogen dioxide sensors. Proceedings 2, 1–5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130759
L. Francioso, A. Forleo, S. Capone, M. Epifani, A.M. Taurino, P. Siciliano, Nanostructured In2O3–SnO2 sol–gel thin film as material for NO2 detection. Sensors Actuators B. 114, 646–655 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.03.124
H. Xuemei, S. Yukun, B. Bo, Fabrication of cubic p-n heterojunction-like NiO/In2O3 composite microparticles and their enhanced gas sensing characteristics. J. Nanomater. 2016, 1–9 (2016)
Y.F. Sun, S.B. Liu, F.L. Meng, J.Y. Liu, Z. Jin, L.T. Kong, J.H. Liu, Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors. 12, 2610–2631 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/s120302610
D. Liu, Z. Tang, Z. Zhang, Comparative study on NO2 and H2S sensing mechanisms of gas sensors based on WS2 nanosheets. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 303, 127114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127114
M.A. Franco, P.P. Conti, R.S. Andre, D.S. Correa, A review on chemiresistive ZnO gas sensors. Sensors Actuators Rep. 4, 100100 (2022)
K.G. Krishna, G. Umadevi, S. Parne, N.P. Othukanuri, Zinc oxide based gas sensors and their derivatives: a critical review. J. Mater. Chem. C (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TC04690C
Funding
The present research did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. So its personal work and the statement of declaration of interests are only mine and support has been subjected during the research work for the past year.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each co-author has made specific unique contributions to the work. The authors ZMA prepared the thin films of ZnO and contributed to conceptualizations writing–original draft. The author QAA prepared the special program for optical properties and contributed to supervision and editing analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors would like to declare that they do not have any conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, Z.M., Abbas, Q.A. Aluminum-doped ZnO nano-laminar structures by pulsed laser ablation for gas sensing application. J Opt 53, 544–557 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01192-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01192-z