Abstract
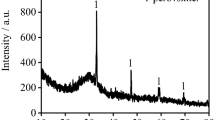
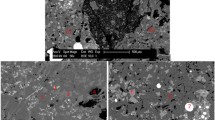
In view of the present problem of sulfur enrichment in the metallurgical recycling process of ladle furnace (LF) refining slag, a simple and efficient method of removing sulfur from this slag was proposed. The proposed method is compatible with current steelmaking processes. Sulfur removal from LF refining slag for SPHC steel (manufactured at a certain steel plant in China) by blowing air in the hot state was studied by using hot-state experiments in a laboratory. The FactSage software, a carbon/sulfur analyzer, and scanning electron microscopy in conjunction with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy were used to test and analyze the sulfur removal effect and to investigate factors influencing sulfur removal rate. The results show that sulfur ions in LF refining slag can be oxidized into SO2 by O2 at high temperature by blowing air into molten slag; SO2 production was observed to reach a maximum with a small amount of blown O2 when the temperature exceeded 1350°C. At 1370°C and 1400°C, experimental LF refining slag is in the liquid state and exhibits good fluidity; under these conditions, the sulfur removal effect by blowing air is greater than 90wt% after 60 min. High temperature and large air flow rate are beneficial for removing sulfur from LF refining slag; compared with air flow rate, temperature has a greater strongly influences on the sulfur removal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Motz and J. Geiseler, Products of steel slags an opportu nity to save natural resources, Waste Manage., 21(2001), No. 3, p. 285.
P. Ahmedzade and B. Sengoz, Evaluation of steel slag coarse aggregate in hot mix asphalt concrete, J. Hazard. Mater., 165(2009), No. 1-3, p. 300.
I.M. Asi, Evaluating skid resistance of different asphalt concrete mixes, Build. Environ., 42(2007), No. 1, p. 325.
M. Ameri and A. Behnood, Laboratory studies to investigate the properties of CIR mixes containing steel slag as a substitute for virgin aggregates, Constr. Build. Mater., 26(2012), No. 1, p. 475.
S. Barella, A. Gruttadauria, F. Magni, C. Mapelli, and D. Mombelli, Survey about safe and reliable use of EAF slag, ISIJ Int., 52(2012), No. 12, p. 2295.
T. Matsumiya, Steelmaking technology for a sustainable society, Calphad, 35(2011), No. 4, p. 627.
H. Qasrawi, F. Shalabi, and I. Asi, Use of low CaO unprocessed steel slag in concrete as fine aggregate, Constr. Build. Mater., 23(2009), No. 2, p. 1118.
I. Papayianni and E. Anastasiou, Production of high-strength concrete using high volume of industrial by-products, Constr. Build. Mater., 24(2010), No. 8, p. 1412.
I. Netinger, I. Kesegic, and I. Guljas, The effect of high temperatures on the mechanical properties of concrete made with different types of aggregates, Fire Saf. J., 46(2011), No. 7, p. 425.
P.E. Tsakiridis, G.D. Papadimitriou, S. Tsivilis, and C. Koroneos, Utilization of steel slag for Portland cement clinker production, J. Hazard. Mater., 152(2008), No. 2, p. 805.
R.I. Iacobescu, D. Koumpouri, Y. Pontikes, R. Saban, and G.N. Angelopoulos, Valorisation of electric arc furnace steel slag as raw material for low energy belite cements, J. Hazard. Mater., 196(2011), p. 287.
T. Tanaka, Y. Ogiso, M. Ueda, and J. Lee, Trial on the application of capillary phenomenon of solid CaO to desulfurization of liquid Fe, ISIJ Int., 50(2010), No. 8, p. 1071.
K. Matsubae-Yokoyama, H. Kubo, and T. Nagasaka, Recycling effects of residual slag after magnetic separation for phosphorus recovery from hot metal dephosphorization slag, ISIJ Int., 50(2010), No. 1, p. 65.
H.X. Yu, X.H. Wang, M. Wang, and W.J. Wang, Desulfurization ability of refining slag with medium basicity, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 21(2014), No. 12, p. 1160.
H. Yi, G.P. Xu, H.G. Cheng, J.S. Wang, Y.F. Wan, and H. Chen, Procedia Environ. Sci., 16(2012), p. 791.
P.L. Cavallotti, C. Mapelli, F. Memoli, and M. Pustorino, Recycling of LF-white slag, Metall. Italy, (2007), No. 10, p. 41.
R. Dippenaar, Industrial uses of slag: the use and re-use of iron and steelmaking slags, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 32(2005), No. 1, p. 35.
J. Geiseler, Use of steelworks slag in Europe, Waste Manage., 16(1996), No. 1-3, p. 59.
M. Kobayashi, Regeneration process of desulphurization slag containing CaF2 by oxidation, CAMP-ISIJ, 48(2008), No. 937.
V.A. Bigeev, L.V. Petrov, K.N. Vdovin, V.N. Kotii, and A.V. Deryabin, Increasing the efficiency of ladle desulfurization of steel by regenerated slags, Metallurg, 31(1987), No. 10, p. 313.
Y.Y. Cui, D.Y. Wang, C.J. Liu, and M.F. Jiang, The novel technology of two-step roasting desulfurization for sulfur- bearing slag, Iron steel Vanadium Titanium, 33(2012), No. 6, p. 31.
A.D. Pelton, J.B. See, and J.F. Elliott, Kinetics of evolution of SO2 from hot metallurgical slags, Metall. Trans., 5(1974), No. 5, p. 1163.
S.K. Wei and G.C. Wang, The desulphurization of molten slags in the gaseous phase during top-blown with air, Acta Metall. Sin., 8(1965), No. 4, p. 419.
S.W. Wu, S.H. Wang, S.T. Jin. Kinetics of gas desulphurization in BOF slag. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 22(2000), No.3, p. 212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Lh., Lin, L. & Wu, Qf. Experimental study on sulfur removal from ladle furnace refining slag in hot state by blowing air. Int J Miner Metall Mater 23, 33–39 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1208-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1208-1