Abstract
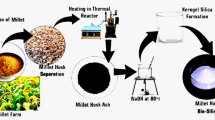
This present study deals about the effect of adding wheat husk biomass converted biosilica into the deionized dielectric medium and its machining effects on high performance engineering alloy Ti-6Al-4 V in electro discharge machining process. The biosilica particles were prepared from wheat husk via thermo-chemical method followed using silane treatment. The activated dielectric was prepared via shear stirring by adding considerable amount (0.25, 0.5 and 1.0wt.%) of biosilica particles. The machining characteristics such as material removal rate (MRR), tool wear rate (TWR), surface roughness (Ra) and microstructure were investigated. According to the results the silane treated biosilica of 1.0wt.% in deionized water gives improved MRR with controlled TWR and surface roughness whereas the as-received biosilica in deionized water produced lesser MRR with high surface roughness and tool wear. However beyond 1.0wt.% of biosilica in water may produce undesirable effects on the machining characteristics. The SEM microscopic images revealed smoothly machined surfaces with no heat affected zones for silane treated biosilica-water dielectric. These machining characteristics improved powder activated dielectric fluids are highly recommended when EDM process of hard alloys and plain metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No data available to deposit as private. There are no rights.
References
Marichamy S, Stalin B, Ravichandran M, Sudha GT (2020) Optimization of machining parameters of EDM for α-β brass using response surface methodology. Mater Today Proc 24:1400–1409
Salcedo A, Torres I, Puertas A, Luis Pérez CJ (2017) Analytical modelling of energy density and optimization of the EDM machining parameters of Inconel 600. Metals 7(5):166
Nair S, Dutta A, Giridharan A (2019) Investigation on EDM machining of Ti6Al4V with negative polarity brass electrode. Mater Manuf Process 34(16):1824–1831
Al-Amin M, Rani AMA, Aliyu AAA, Razak MAA, Hastuty S, Bryant MG (2020) Powder mixed-EDM for potential biomedical applications: A critical review. Mater Manuf Process 35(16):1789–1811
Joshi AY, Joshi AY (2021) Feasibility analysis of powder-mixed deionized water as dielectric for machining Ti6Al4V. J Inst Eng (India): C 102(2):337–347
Alam ST, Nurul Amin AKM, Hossain MI, Huq M, Tamim SH (2021) Performance evaluation of graphite and Titanium Oxide powder mixed dielectric for electric disharge machining of Ti–6Al–4V. SN Appl Sci 3(4):1–12
Singaravel B, Chandra Shekar K, Gowtham Reddy G, Deva Prasad S (2020) Experimental investigation of vegetable oil as dielectric fluid in Electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Ain Shams Eng J 11(1):143–147
Kuriachen B, Mathew J (2016) Effect of powder mixed dielectric on material removal and surface modification in microelectric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Mater Manuf Process 31(4):439–446
Ishfaq K, Asad M, Anwar S, Pruncu CI, Saleh M, Ahmad S (2021) A comprehensive analysis of the effect of graphene-based dielectric for sustainable electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Materials 14(1):23
Prakash VRA, Viswanthan R (2019) Fabrication and characterization of echinoidea spike particles and kenaf natural fibre-reinforced Azadirachta-Indica blended epoxy multi-hybrid bio composite. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 118:317–326
Inbakumar J, Parivendhan, Ramesh S (2018) "Mechanical, wear and thermal behaviour of hemp fibre/egg shell particle reinforced epoxy resin bio composite. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 42(3):280–285
Jagatheesan K, Babu K (2020) Taguchi optimization of minimum quantity lubrication turning of AISI-4320 steel using biochar nanofluid. Biomass Convers Biorefin :1–8
Karthigairajan M, Nagarajan PK, Raviraja Malarvannan R, Ramesh Bapu BR, Jayabalakrishnan D, Maridurai T, Shanmuganathan VK (2020) Effect of silane-treated rice husk derived biosilica on visco-elastic, thermal conductivity and hydrophobicity behavior of epoxy biocomposite coating for air-duct application. Silicon :1-10
Vinothkumar M, Sasikumar M (2021) Silane grafted cellulose and biosilica toughened glass-epoxy composite: mechanical, hydrophobicity and low velocity impact behavior. Silicon :1-13
Iftikhar Maira, Asghar Anam, Ramzan N, Sajjadi B, Chen W-y (2019) Biomass densification: Effect of cow dung on the physicochemical properties of wheat straw and rice husk based biomass pellets. Biomass Bioenergy 122:1–16
Das S, Paul S, Doloi B, Kumar Rahul D (2020) Performance evaluation of Si–Cu-hybrid dust as a powder additive of EDM dielectrics to machine Ti6Al4V with copper electrode. Adv Unconv Mach Compos. Springer, Singapore, pp 239–254
Rajadurai A (2016) Thermo-mechanical characterization of siliconized E-glass fiber/hematite particles reinforced epoxy resin hybrid composite. Appl Surf Sci 384:99–106
Rajadurai A (2017) Inter laminar shear strength behavior of acid, base and silane treated E-glass fibre epoxy resin composites on drilling process. Def Technol 13(1):40–46
Terzioğlu P, Yücel S, Kuş C (2019) Review on a novel biosilica source for production of advanced silica-based materials: Wheat husk. Asia‐Pac J Chem Eng 14(1):e2262
Arun Prakash VR, Rajadurai A (2016) Radio frequency shielding behaviour of silane treated Fe2O3/E-glass fibre reinforced epoxy hybrid composite. Appl Phys A 122:875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0411-2
Marashi H, Jafarlou DM, Sarhan ADA, Hamdi M (2016) State of the art in powder mixed dielectric for EDM applications. Precis Eng 46:11–33
Ishfaq K, Zahoor S, Khan SA, Rehman M, Alfaify A, Anwar S (2021) Minimizing the corner errors (top and bottom) at optimized cutting rate and surface finish during WEDM of Al6061. Eng Sci Technol 24(4):1027–1041
Jing Q, Zhang Y, Kong L, Xu M, Ji F (2021) An investigation into accumulative difference mechanism in time and space for material removal in micro-EDM milling. Micromachines 12(6):711
Dewan PR, Kundu PK, Phipon R (2020) Powder mixed electric discharge machining–A review. In AIP Conference Proceedings, vol 2273, no 1, p 050075. AIP Publishing LLC, Melville
Yuliani S, Hidayat T, Wahyuningsih K (2021) Surface modification of nano-biosilica extracted from rice husk using a silane coupling agent. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, vol 752, no 1, p 012053. IOP Publishing, Bristol
Jeavudeen S, Siddhi Jailani H, Murugan M (2020) Powder additives influence on dielectric strength of EDM fluid and material removal. Int J Mach Mach Mater 22(1):47–61
Bayraktar Ş, Turgut Y (2018) Effects of different cutting methods for electrical steel sheets on performance of induction motors. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 232(7):1287–1294
Sarhan AAD, Maher I, Hamdi M (2021) Development of a new Cost Performance Index (CPI) for selecting the most suitable wire electrode in wire-EDM machining. Arab J Sci Eng :1–14
Kirwin RM, Jahan MP (2021) Effects of non-electrical parameters on profile accuracies and surface characteristics during wire-EDM of titanium alloy. Mach Sci Technol :1–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All have done equal contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Yes this article compliance with ethical standards of journal.
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interests
There is no conflict of interest by any form for this manuscript.
Consent to Participate
Yes. All permission granted.
Consent for Publication
Yes. All permission granted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, K., Karuppasamy, K., Palani, S. et al. Effect of Silane Treated Wheat Husk Biosilica (WHB) Deionized Water Dielectric on EDM Drilling of Ti-6Al-4 V Alloy. Silicon 14, 9143–9151 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01526-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01526-1