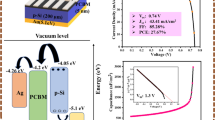
Abstract
The primary concern of the Si-based solar cells heterostructure devices is the dopant-free selectively contacting carriers with p-type Si wafers. The obvious potential of a highly straightforward fabrication technique and the decreased energy consumption is primarily what has attracted such significant attention. In the present investigations, computational simulation via SCAPS-1D has been executed on p-Si/n-CdS/ALD-ZnO heterojunction solar cells and attained the champion conversion efficiency of∼19.97% with the help of some considerably amended device parameters. With the proper optimization of the device, we have obtained better photovoltaic parameters by varying the thickness of the p-Si, n-CdS, and atomic layer deposited ALD-ZnO, noted the effect of series and shunt resistance, effect of temperature and incident radiation on the p-Si/n-CdS/ALD-ZnO device. The final proposed photovoltaic parameters have the %PCE = 19.97%, %FF = 83.37%, Jsc = 37.71 mA/cm2, and Voc = 635.3 mV. Finally, the collected performance metrics are compared to the findings from comparable experimental setups. After reaching these findings in the experimental laboratory and meeting the demand for renewable energy globally, it is assumed that such a device may be a turning point for future photovoltaic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Green MA et al (2020) Solar cell efficiency tables. Prog Photovolt 28:3–15
Shockley W, Queisser HJ (1961) Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J Appl Phys 32(3):510–519
Yoshikawa K et al (2017) Exceeding conversion efficiency of 26% by heterojunction interdigitated back contact solar cell with thin film Si technology. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 173:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.06.024
Singh VK et al (2019) Radial Junction silicon solar cells with micro-pillar array and planar electrode interface for improved photon management and carrier extraction. Curr Appl Phys 19(3):341–346
Zhao Y, Procel P, Smets A, Mazzarella L, Han C, Yang G, Cao L, Yao Z, Weeber A, Zeman M, Isabella O (2022) Effects of (i)a-Si:H deposition temperature on high-efficiency silicon heterojunction solar cells. Prog Photovolt Res Appl. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3620
Akhil S, Akash S, Pasha A, Kulkarni B, Jalalah M, Alsaiari M, Harraz FA, Balakrishn RG (2021) Review on perovskite silicon tandem solar cells: Status and prospects 2T, 3T, and 4T for real-world conditions. Mater Des 211:110138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110138
Islam R, Shine G, Saraswat KC (2014) Schottky barrier height reduction for holes by Fermi level depinning using metal/nickel oxide/silicon contacts. Appl Phys Lett 105:182103
Grilli ML, Aydogan S, Yilmaz M (2016) A study on non-stoichiometric p-NiOx/n-Si heterojunction diode fabricated by RF sputtering: Determination of diode parameters. Superlattices Microstruct 100:924
Bivour M, Temmler J, Steinkemper H, Hermle M (2015) Molybdenum and tungsten oxide: High work function wide band gap contact materials for selective hole contacts of silicon solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 142:34–41
Gerling LG, Mahato S, Morales-Vilches A, Masmitja G, Ortega P, Voz C, Alcubilla R, Puigdollers J (2016) Transition metal oxides as hole-selective contacts in silicon heterojunctions solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 145:109–115
Bullock J, Cuevas A, Allen T, Battaglia C (2014) Molybdenum oxide MoOx: A versatile hole contact for silicon solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 105:232109
Sharma AK, Chourasia NK, Chourasia RK (2022) Optical, temperature, and bulk analysis theoretically in p-Si/n-CdS heterojunction solar cell. Mater Today Proc 67:632–636
Geissbühler J, Werner J, Martin de Nicolas S, Barraud L, Hessler-Wyser A, Despeisse M, Nicolay S, Tomasi A, Niesen B, De Wolf S, Ballif C (2015) 22.5% efficient silicon heterojunction solar cell with molybdenum oxide hole collector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107:081601
Gerling L, Mahato S, Voz C, Alcubilla R, Puigdollers J (2015) Characterization of Transition Metal Oxide/Silicon Heterojunctions for Solar Cell Applications. Appl Sci 5:695
Almora O, Gerling LG, Voz C, Alcubilla R, Puigdollers J, Garcia-Belmonte G (2017) Superior performance of V2O5 as hole-selective contact over other transition metal oxides in silicon heterojunction solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 168:221
Bullock J, Hettick M, Geissbühler J, Ong AJ, Allen T, Sutter-Fella CM, Chen T, Ota H, Schaler EW, De Wolf S, Ballif C, Cuevas A, Javey A (2016) Efficient silicon solar cells with dopant-free asymmetric hetero-contacts. Nat Energy 1:15031
Um HD, Kim N, Lee K, Hwang I, Seo JH, Seo K (2016) Dopant-Free All-Back-Contact Si Nanohole Solar Cells Using MoOx and LiF Films. Nano Lett 16:981–987
Yu J, Fu Y, Zhu L, Yang Z, Yang X, Ding L, Zeng Y, Yan B, Tang J, Gao P, Ye J (2018) Heterojunction solar cells with asymmetrically carrier-selective contact structure of molybdenum-oxide/silicon/magnesium-oxide. Sol Energy 159:704
Wu W, Lin W, Zhong S, Paviet-Salomon B, Despeisse M, Liang Z, Boccard M, Shen H, Ballif C (2018) 22% efficient dopant-free interdigitated back contact silicon solar cells. In The 8th Int. Conf. Crystalline Silicon Photovoltaics (SiliconPV). AIP Publishing, New York 040025–1–040025–6. https://aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5049288. Accessed Feb 2023
José Luis H, Kunta Y, Andrea F, Nicolas M, Nick V, Van Elisabeth A, Dries S, Kevin V, Harold P, Jef P, Daisuke A, Masashi Y, Toshihiko U, Hisashi U, Takashi K, Christophe A, Naoaki N, Toru T, Takahisa F, Gensuke K, Kenji Y (2012) High-Efficiency Silver-Free Heterojunction Silicon Solar Cell. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51:10NA04
Green MA, Hishikawa Y, Dunlop ED, Levi DH, Hohl-Ebinger J, Ho-Baillie AWY (2018) Solar cell efficiency tables (version 52). Prog Photovoltaics 26:427
Fara L, Chilibon I, Craciunescu D, Diaconu A, Fara S (2023) Review: Heterojunction Tandem Solar Cells on Si-Based Metal Oxides. Energies 16(7):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16073033
Belarbi M et al (2022) Efficiency enhancement of triple absorber layer perovskite solar cells with the best materials for electron and hole transport layers: a numerical study. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 37:095016
Untila GG, Kost TN, Chebotareva AB (2016) Bifacial 8 3%/5 4% front/rear efficiency ZnO:Al/n-Si heterojunction solar cell produced by spray pyrolysis. Solar Energy 127:184–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.01.028
Zhang W, Shen H, Yin M, Linfeng Lu, Binbin Xu, Li D (2022) Heterostructure Silicon Solar Cells with Enhanced Power Conversion Efficiency Based on Six/Ni3+ Self-Doped NiOx Passivating Contact. ACS Omega 7(19):16494–16501
Chen L et al (2017) Research on ZnO/Si heterojunction solar cells. J. Semicond. 38:054005
Chirila A, Buecheler S, Pianezzi F, Bloesch P, Gretener C, Uhl AR, Fella C, Kranz L, Perrenoud J, Seyrling S, Verma R, Nishiwaki S, Romanyuk YE, Bilger G, Tiwari AN (2011) Highly efficient Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cells grown on flexible polymer films. Nat Mater 10:857
Wang W, Winkler MT, Gunawan O, Gokmen T, Todorov TK, Zhu Y, Mitzi DB (2014) Device Characteristics of CZTSSe Thin-Film Solar Cells with 12.6% Efficiency. Adv Energy Mater 4:1301465
Suryawanshi MP, Agawane GL, Bhosale SM, Shin SW, Patil PS, Kim JH, Moholkar AV (2013) CZTS based thin film solar cells: a status review. Mater Technol 28:98
Kumar SG, Rao KSRK (2014) Physics and Chemistry of CdTe/CdS thin film heterojunction photovoltaic devices: fundamental and critical aspects. Energy Environ Sci 7:45
Sun H, Sun K, Huang J, Yan C, Liu F, Park J, Pu A, Stride JA, Green MA, Hao X (2018) Efficiency Enhancement of Kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 Solar Cells via Solution-Processed Ultrathin Tin Oxide Intermediate Layer at Absorber/Buffer Interface. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1:154
Cai L, Wang W et al (2019) 12.29% Low temperature-processed dopant-free CdS/p-Si heterojunction solar cells. Adv Mater Interfaces 6(12):1900367
Jha PK, Chourasia NK, Sharma AK, Chourasia RK (2022) Optimization of electrical properties for performance analysis of p-Si/n-CdS/ITO heterojunction photovoltaic cell. Mater Today Proc 67:620–624
Yadav P, Pathak C, Mandalia HC, Pandey K (2012) High-efficiency ZnO: In/SiO2/n-Si heterojunction solar cells. Int J Chem Anal Sci 3(4):1344–1348
Moret M, Chaaya AA, Bechelany M, Miele P, Robin Y, Briot O (2014) Atomic Layer Deposition of zinc oxide for solar cell applications. Superlattices Microstruct 75:477–484
Lee J, Jeon DH, Hwang DK, Yang KJ, Kang JK, Sung SJ, Park H, Kim DH (2011) Atomic Layer Deposition of Ultrathin ZnO Films for Hybrid Window Layers for Cu (Inx, Ga1−x) Se2 Solar Cells. Nanomaterials 11:2779
Avasthi S, Mcclain WE, Man G, Kahn A, Schwartz J, Sturn JC (2013) Hole-blocking titanium-oxide/silicon heterojunction and its application to photovoltaics. Applied Physics Letter 102:203901
Kim AN, Um H-D, Choi I, Kim K-H, Seo K (2016) 18 4% efficient heterojunction Si solar cells using optimized ITO/Top electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8:11412–11417
Bullock J, Hettick M, Geissbühler J, Ong AJ, Allen T et al (2016) Efficient silicon solar cells with dopant-free asymmetric hetero-contacts. Nat Energy 1:15031
Chistiakova G, Macco B, Korte L (2020) Low-temperature atomic layer deposited magnesium oxide as a passivating electron contact for c-Si-based solar cells. IEEE J Photovoltaics 10(2):398–406
Ravindra P, Mukherjee R, Avasthi S (2017) Hole-selective electron-blocking copper oxide contact for silicon solar cells. IEEE J Photovoltaics 7(5):1278–1283
Hancox J, Rochford LA, Clare D et al (2011) Utilizing n-type Vanadium oxide films as hole-extracting layers for small molecular organic photovoltaics. APL 99:013304
Geissbuhler J, Werner J, De Nicolas SM, Barraud L et al (2015) 22.5% efficient silicon heterojunction solar cell with molybdenum oxide hole collector. APL 107:081601
Nayak M, Mandal S, Pandey A, Mudgal S, Singh S, Kumarala VK (2019) Nickel oxide hole-selective hetero-contact for silicon solar cells: role of SiOx interlayer on device performance. Sol RRL 3(11):1900261
Mews M, Lemaire A, Korte L (2017) Sputtered tungsten oxide as hole contact for silicon heterojunction solar cells. J Photovolt 7(5):1209–1215
Kasap SO (2018) Principles of electronic materials and devices, 4th edn, ch 5. McGraw-Hill Education, New York, NY
Sze SM (1981) Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 2nd IOP Science 81-265-1104-4
Green MA (1981) Solar cell fill factors: General graph and empirical expressions. Solid State Electron 24(8):788–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1101(81)90062-9
Jha PK, Chourasia NK, Srivastava A, Sharma AK, Kumar R, Sharma S, Kumar M, Chourasia RK (2023) Study of Eco-Friendly Organic-Inorganic Heterostructure CH3NH3SnI3 Perovskite Solar Cell via SCAPS Simulation. J Electron Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10267-3
Sharma AK, Chourasia NK, Jha PK, Kumar R, Kumar M, Chourasia RK (2023) Characteristic Features and Performance Investigations of a PTB7:PC71BM/PFN:Br Pure Organic Solar Cell Using SCAPS-1D. J Electron Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10202-y
Würfel P, Würfel U (2009) Physics of solar cells from basic principles to advanced concepts, 3rd edn. Wiley-VCHVerlag GmbH & Co KGaA, Weinheim, Germany
Holman ZC, Descoeudres A, de Wolf S, Ballif C (2013) Record Infrared Internal Quantum Efficiency in Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells With Dielectric/Metal Rear Reflectors. IEEE J Photovoltaics 3:1243
Pietruszka R, Witkowski BS, Zielony E, Gwozdz K, Placzek-Popko E, Godlewski M (2017) ZnO/Si heterojunction solar cell fabricated by atomic layer deposition and hydrothermal methods. Sol Energy 155:1282–1288
Shah DK, Akhtar MS, Kim CY, Yang OB (2020) Vertically Arranged Zinc Oxide Nanorods as Antireflection Layer for Crystalline Silicon Solar Cell: A Simulation Study of Photovoltaic Properties. Appl Sci 10:6062
Srivastava S, Singh S, Singh VK (2021) Bulk and interface defects analysis of n-CdS/p-Si heterojunction solar cell. Opt Mater 111:110687
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Marc Burgelman, University of Gent, Belgium, for the SCAPS-1D simulation software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Atish Kumar Sharma: Writing - Original Draft, Software, Validation; Rakesh Kumar: Software, Formal Analysis, Prakash Kumar Jha: Formal Analysis, Manish Kumar: Review & Editing, Formal Analysis; Nitesh K. Chourasia: Writing Original draft, Review & Editing, Formal analysis; Ritesh Kumar Chourasia: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Software, Validation, Supervision, Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft, Formal analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This is the first original research article. This original work has not been published or offered for publication in any other journal. This theoretical, computational, and simulation study does not belong to the extension of any earlier work.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Yes.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A.K., Kumar, R., Jha, P.K. et al. Bulk Parameters Effect and Comparative Performance Analysis of p-Si/n-CdS/ALD-ZnO Solar Cell. Silicon 15, 6497–6508 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02518-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02518-z