Abstract
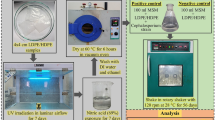
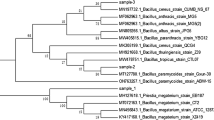
This paper presents the results of an experimental study of the bacterial-mediated biodegradation of linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) by Serratia marcescens subsp. marcescens (S. marcescens marcescens) bacterium without prior exposure of the LLDPE to thermo-oxidative aging. Degradation promoted by supernatant from S. marcescens marcescens was also studied, and compared to that promoted by direct exposure to S. marcescens marcescens cells. The results show that the cell-free extracts degrade LLDPE faster than the S. marcescens marcescens. The mechanisms of degradation are also elucidated via Scanning Electron Microscopy, Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy. These methods show that the S. marcescens marcescens and its supernatant both degrade LLDPE. There was also an increase in the concentrations of the carbonyl groups (new peaks) after the microbial degradation of LLDPE. The degradation process results in the formation and growth of microvoids. The latter are also found to coalesce to form larger defects with increasing exposure to supernatant/cell-free extracts or S. marcescens marcescens.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seymour, R.B.: Polymer science before and after 1899: notable developments during the lifetime of Maurtis Dekker. J. Macromol. Sci., Pure Appl. Chem. 26, 1023–1032 (1899)
Scott, G.: Polymers in Modern Life; Polymers and the Environment. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (1999)
Mueller, R.: Biological degradation of synthetic polyesters—enzymes as potential catalysts for polyester recycling. Proc. Biochem. 41, 2124–2128 (2006)
Sivan, A.: New perspectives in plastic biodegradation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 22, 422–426 (2011)
Shah, A.A., Hasan, F., Hameed, A., Ahmed, S.: Biological degradation of plastics: a comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 26, 246–265 (2008)
Nanda, S., Sahu, S.S.: Biodegradability of polyethylene by Brevibacillus, Pseudomonas, and Rhodococcus spp. N. Y. Sci. J. 3(7), 95–98 (2010)
Nanda, S., Sahu, S.S., Abbraham, J.: Studies on the biodegradation of natural and synthetic polyethylene by Pseudomonas spp. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage. 14(2), 57–60 (2010)
Orhan, Y., Buyukgungor, H.: Enhancement of biodegradability of disposable polyethylene in controlled biological soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 45, 49–55 (2000)
Shimao, M.: Biodegradation of plastics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 242–247 (2001)
Ghosh, S.K., Pal, S., Ray, S.: Study of microbes having potentiality for biodegradation of plastics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. (2013). doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1706-x
Rivard, C., Moens, L., Roberts, K., Brigham, J., Kelley, S.: Starch esters as biodegradable plastics: effects of ester group chain length and degree of substitution on anaerobic biodegradation. Enzym Microb. Technol. 17, 848–852 (1995)
Pospisil, J., Nespurek, S.: Highlights in chemistry and physics of polymer stabilization. Macromol. Symp. 115, 143–163 (1997)
Zheng, Y., Yanful, E.K.: A review of plastic waste biodegradation. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 25, 243–250 (2005)
Sangale, M.K., Shanawaz, M., Ade, A.B.: A review on biodegradation of polythene: the microbial approach. J. Bioremed. Biodeg. 3, 164 (2012)
Singh, B., Sharma, N.: Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93(3), 561–584 (2008)
Bonhomme, S., Cuer, A., Delort, A.M., Lemaire, J., Sancelme, M., Scott, G.: Environmental biodegradation of polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 81, 441–452 (2003)
Piringer, O.G., Baner, A.L.: Plastic Packaging: Interactions with Food and Pharmaceuticals (2ed.). Wiley, ISBN: 9783527314553
Johnson, E., Pometto, A.L., Nikolov, Z.L.: Degradation of degradable starch-polyethylene plastics in a compost environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 1155–1161 (1993)
Mahalakshmi, V., Andrew, S.N.: Assessment of physicochemically treated plastic by fungi. Ann. Biol. Res. 3(9), 4374–4381 (2012)
Kawai, F.: Breakdown of plastics and polymers by microorganisms. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 52, 151–194 (1995)
Augusta, J., Müller, R.J., Widdecke, H.: A rapid evaluation plate-test for the biodegradability of plastics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39, 673–678 (1993)
Witt, U., Müller, R.J., Deckwer, W.D.: Biodegradation behavior and material properties of aliphatic/aromatic polyesters of commercial importance. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 15, 81–89 (1997)
Witt, U., Einig, T., Yamamoto, M., Kleeberg, I., Deckwer, W.D., Müller, R.J.: Biodegradation of aliphatic–aromatic copolyesters: evaluation of the final biodegradability and ecotoxicological impact of degradation intermediates. Chemosphere 44, 289–299 (2001)
Hoffmann, J., Reznícková, I., Kozáková, J., Ružicka, J., Alexy, P., Bakoš, D., Precnerová, L.: Assessing biodegradability of plastic based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and protein wastes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 79, 511–519 (2003)
Hadad, D., Geresh, S., Sivan, A.: Biodegradation of polyethylene by thermophilic bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98, 1093–1100 (2005)
Mahalakshmi, V., Siddiq, A., Andrew, S.N.: Analysis of polyethylene degrading potentials of microorganisms isolated from compost soil. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 3(5), 1190–1196 (2012)
Albertsson, A.C.: The shape of the biodegradation curve for low and high density polyethylenes in prolonged series of experiments. J. Eur. Polym. 16, 623–630 (1980)
Yamada-Onodera, K., Mukumoto, H., Katsuyaya, Y., Saiganji, A., Tani, Y.: Degradation of polyethylene by a fungus. Penicillium simplicissimum YK. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 72, 323–327 (2001)
Aamer, A.S., Hasan, F., Hameed, A., Javed, I.A.: Isolation of Fusarium sp. AF4 from sewage sludge, with the ability to adhere the surface of 45 polyethylene, African. J. Microbiol. Res. 3(10), 658–663 (2009)
Gu, J.D., Ford, T.E., Mitton, D. B., Mitchell, R.: Microbial degradation and deterioration of polymeric materials. In: Review (ed) The Uhlig Corrosion Handbook (2nd Ed.), pp. 439–460. Wiley, New York (2000)
Gu, J.D.: Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials. Recent Res. Adv. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 52, 69–91 (2003)
Restrepo-Flórez, J.-M., Bassi, A., Thompson, M.R.: Microbial degradation and deterioration of polyethylene—a review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 88, 83–90 (2014)
Bikiaris, D., Aburto, J., Alric, I., Borredon, E., Botev, M., Betchev, C.: Mechanical properties and biodegradability of LLDPE blends with fatty-acid esters of amylase and starch. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 71, 1089–1100 (1999)
Tribedi, P., Sil, A.K.: Low-density polyethylene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 biofilm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20(6), 4146–4153 (2013)
Olsen, R.A., Bakken, L.R.: Viability of soil bacteria: optimization of plate-counting technique and comparison between total counts and plate counts within different size groups. Microb. Ecol. 13, 59–74 (1987)
Kleinheinz, G.T., Bagley, S.T.: A filter-plate method for the recovery and cultivation of microorganisms utilizing volatile organic compounds. J. Microbiol. Methods 29, 139–144 (1997)
Touno, K., Harada, K., Yoshimatsu, K., Yazaki, K., Shimomura, S.: Derivative formation on the stem of cultured shoots in Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Plant Cell Rep. 19(11), 1121–1126 (2000)
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15(3), 473–497 (1962)
Wundelick, B., Cormier, C.M.: Heat of fusion of polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 5, 987–988 (1967)
Mirabella, F.M., Bafna, A.: Determination of the crystallinity of polyethylene/α-olefin copolymers by thermal analysis: Relationship of the heat of fusion of 100% polyethylene crystal and the density. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 40(15), 1637–1643 (2002)
Williams, R.F., Gott, C.L., Qadri, S.M.H., Scott, R.H.: Influence of temperature of incubation and type of growth medium on pigmentation in Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 106, 438–443 (1971)
Rjazantseva, I.N., Andreeva, I.N., Ogorodnikova, T.I.: Effect of various growth conditions on pigmentation of Serratia marcescens. Microbios 79(320), 155–161 (1984)
Hejazi, A., Falkiner, F.R.: Serratia marcescens. J. Med. Microbiol. 46, 903–912 (1997)
Venil, C.K., Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P.: An insightful overview on microbial pigment, prodigiosin. Electron. J. Biol. 5, 49–61 (2009)
Sudhakar, M., Doble, M., Murthy, P.S., Venkatesan, R.: Marine microb-mediated biodegradation of low- and high-density polyethylenes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 61, 203–213 (2008)
Raghavan, D., Torma, A.E.: DSC and FTIR characterization of biodegradation of polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 32, 438–442 (1992)
Albertsson, A.-C., Barensted, C., Karlsson, S., Lindberg, T.: Degradation product pattern and morphology changes as means to differentiate abiotically and biotically aged degradable polyethylene. Polymer 36, 3075–3083 (1995)
Manzur, A., Cuamatzi, F., Favela, E.: Effect of the growth of Phanerochaete Chrysosporium in a blend of low density polyethylene and sugar cane bagasse. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 66, 105–111 (1997)
Volke-Sepulveda, T., Saucedo-Castañeda, G., Gutierrez-Rojas, M., Manzur, A., Favela-Torres, E.: Thermally treated low density polyethylene biodegradation by Penicillium pinophilum and Aspergillus niger. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 83, 305–314 (2002)
Santo, M., Weitsman, R., Sivan, A.: The role of the copper-binding enzyme–laccase—in the biodegradation of polyethylene by the actinomycete Rhodococcus ruber. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 208, 1–7 (2012)
Khabbaz, F., Albertsson, A.C., Karlsson, S.: Chemical and morphological changes of environmentally degradable poly(ethylene) films exposed to thermo-oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 63, 127–138 (1999)
Balasubramanian, V., Natarajan, K., Hemambika, B., Ramesh, N., Sumathi, C., Kottaimuthu, R., Rajesh Kannan, V.: High-density polyethylene (HDPE)- degrading potential bacteria from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 51, 205–211 (2010)
Nowak, B., Pająk, J., Drozd-Bratkowicz, M., Rymarz, G.: Microorganisms participating in the biodegradation of modified polyethylene films in different soils under laboratory conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 65, 757–767 (2011)
Gilan, I., Hadar, Y., Sivan, A.: Colonization, biofilm formation and biodegradation of polyethylene by a strain of Rhodococcus ruber. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 65, 97–104 (2004)
Manzur, A., Limón-González, M., Favela-Torres, E.: Biodegradation of physicochemically treated LLDPE by a consortium of filamentous fungi. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 92, 265–271 (2004)
Chiellini, E., Corti, A., D’Antone, S.: Oxo-biodegradable full carbon backbone polymers–biodegradation behaviour of thermally oxidized polyethylene in an aqueous medium. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 92, 1378–1383 (2007)
Albertsson, A.-C., Andersson, S.O., Karlsson, S.: The mechanism of biodegradation of polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 18, 73–87 (1987)
Harshvardhan, K., Jha, B.: Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by marine bacteria from pelagic waters, Arabian Sea, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 77(1), 100–106 (2013)
Devi, R.S., Kannan, V.R., Nivas, D., Kannan, K., Chandru, S., Antony, A.R.: Biodegradation of HDPE by Aspergillus spp. from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 96(1–2), 32–40 (2015)
Artham, T., Sudhakar, M., Venkatesan, R., Madhavan Nair, C., Murty, K., Doble, M.: Biofouling and stability of synthetic polymers in sea water. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 63, 884–890 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the STEP B program of the World Bank, the World Bank African Centers of Excellence Program, the African Capacity Building Foundation, the Sheda Science and Technology Complex (SHESTCO), Princeton University and the Nelson Mandela Institution and the African University of Science and Technology. The authors are grateful to these sponsors for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azeko, S.T., Etuk-Udo, G.A., Odusanya, O.S. et al. Biodegradation of Linear Low Density Polyethylene by Serratia marcescens subsp. marcescens and its Cell Free Extracts. Waste Biomass Valor 6, 1047–1057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9421-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9421-0