Abstract
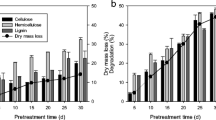
In this study, we used dry corn stover (DCS) silage as feedstock to produce ethanol using hot-washing treatment (HWT) followed by prehydrolysis and fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (FD-SSF) using cellulase and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The inoculants product for ensiling of DCS was composed of lactic acid-producing organisms, such as Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus fermentum and Enterococcus durans. Moreover, the appropriate condition was selected by the dynamic analysis of silage quality. Among test conditions, the pH value (4.22), pretreatment time (4 week) and the content of lactic acid in DCS silage (4.32%) could be considered as important indicators of the success of microbial ensiling. The 16S rRNA gene-based pyrosequencing was used to analyze the community of the resulting silage, and the results indicated that Lactobacillus was the advantageous species. The observed glass transition temperature (Tg) value for DCS silage occurred at a temperature of 124.2 °C (Tmid). DCS silage was hydrothermally treated at temperature of Tg for 20 min. It was proved that biomass can be pretreated for cellulosic ethanol production by the integrated process of microbial ensiling and HWT. Ethanol fermentation of HWT-treated (at 30% glucan loading) DCS silage hydrolyzate (resulting in 61.92 g/L ethanol at 59.15% metabolic yield of FD-SSF) was reported in this work.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chundawat, S.P., Beckham, G.T., Himmel, M.E.: Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass to fuels and chemicals. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. 2(1), 21–45 (2011)
Sun, S., Wen, J., Ma, M., Sun, R.: Enhanced enzymatic digestibility of bamboo by a combined system of multiple steam explosion and alkaline treatments. Appl. Energy. 136, 519–526 (2014)
Ruiz, E., Cara, C., Manzanares, P., Ballesteros, M., Castro, E.: Evaluation of steam explosion pre-treatment for enzymatic hydrolysis of sunflower stalks. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 42, 160–166 (2008)
Chen, W., Tu, Y., Sheen, H.K.: Disruption of sugarcane bagasse lignocellulosic structure by means of dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment with microwaveassisted heating. Appl. Energy 88, 2726–2734 (2011)
Lima C.S.S., Conceição, M.M., Silva FLH, Lima, E.E., Conrado, L.S., Leão, D.A.: Characterization of acid hydrolysis of sisal. Appl. Energy 102, 254–259 (2013)
Mood, S.H., Golfeshan, A.H., Tabatabaei, M., Jouzani, G.S., Najafi, G.H., Gholami, M.: Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 27, 77–93 (2013)
Alvira, P., Tomás-Pejó, E., Ballesteros, M., Negro, M.J.: Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 4851–4861 (2010)
Zhang, X., Yu, H., Huang, H., Liu, Y.: Evaluation of biological pretreatment with white rot fungi for the enzymatic hydrolysis of bamboo culms. Int. Biodeterior Biodegrad. 60, 159–164 (2007)
Wan, C.X., Li, Y.B.: Microbial delignification of corn stover by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora for improving cellulose digestibility. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 47, 31–36 (2010)
Shinners, K.J., Wepner, A.D., Muck, R.E., Weimer, P.J.: Aerobic and anaerobic storage of single-pass, chopped corn stover. Bioenergy Res. 4(1), 61–75 (2011)
Shinners, K.J., Binversie, B.N., Muck, R.E., Weimer, P.J.: Comparison of wet and dry corn stover harvest and storage. Biomass Bioenerg. 31(4), 211–221 (2007)
Holzer, M., Mayrhuber, E., Danner, H., Braun, R.: The role of Lactobacillus buchneri in forage preservation. Trends Biotechnol. 21, 282–289 (2003)
Keller, F.A., Hamilton, J.E., Nguyen, Q.A.: Microbial pretreatment of biomass potential for reducing severity of thermochemical biomass pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 105–108, 27–41 (2003)
Wan, C. X., Li, Y. B.: Microbial pretreatment of corn stover with Ceriporiopsis subvermispora for enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 6398–6403 (2010)
Fenlon, D.R., Henderson, A.R., Rooke, J.A.: The fermentative preservation of grassed and forage crops. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 79, 118–131 (1995)
Graves, T., Narendranath, N.V., Dawson, K., Power, R.: Effect of pH and lactic or acetic acid on ethanol productivity by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in corn mash. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33(6), 469–474 (2006)
Chen, Y., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Chen, C.: Ensiling agricultural residues for bioethanol production. Appl Biochem. Biotech. 143, 80–92 (2007)
Sun, S., Cao, X., Sun, S., Xu, F., Song, X., Sun, R., Jones, G.L.: Improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of thermo-mechanical fiber from Eucalyptus urophylla by a combination of hydrothermal pretreatment and alkali fractionation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 7, 116–128 (2014)
Ko, J.K., Kim, Y., Ximenes, E., Ladisch, M.R.: Effect of liquid hot water pretreatment severity on properties of hardwood lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112, 252–262 (2015)
Yang, X., Li, H.L., Ma, X.J., Cheng, J.Y., Fang, S.Q.: Effects of hot-washing process on structure and enzymatic hydrolysis of treated steam explosion corn stover. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 3, 39–47 (2016)
Sluiter A., Hames B., Ruiz R., Scarlata C., Sluiter J., Templeton D., Crocker D.: Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. NREL Technical Report. REL/TP-510-42618 (Version 07.08.2011). National Renewable Energy Laboratory; 1 Boulder, Colorado (2011)
Megías, M.D., Hernández, F., Cano, J., Martinez-Teruel, A., Gallego, J.A.: Effects of different additives on the cell wall and mineral fractions of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and orange (Citrus aurantium L.) by-product silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 76, 173–181 (1998)
Ambye-Jensen, M., Thomsen, S.T., Kádár, Z., Meyer, A.S.: Ensiling of wheat straw decreases the required temperature in hydrothermal pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 6, 116–125 (2013)
Holzer, M., Mayrhuber, E., Danner, H., Braun, R.: The role of Lactobacillus buchneri in forage preservation. Trends Biotechnol. 21(6), 282–287 (2003)
Danner, H., Holzer, M., Mayrhuber, E., Braun, R.: Acetic acid increases stability of silage under aerobic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microb. 69(1), 562–567 (2003)
Penttilä, P.A., Várnai, A., Pere, J., Tammelin, T., Salmén, L., Siika-aho, M., et al.: Xylan as limiting factor in enzymatic hydrolysis of nanocellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 129, 135–141 (2013)
Marcinakova, M., Laukova, A., Simonova, M., Strompfova, V., Korenekova, B., Nad, P.: A new probiotic and bacteriocin-producing strain of Enterococcus faecium EF9296 and its use in grass ensiling. Czech. J. Anim. Sci. 53(8), 336–345 (2008)
Ennahar, S., Cai, Y.M., Fujita, Y.: Phylogenetic diversity of lactic acid bacteria associated with paddy rice silage as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA analysis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 69(1), 444–451 (2003)
Cai, Y., Ohmomo, S., Ogawa, M., Kumai, S.: Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 82, 520–526 (1999)
Sebastian, S., Phillip, L.E., Fellner, V., Idziak, E.S.: Comparative assessment of bacterial inoculated corn and sorghum silages. J. Anim. Sci. 71, 505–514 (1996)
Amarasekara A.S.: Handbook of Cellulosic Ethanol [M]. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2013).
Pedersen, M., Meyer, A.S.: Lignocellulose pretreatment severity: relating pH to biomatrix opening. New Biotechnol. 27(6), 739–750 (2010)
Samuel, R., Pu, Y., Raman, B., Ragauskas, A. J.: Structural characterization and comparison of switchgrassbass-milled lignin before and after dilute acid pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 162, 62–74 (2010)
Ruel, K., Barnoud, F., Eriksson, K.E.: Ultrastructural aspects of wood degradation by Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Holzforschung 38, 61–68 (1982)
Pahlow G., Muck R.E., Driehuis F., Elferink S.J.W.H.O., Spoelstra S.F.: Microbiology of ensiling. In: Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H. Silage Science and Technology, pp. 31–94. American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, Wisconsin (2003)
Palonen, H., Tjerneld, F., Zacchi, G., Tenkanen, M.: Adsorption of Trichoderma reesei CBH I and EG II and their catalytic domains on steam pretreated softwood and isolated lignin. J. Biotechnol. 107, 65–72 (2004)
Uppugundla, N., da Costa, S. L., Chundawat S.P.S., et al.: A comparative study of ethanol production using dilute acid, ionic liquid and AFEXTM pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 7, 22 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Li, H., Chang, C. et al. The Integrated Process of Microbial Ensiling and Hot-Washing Pretreatment of Dry Corn Stover for Ethanol Production. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 2031–2040 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0007-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0007-x