Abstract
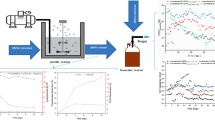
Anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater (OMW) and sewage sludge (SS) is a promising technique in terms of biogas production and quality. An OMW mixture was subjected to pre-treatment (thermal drying), which can reduce the total COD by 72.8% of 10% OMW mixture. OMW mixtures at concentrations of 2, 5, and 10% were tested. OMW addition can improve biogas production if the mixture exceeds 5% (v/v) concentration in the feed. The digestion of SS produced 31 Nm3/Kgvs and with an addition of OMW increased biogas production in the range of 0.337–0.42 Nm3/Kgvs (2–10% v/v in the feed), where the best addition was 10% with 0.42 Nm3/Kgvs of biogas. VS removal was estimated, it was over 55.2% of 10% OMW about 2.2 times of digestion of SS. Also, COD removal efficiency exceeded 72.2% of 10% OMW which is 1.2 times of 100% SS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishna, D.M., Viraraghavan, T.: Strategies for sludge minimization in activated sludge process-a review. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 14(1), 2–12 (2005)
Brisolara, K.F., Qi, Y.: Biosolids and sludge management. Water Environ. Res. 83(10), 1351–1375 (2011)
Bolzonella, D., Battistoni, P., Susini, C., Cecchi, F.: Anaerobic codigestion of waste activated sludge and OFMSW: the experiences of Viareggio and Treviso plants (Italy). Water Sci. Technol. 53, 203–211 (2006)
Cabbai, V., Ballico, M., Aneggi, E., Goi, D.: BMP tests of source selected OFMSW to evaluate anaerobic codigestion with sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 33, 1626–1632 (2013)
Alrawashdeh, K.A., Pugliese, A., Slopiecka, K., Pistolesi, V., Massoli, S., Bartocci, P., Bidini, G., Fantozzi, F.: Codigestion of untreated and treated sewage sludge with the organic fraction of municipal solid wastes. Fermentation. 3(3), 35 (2017)
Fountoulakis, M., Petousi, I., Manios, T.: Co-digestion of sewage sludge with glycerol to boost biogas production. Waste Manage. 30, 1849–1853 (2010)
Cavinato, C., Bolzonella, D., Pava, P., Fatone, F., Cecchi, F.: Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of waste active sludge and source sorted biowaste in pilot and full scale reactors. Renew. Energy. 55, 260–265 (2013)
Nielfa, A., Cano, R., Fdz-Polanco, M.: Theoretical methane production generated by the co-digestion of organic fraction municipal solid waste and biological sludge. Biotechnol. Rep. 5, 14–21 (2015)
Lo, K., Liao, P.: Anaerobic–aerobic biological treatment of a mixture of cheese whey and dairy manure. Biol. Wastes. 28(2), 91–101 (1989)
Goncalves, M.R., Freitas, P., Marques, I.P.: Bioenergy recovery from olive milleffluent in a hybrid reactor. Biomass Bioenergy. 39, 253–260 (2012)
González-González, A., Cuadros, F.: Effect of aerobic pretreatment on anaerobicdigestion of olive mill wastewater (OMWW): an ecoefficient treatment. Food Bioprod. Process. 95, 339–345 (2015)
Inan, H., Dimoglo, A., ims¸, H.S., ek, M.: Karpuzcu, olive oil mill wastewatertreatment by means of electro-coagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 36, 23–31 (2004)
Sabbah, I., Marsook, T., Basheer, S.: The effect of pretreatment on anaerobicactivity of olive mill wastewater using batch and continuous systems. Process Biochem. 39, 1947–1951 (2004)
Rincón, B., Bujalance, L., Fermoso, F.G., Martín, A., Borja, R.: Biochemicalmethane potential of two-phase olive mill solid waste: influence of thermalpretreatment on the process kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 140, 249–255 (2013)
Maragkaki, A.E., Vasileiadis, I., Fountoulakis, M., Kyriakou, A., Lasaridi, K., Manios, T.: Improving biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge with a thermal dried mixture of food waste, cheese whey and olive mill wastewater. Waste Manage 71, 644–651 (2017)
Zupancica, D.G., Uranjek-Zevartb, N., Roša, M.: Full-scale anaerobic co-digestion of organic waste and municipal sludge. Biomass Bioenergy. 32, 162–167 (2008)
El-Gohary, F., Tawfik, A., Badawy, M., El-Khateeb, M.A.: Potentials of anaerobic treatment for catalytically oxidized olive mill wastewater (OMW). Bioresour. Technol. 100, 2147–2154 (2009)
Camarillo, R., Rincón, J.: Effect of inhibitory compounds on the two-phase anaerobic digestion performance of diluted wastewaters from the alimentary industry. Chem. Eng. J. 193–194, 68–76 (2012)
Oz, N.A., Uzun, A.C.: Ultrasound pretreatment for enhanced biogas production from olive mill wastewater. Ultrason. Sonochem. 22, 565–572 (2015)
Dareioti, M., Dokianakis, S., Stamatelatou, K., Zafiri, C., Kornaros, M.: Expoitation of olive mill wastewater and liquid cow manure for biogas production. Waste Manag. 30, 1841–1848 (2009)
Raposo, F., Borja, R., Sánchez, E., Martín, M.A., Martín, A.: Performance and kinetic evaluation of the anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive milleffluents in reactors with suspended and immobilized biomass. Water Res. 38, 2017–2026 (2004)
El-Mashad, H.M., McGarvey, J.A., Zhang, R.: Performance and microbial analysis of anaerobic digesters treating food waste and dairy manure. Biol. Eng. 1, 233–242 (2008)
Azaizeh, H.: Co-digestion of olive mill wastewater and swine manure usingup-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor for biogas production. J. Water Resour. Prot. 02, 314–321 (2010)
Rizzo, L., Lofrano, G., Grassi, M., Belgiorno, V.: Pre-treatment of olive millwastewater by chitosan coagulation and advanced oxidation processes. Sep.Purif. Technol. 63, 648–653 (2008)
Dareioti, M., Dokianakis, S.N., Stamatelatou, K., Zafiri, C., Kornaros, M.: Exploitation of olive mill wastewater and liquid cow manure for biogas production. Waste Manag. 30, 1841–1848 (2010)
Liu, C., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, C.: Improve biogas production from low-organiccontent sludge through high-solids anaerobic co-digestion with food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 219, 252–260 (2016)
Xie, S., Wickham, R., Nghiem, L.: Synergistic effect from anaerobic codigestion of sewage sludge and organic wastes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 116, 191–197 (2017)
Karadag, D., Mäkinen, A.E., Efimova, E., Puhakka, J.: Thermophilic biohydrogenproduction by an anaerobic heat treated-hot spring culture. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 5790–5795 (2009)
Madsen, M., Holm-Nielsen, J.B., Esbensen, K.H.: Monitoring of anaerobicdigestion processes: a review perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 3141–3155 (2011)
Iacovidou, E., Ohandja, D.G., Voulvoulis, N.: Food waste co-digestion with sewage sludge–realising its potential in UK. Environ. Manage. 112, 267–274 (2012)
Angelidaki, I., Ahring, B.K.: Co-digestion of olive oil mill wastewaters with manure, household waste or sewage sludge. Biodegradation. 8(4), 221–226 (1997)
Gelegenis, J., Georgakakis, D., Angelidaki, I., Christopoulou, N., Goumenaki, M.: Optimization of biogas production from olive oil mill wastewater, by codigestingwith diluted poultry manure. Appl. Energy. 84(6), 646–663 (2007)
Metcalf, E., Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F.L., Stensel, H.D.: Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse. Metcalf & Eddy, Inc., Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi (2003)
Chu, C.F., Li, Y.Y., Xu, K.Q., Ebie, Y., Inamori, Y., Kong, H.N.: A pH- and temperature-phased two-stage process for hydrogen and methane production from food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 33, 4739–4746 (2008)
Cecchi, F., Fraverro, P.G., Perin, G., Vallini, G.: Comparison of co-digestion performance of two differently collected organic fractions of municipal solid wastes with sewage sludges. Environ. Technol. Lett. 9, 391–400 (1998)
Martinez-Garcia, G., Johnson, A.C., Bachmann, R.T., Williams, C.J., Burgoyne, A., Edyvean, R.G.J.: Two-stage biological treatment of olive mill wastewater with whey as co-substrate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 59(4), 273–282 (2007)
El Hajjouji, H., Ait Baddi, G., Yaacoubi, A., Hamdi, H., Winterton, P., Revel, J.C., Hafidi, M.: Optimisation of biodegradationconditions for the treatment of olive mill wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 99(13), 5505–5510 (2008)
Ma, J., Van Wambeke, M., Carballa, M., Verstraete, W.: Improvement of the anaerobic treatment of potato processing wastewater in a UASB reactor by codigestion with glycerol. Biotech. Lett. 30, 861–867 (2008)
Hamawand, I.: Anaerobic digestion process and bio-energy in meat industry:a review and a potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 44, 37–51 (2015)
Karadag, D., Koroglu, O.E., Ozkaya, B., Cakmakci, M.: A review on anaerobic biofilm reactors for the treatment of dairy industry wastewater. Process Biochem. 50, 262–271 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Statement of Novelty: This paper introduces a new technique to enhance the production of biogas and increase the efficiency of COD removal. This technique is to digest sewage sludge and dried olive mill waste in different concentration, BMP tests were used to investigate and improve the effect of these co-substrate on the co-digestion process and on the performance of anaerobic digestion in mesophilic conditions. Where the olive mill waste was dried thermally through solar energy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al bkoor Alrawashdeh, K. Improving Anaerobic Co-digestion of Sewage Sludge with Thermal Dried Olive Mill Wastewater. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 2213–2219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0234-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0234-9