Abstract
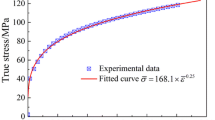
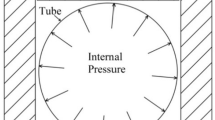
In this paper, cold bulge forming process of a tube made of aluminum alloy 6061 is performed experimentally using a solid medium polyurethane. The results of the bulged tube show that the bulge forming process can successfully form the 6061 aluminum tube without necking due to uniform compression of polyurethane medium. The results of thickness measurements prove that the thickness reduction in the formed tube after bulge forming process is less than 12%. In addition, numerical simulation of bulge forming process of Al-6061 tube is performed using ABAQUS finite element software. After validating numerical results with experimental measurements, the effects of geometrical and process parameters such as initial tube thickness, radius of die curvature, tube/die friction coefficient and bulge forming speed on thickness variations in the bulged tube are investigated for aluminum tubes made of Al-5052, Al-5083, Al-7072 and Al–Mg. Moreover, several numerical models are analyzed in order to study the residual stress and spring back of the bulged aluminum tubes. It is concluded that the residual stresses in the bulged tube after unloading step are approximately two times lower than the stresses at the end of loading step. It will be shown that by decreasing the bulge forming speed, friction coefficient between die and tube and initial thickness of the tube, better correlation can be seen between experimental and numerical results. The results show with an increase in the radius of die curvature, thickness of bulged tube at the end part converges to a constant value for all types of aluminum alloys.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang Y M, Lina Y K, and Altan T, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47 (2007) 343.
Yang B, Zhang W G, and Li S H, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29 (2006) 453.
Ramezani M, and Ripin Z M, J Mater Process Technol 210 (2010) 1061.
Lianfa Y, and Cheng G, Thin-Walled Struct 46 (2008) 147.
Velasco R, and Boudeau N, J Mater Process Technol 205 (2008) 51.
Mac Donald B J, and Hashmi M S J, Finite Elem Anal Des 37 (2001) 107.
Mac Donald B J, and Hashmi M S J, J Mater Process Technol 103 (2000) 333.
Mac Donald B J, and Hashmi M S J, Finite Elem Anal Des 39 (2002) 137.
Zhang Q, Lang L, Wang Y, and Sun Z, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87 (2016) 2861.
Imaninejad M, Subhash G, and Loukus A, J Mater Process Technol 147 (2004) 247.
Boudeau N, and Malecot P, Int J Mech Sci 65 (2012) 1.
Hwang Y M, and Wang C W, J Mater Process Technol 209 (2009) 4423.
Safari M, Salimi J, and Hamidipoor S, J Mech Eng Technol 9 (2017) 59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabatabaei, S.M., Dehkordi, R.K. & Safari, M. Cold Bulge Forming of Aluminum Tubes: Effects of Geometrical and Process Parameters on Formability and Thickness Variation in Bulged Tubes. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 2649–2661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01733-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01733-w