Abstract
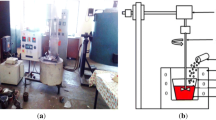
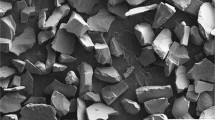
Stir casting process is a prominent technique for the fabrication of aluminium matrix composites (AlMMCs). Regular feeding, two-step feeding, capsulate feeding, pre-melt feeding and double-layer feeding are different feeding methods used in stir casting technique. In this study, Al7075-MMCs reinforced with nano-sized Al2O3 are manufactured through five different feeding methods. The bonding between the matrix and ceramic interface, agglomeration of the particles and porosity are evaluated through scanning electron microscope. From the micro-structural characterization results, it is observed that double-layer feeding method ensures the better particle distribution and improved bonding between the Al7075 and Al2O3. Alumina particles of 50 nm size, 2.5 wt% are incorporated to the Al7075 matrix. The intensive porosity and high agglomeration are noticed in other methods. It is understood from the results that double-layer feeding technique is a promising route for producing the defect-free Al7075-MMCs. The density, micro-hardness, and tensile strength of the resultant composites are measured according to ASTM standards. Due to homogenous particle distribution, the ultimate tensile strength is increased from 280 to 387 MPa, which is 38% higher than Al7075. The yield strength of the composite is increased from 140 to 198 MPa. The micro-hardness is increased from 661 to 878 MPa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbero E J, Introduction to Composite Materials Design. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2017).
Noton B R, ed. Engineering Applications of Composites: Composite Materials. Vol. 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2016).
Dursun T, and Soutis C, Mater Des (1980–2015) 56 (2014) 862.
Beffort O, Long S, Cayron C, Kuebler J, and Buffat P A, Compos Sci Technol67 (2007) 737.
Suresh S, Moorthi N S V, Vettivel S C, and Selvakumar N. Mater Des59 (2014) 383.
Rohatgi P K, Weiss D, and Gupta N, JOM58 (2006) 71.
Yang B, Wang F, and Zhang J S, Actamaterialia51 (2003) 4977.
Peat T, Galloway A, Toumpis A, Steel R, Zhu W, and Iqbal N, Mater Des120 (2017) 22.
Rangaraj L, Sagar R V, Stalin M, Raghavendra K, and Venkateswarlu K, Synth Metall Mater Trans A50 (2019) 3714.
Sajjadi S, Ezatpour H R, and TorabiParizi M, Mater Des34 (2012) 106.
Hashim J, Looney L, and Hashmi M S J, J Mater Process Technol92 (1999) 1.
Arunachalam R, Al-Maharbi M, Al Kiyumi Y, Aal-Thani E, and Al Mafraji M, Appl Mech Mater 772 (2015) 263.
Sahu M K, and Sahu R K, Advanced Casting Technologies, IntechOpen (2018).
Manivannan A., and Sasikumar R, Mater Today Proc 5 (2018) 8618.
Umanath K, Selvamani S T, Palanikumar K, and Niranjanavarma D, Proc Eng 97 (2014) 703.
Ceschini L, Dahle A, Gupta M, Wollmar Jarfors A E, Jayalakshmi S, Morri A, Rotundo F, Toschi S, and Arvind Singh R, Aluminum and Magnesium Metal Matrix Nanocomposites, Springer, Singapore (2017), pp 41-93.
Hashim J, Looney L, and Hashmi M S J, J Mater Process Technol123 (2002) 251.
Hashim J, Looney L, and Hashmi M S J, J Mater Process Technol123 (2002) 258.
Gopalakrishnan S, and Murugan N, Compos Part B Eng43 (2012) 302.
Moses J J, Dinaharan I, and Joseph Sekhar S, Proc Mater Sci5 (2014) 106.
Ezatpour H R, Sajjadi S A, Haddad Sabzevar M, and Huang Y, Mater Des55 (2014) 921.
Prabu S B, Karunamoorthy L, Kathiresan S, and Mohan B, J Mater Process Technol171 (2006) 268.
Ravi K R, Sreekumar V M, Pillai R M, Mahato C, Amaranathan K R, and Pai B C, Mater Des28 (2007) 871.
Surappa M K, Sadhana28 (2003) 319.
Kala H, Mer K K S, and Kumar S, Proc Mater Sci6 (2014) 1951.
Kandpal B C, Kumar J, and Singh H, Mater Today Proc5 (2018) 5.
Hashim J, Looney L, and Hashmi M S J, J Mater Process Technol119 (2001) 329.
Viswanath A, Dieringa H, Ajith Kumar K K, Pillai U T S, and Pai B C, J Magn Alloys3 (2015) 16.
Wang Y, Wang H-Y, Xiu K, Wang H-Y, and Jiang Q-C, Mater Lett60 (2006) 1533.
Bandhu D, Thakur A, Purohit R, Verma R K, and Abhishek K, J Mech Sci Technol 32 (2018) 3123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, S., Sasikumar, R., Natarajan, E. et al. Influence of Feeding Techniques in Bottom Tapping Stir Casting Process for Fabrication of Alumina Nano-filler-reinforced Aluminium Composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 1265–1272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01975-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01975-z