Abstract
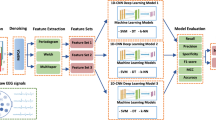
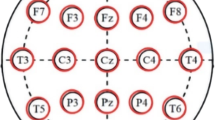
Schizophrenia (SZ) is a severe disorder of the human brain which disturbs behavioral characteristics such as interruption in thinking, memory, perception, speech and other living activities. If the patient suffering from SZ is not diagnosed and treated in the early stages, damage to human behavioral abilities in its later stages could become more severe. Therefore, early discovery of SZ may help to cure or limit the effects. Electroencephalogram (EEG) is prominently used to study brain diseases such as SZ due to having high temporal resolution information, and being a noninvasive and inexpensive method. This paper introduces an automatic methodology based on transfer learning with deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the diagnosis of SZ patients from healthy controls. First, EEG signals are converted into images by applying a time–frequency approach called continuous wavelet transform (CWT) method. Then, the images of EEG signals are applied to the four popular pre-trained CNNs: AlexNet, ResNet-18, VGG-19 and Inception-v3. The output of convolutional and pooling layers of these models are used as deep features and are fed into the support vector machine (SVM) classifier. We have tuned the parameters of SVM to classify SZ patients and healthy subjects. The efficiency of the proposed method is evaluated on EEG signals from 14 healthy subjects and 14 SZ patients. The experiments showed that the combination of frontal, central, parietal, and occipital regions applied to the ResNet-18-SVM achieved best results with accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of 98.60% ± 2.29, 99.65% ± 2.35 and 96.92% ± 2.25, respectively. Therefore, the proposed method as a diagnostic tool can help clinicians in detection of the SZ patients for early diagnosis and treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savio A, Charpentier J, Termenón M, Shinn AK, Grana M (2010) Neural classifiers for schizophrenia diagnostic support on diffusion imaging data. Neural Netw World 20(7):935
Chatterjee I, Agarwal M, Rana B, Lakhyani N, Kumar N (2018) Bi-objective approach for computer-aided diagnosis of schizophrenia patients using fMRI data. Multimed Tools Appl 77(20):26991–27015
Bowie CR, Harvey PD (2006) Cognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2(4):531–536
Joyce EM, Roiser JP (2007) Cognitive heterogeneity in schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry 20(3):268–272
Tibbetts PE (2013) Principles of cognitive neuroscience. Q Rev Biol 88:139–140
WHO: https://www.who.int/mental_health/management/schizophrenia/en/.
Afshani F, Shalbaf A, Shalbaf R, Sleigh J (2019) Frontal–temporal functional connectivity of EEG signal by standardized permutation mutual information during anesthesia. Cogn Neurodyn 13(6):531–540
Shalbaf A, Saffar M, Sleigh JW, Shalbaf R (2017) Monitoring the depth of anesthesia using a new adaptive neurofuzzy system. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22(3):671–677
Saeedi A, Saeedi M, Maghsoudi A, Shalbaf A (2020) Major depressive disorder diagnosis based on effective connectivity in EEG signals: a convolutional neural network and long short-term memory approach. Cogn Neurodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09619-0
López JD, Litvak V, Espinosa JJ, Friston K, Barnes GR (2014) Algorithmic procedures for Bayesian MEG/EEG source reconstruction in SPM. NeuroImage 84:476–487
Friston KJ, Frith CD (1995) Schizophrenia: a disconnection syndrome. Clin Neurosci 3(2):89–97
Jatoi MA, Kamel N, Malik AS, Faye I (2014) EEG based brain source localization comparison of sLORETA and eLORETA. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 37(4):713–721
Jatoi MA, Dharejo FA, Teevino SH (2020) Comparison of machine learning techniques based brain source localization using eeg signals. Curr Med Imaging. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573405616666200226122636
Jatoi MA, Kamel N, López JD (2020) Multiple sparse priors technique with optimized patches for brain source localization. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 30(1):154–167
Jatoi MA, Kamel N, Teevino SH (2020) Trend analysis for brain source localization techniques using EEG signals. In: 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), pp 1–5
Gaho AA, Jatoi MA, Musavi SHA, Shafiq M (2019) Brain mapping of cortical epileptogenic zones and their EEG source localization. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), pp 1–6
Dvey-Aharon Z, Fogelson N, Peled A, Intrator N (2015) Schizophrenia detection and classification by advanced analysis of EEG recordings using a single electrode approach. PLoS ONE 10:e0123033
Kim JW, Lee YS, Han DH, Min KJ, Lee J, Lee K (2015) Diagnostic utility of quantitative EEG in un-medicated schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 589:126–131
Chen C-MA, Jiang R, Kenney JG, Bi J, Johannesen JK (2016) Machine learning identification of EEG features predicting working memory performance in schizophrenia and healthy adults. Neuropsychiatr Electrophysiol 2(1):1–21
Santos-Mayo L, San-José-Revuelta LM, Arribas JI (2017) A computer-aided diagnosis system with EEG based on the P3b wave during an auditory odd-ball task in schizophrenia. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(2):395–407
Ibáñez-Molina AJ, Lozano V, Soriano MF (2018) EEG multiscale complexity in schizophrenia during picture naming. Front Physiol 9:1–12
Aharon ZD, Fogelson N, Peled A, Intrator N (2017) Connectivity maps based analysis of EEG for the advanced diagnosis of schizophrenia attributes. PLoS ONE 12(10):e0185852
Olejarczyk E, Jernajczyk W (2017) Graph-based analysis of brain connectivity in schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188629
Sun J, Tang Y, Lim KO (2014) Abnormal dynamics of eeg oscillations in schizophrenia patients on multiple time scales. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(6):1756–1764
Buettner R; Hirschmiller M; Schlosser K (2019) High-performance exclusion of schizophrenia using a novel machine learning method on EEG data. In: IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services, Bogotá, Colombia, pp 14–19
Jahmunah V, Oh SL, Rajinikanth V, Ciaccio EJ, Cheong KH, Arunkumar N, Acharya UR (2019) Automated detection of schizophrenia using nonlinear signal processing methods. Artif Intell Med 100:101698
Buettner R, Beil D, Scholtz S, Djemai A (2020) Development of a machine learning based algorithm to accurately detect schizophrenia based on one-minute EEG recordings. In: Proceedings: 53rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, Hawaii, pp 7–10
Liu T, Zhang J, Dong X, Li Z, Shi X, Tong Y et al (2019) Occipital alpha connectivity during resting-state electroencephalography in patients with ultra-high risk for psychosis and schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry 10:553
Boostani R, Sadatnejad K, Sabeti M (2009) An efficient classifier to diagnose of schizophrenia based on EEG signals. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):6492–6499
Li F, Wang J, Liao Y, Yi C, Jiang Y, Si Y et al (2019) Differentiation of schizophrenia by combining the spatial EEG brain network patterns of rest and task P300. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(4):594–602
Guo Y, Liu Y, Oerlemans A, Lao S, Wu S, Lew MS (2016) Deep learning for visual understanding: a review. Neurocomputing 187:27–48
Bengio Y, Goodfellow I, Courville A (2017) Deep learning. MIT press, Cambridge
Sun W, Tseng TL, Zhang J, Qian W (2017) Enhancing deep convolutional neural network scheme for breast cancer diagnosis with unlabeled data. Comput Med Imaging Graph 57:4–9
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M et al (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88
Greenspan H, van Ginneken B, Summers RM (2016) Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1153–1159
Poplin R, Varadarajan AV, Blumer K, Liu Y, McConnell MV, Corrado GS et al (2018) Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nat Biomed Eng 2(3):158
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, Thrun S (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Litjens G, Ciompi F, Wolterink JM, de Vos BD, Leiner T, Teuwen J, Išgum I (2019) State-of-the-art deep learning in cardiovascular image analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 12(8):1549–1565
De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, Nikolov S, Tomasev N, Blackwell S et al (2018) Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med 24(9):1342–1350
Litjens G, Sánchez CI, Timofeeva N, Hermsen M, Nagtegaal I, Kovacs I et al (2016) Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci Rep 6:26286
Acharya UR, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adeli H (2018) Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 100:270–278
Roy Y, Banville H, Albuquerque I, Gramfort A, Falk TH, Faubert J (2019) Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: a systematic review. J Neural Eng 16(5):051001
Faust O, Hagiwara Y, Hong TJ, Lih OS, Acharya UR (2018) Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: a review. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 161:1–3
Zhang X, Yao L, Wang X, Monaghan J, Mcalpine D (2019) A survey on deep learning based brain computer interface: recent advances and new frontiers. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.1145/1122445.1122456
Chaudhary S, Taran S, Bajaj V, Sengur A (2019) Convolutional neural network-based approach towards motor imagery tasks EEG signals classification. IEEE Sens J 19(12):4494–4500
Oh SL, Vicnesh J, Ciaccio EJ, Yuvaraj R, Acharya UR (2019) Deep convolutional neural network model for automated diagnosis of schizophrenia using EEG signals. Appl Sci 9(14):2870
Phang CR, Noman F, Hussain H, Ting CM, Ombao H (2019) A multi-domain connectome convolutional neural network for identifying schizophrenia from EEG connectivity patterns. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(5):1333–1343
Oh K, Kim W, Shen G, Piao Y, Kang NI, Oh IS, Chung YC (2019) Classification of schizophrenia and normal controls using 3D convolutional neural network and outcome visualization. Schizophr Res 212:186–195
Qureshi MNI, Oh J, Lee B (2019) 3D-CNN based discrimination of schizophrenia using resting-state fMRI. Artif Intell Med 98:10–17
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2818–2826
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Khan SanaUllah, Islam N, Jan Z (2019) A novel deep learning based framework for the detection and classification of breast cancer using transfer learning. Pattern Recogn Lett 125:1–6
Shin H-C, Roth HR, Gao M (2016) Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1285–1298
Byra M, Styczynski G, Szmigielski C (2018) Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for liver steatosis assessment in ultrasound images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 13:1895–1903
Acharya UR, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adeli H, Subha DP (2018) Automated EEG-based screening of depression using deep convolutional neural network. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 161:103–113
Craik A, He Y, Contreras-Vidal JL (2019) Deep learning for electroencephalogram (EEG) classification tasks: a review. J Neural Eng 16(3):031001
Shiao HT, Cherkassky V, Lee J, Veber B, Patterson EE, Brinkmann BH, Worrell GA (2016) SVM-based system for prediction of epileptic seizures from iEEG signal. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(5):1011–1022
Rasheed W, Boon T (2019) Anomaly detection of moderate traumatic brain injury using auto-regularized multi-instance one-class SVM. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(1):83–93
Shalbaf A, Shalbaf R, Saffar M, Sleigh J (2019) Monitoring the level of hypnosis using a hierarchical SVM system. J Clin Monit Comput 15:1–8
Gholami R, Fakhari N (2017) Support vector machine: principles, parameters, and applications. Handbook of neural computation. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 515–535
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21
Molina V, Reig S, Sanz J, Palomo T, Benito C, Sánchez J, Sarramea F, Pascau J, Desco M (2005) Increase in gray matter and decrease in white matter volumes in the cortex during treatment with atypical neuroleptics in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 80(1):61–71
Mitelman SA, Brickman AM, Shihabuddin L, Newmark RE, Hazlett EA, Haznedar MM, Buchsbaum MS (2007) A comprehensive assessment of gray and white matter volumes and their relationship to outcome and severity in schizophrenia. Neuroimage 37(2):449–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained by data owner from the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Psychiatry and Neurology in Warsaw, Poland.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shalbaf, A., Bagherzadeh, S. & Maghsoudi, A. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for automated detection of schizophrenia from EEG signals. Phys Eng Sci Med 43, 1229–1239 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00925-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00925-9