Abstract
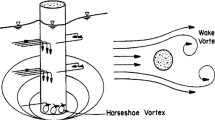
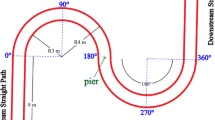
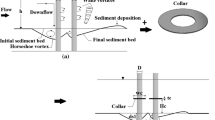
Bridge pier local scouring has forever been under consideration as an unwelcome phenomenon that threatens the safety of bridges. Hence, an investigation into methods of scour reduction around piers is of great importance regarding the hydraulic and environmental aspects. This study mainly focused on the role of submerged parallel vanes’ positioning across the channel width in decreasing the depth of scouring around the pier. This experiment was conducted in a channel made of a 180° sharp bend. The bridge pier was positioned at the 90° cross section, while the submerged vanes were located upstream of the pier in different arrangements. The results demonstrated that placing the submerged vanes at the channel’s central axis caused the greatest reduction in scouring depth compared to the tests with no vanes. With the minimum scour hole volume around the pier, a 51% scour reduction resulted compared with the test without submerged vanes. In addition, the maximum scour reduction occurred with the submerged vanes placed at 2.5 times the pier diameter away from the pier’s centerline and at intervals of 1 and 1.5 times the pier diameter. This pattern resulted in 30% and 25% local scour reductions around the pier. Moreover, the lowest and the highest sedimentation values were, respectively, larger than the pier diameter by factors of 6.1 and 2.2, occurring at distances of 9 and 24% of channel width away from the inner bank. These results led to the proposed experimental equations with an acceptable accuracy in calculating the maximum scouring depth.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
If requested, yes.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Akbari M, Vaghefi M (2017) Experimental investigation on streamlines in a 180º sharp bend. Acta Sci Tech 39(4):425–432. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascitechnol.v39i4.29032
Akbari M, Vaghefi M, Chiew YM (2021) Effect of T-shaped spur dike length on mean flow characteristics along a 180-degree sharp bend. J Hydrol Hydromech 69(1):98–107. https://doi.org/10.2478/johh-2020-0045
Asadollahi M, Vaghefi M, Tabibnejad Motlagh MJ (2021) Experimental and numerical comparison of flow and scour patterns around a single and triple bridge piers located at a sharp 180 degrees bend. Sci Iran Trans A 28(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2019.5637.1391
Ayaseh A, Salmasi F, Hossienzade Dalir A, Arvanaghi H (2019) A performance comparison of CCHE2D model with empirical methods to study sediment and erosion in gravel-bed rivers. Int J Environ Sci Te 16:7933–7942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02229-2
Bejestan MS, Khademi K, Kozeymehnezhad H (2015) Submerged vane-attached to the abutment as scour countermeasure. Ain Shams Eng J 6(3):775–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2015.02.006
Biswas P, Barbhuiya AK (2018) Countermeasure of river bend scour using a combination of submerged vanes and riprap. Int J Sediment Res 33(4):478–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2018.04.002
Chauhan V, Singhal GD, Chavan R (2022) A review of sediment deflection in rivers using submerged vanes. ISH J Hydraul Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2022.2084352
Chiew YM, Melville BW (1987) Local scour around bridge piers. J Hydraul Res 25(1):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221688709499285
Chooplou CA, Vaghefi M (2019) Experimental study of the effect of displacement of vanes submerged at channel width on distribution of velocity and shear stress in a 180 degree bend. J Appl Fluid Mech 12(5):1417–1428. https://doi.org/10.29252/jafm.12.05.29329
De Medeiros IC, da Costa SJFCB, Silva RM, Santos CAG (2019) Run-off–erosion modelling and water balance in the Epitácio Pessoa Dam river basin, Paraíba State in Brazil. Int J Environ Sci Te 16:3035–3048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1940-3
Dehghan D, Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M (2021) The effect of collar width ratio on the flow pattern around an oblong pier in a bend. Water Supp 21(8):4130–4144. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.165
Dey L, Barbhuiya AK, Biswas P (2017) Experimental study on bank erosion and protection using submerged vane placed at an optimum angle in a 180° laboratory channel bend. Geomorphology 283:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.01.022
Elçiçek H, Güzel B (2020) On non-axisymmetric flow structures of graphene suspensions in Taylor-Couette reactors. Int J Environ Sci Te 17:3475–3484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02713-0
Fathi A, Zomorodian SM, Zolghadr M, Chadee A, Chiew YM, Kumar B, Martin H (2023) Combination of riprap and submerged vane as an abutment scour countermeasure. Fluids 8(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8020041
Gaudio R, Tafarojnoruz A, Calomino F (2012) Combined flow-altering countermeasures against bridge pier scour. J Hydraul Res 50(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2011.649548
Ghorbani B, Kells JA (2008) Effect of submerged vanes on the scour occurring at a cylindrical pier. J Hydraul Res 46(5):610–619. https://doi.org/10.3826/jhr.2008.3003
Günal M, Günal AY, Osman K (2019) Simulation of blockage effects on scouring downstream of box culverts under unsteady flow conditions. Int J Environ Sci Te 16:5305–5310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02461-w
Hemmati M, Daraby P (2019) Erosion and sedimentation patterns associated with restoration structures of bendway weirs. J Hydro-Environ Res 22:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2018.11.001
Keshavarz A, Vaghefi M, Ahmadi G (2021) Investigation of flow patterns around rectangular and oblong piers with collar located in a 180-degree sharp bend. Sci Iran Trans A 28(5):2479–2492. https://doi.org/10.24200/SCI.2021.55320.4169
Keshavarz A, Vaghefi M, Ahmadi G (2022) Effect of the shape and position of the bridge pier on the bed changes in the sharp 180-degree bend. IJST-T Civ Eng 46:2449–2467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00787-5
Khajeh SBM, Vaghefi M, Mahmoudi A (2017) The scour pattern around an inclined cylindrical pier in a sharp 180-degree bend: an experimental study. Int J River Basin Manag 15(2):207–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2016.1274322
Lauchlan CS (1999) Pier scour countermeasures. Dissertation, University of Auckland
Maatooq JS, Adhab B (2017) Effect of distance of the submerged vanes from the outer bank on sediment movement within 180 bend. Am J Eng App Sci 10(3):679–683. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajeassp.2017.679.684
Marelius F (2001) Experimental investigation of vanes as a means of beach protection. Coast Eng 42(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-3839(00)00044-2
Moghanloo M, Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M (2020) Experimental investigation on the effect of increasing the collar thickness on the flow pattern around the oblong pier in 180° sharp bend with balanced bed. J Appl Fluid Mech 13(1):245–260. https://doi.org/10.29252/jafm.13.01.30164
Moghanloo M, Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M (2022) Experimental study on the effect of thickness and level of the collar on the scour pattern in 180° sharp bend with bridge pier. IJST-T Civ Eng 46:535–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00511-9
Neill C (1967) Mean-velocity criterion for scour of coarse uniform bed-material. In: 12th congress of the international association for hydraulics research, Colorado
Odgaard AJ, Kennedy JF (1983) River-bend bank protection by submerged vanes. J Hydraul Eng 109(8):1161–1173. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9429(1983)109:8(1161)
Odgaard AJ, Spoljaric A (1986) Sediment control by submerged vanes. J Hydraul Eng 112(12):1164–1180. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9429(1986)112:12(1164)
Odgaard AJ, Wang Y (1991) Sediment management with submerged vanes. J Hydraul Eng 117(3):963–968. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1991)117:3(267)
Ouyang HT, Lin CP (2016) Characteristics of interactions among a row of submerged vanes in various shapes. J Hydro-Environ Res 13:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2016.05.003
Ouyang H, Lu C (2016) Optimizing the spacing of submerged vanes across rivers for stream bank protection at channel bends. J Hydraul Eng 142(12):04016062. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hy.1943-7900.0001210
Raudkivi AJ, Ettema R (1983) Clear-water scour at cylindrical piers. J Hydraul Eng 109(3):338–350. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1983)109:3(338)
Roushangar K, Shahnazi S (2019) Bed load prediction in gravel-bed rivers using wavelet kernel extreme learning machine and meta-heuristic methods. Int J Environ Sci Te 16:8197–8208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02287-6
Roy P, Das S, Dey A, Das R (2022) Analytical study of scour mechanism around immersed rectangular vane structures. In: Rao CM, Patra KC, Jhajharia D, Kumari S (eds) Advanced modelling and innovations in water resources engineering. Lecture notes in civil engineering, vol 176. Springer, Berlin, pp 703–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4629-4_49
Safaripour N, Vaghefi M, Mahmoudi A (2022) Experimental study of the effect of submergence ratio of double submerged vanes on topography alterations and temporal evaluation of the maximum scour in a 180-degree bend with a bridge pier group. Int J River Basin Manag 20(4):427–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2020.1837144
Sedighi F, Vaghefi M, Ahmadi G (2021) The effect of inclined pair piers on bed topography: clear water, incipient motion and live bed. IJST-T Civ Eng 45:1871–1890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00481-y
Serajian MT, Kamanbedast AA, Masjedi A, Heidarnejad M, Hasonizadeh H (2019) Laboratory evaluation of the combined effect of convergence and submerged vanes on lateral Intakes’ sediment input at 90° river bends. Ain Shams Eng J 11(1):245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2019.09.008
Sharma H, Ahmad Z (2020) Turbulence characteristics of flow past submerged vanes. Int J Sediment Res 35(1):42–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.07.002
Solanki K, Sharma H, Joshi N (2020) Flow and parameter optimization of tapered vane. J Ecohydraul. https://doi.org/10.1080/24705357.2020.1771223
Tan SK, Yu G, Lim SY, Ong MC (2005) Flow structure and sediment motion around submerged vanes in open channel. J Waterw Port C 131(3):132–136. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-950x(2005)131:3(132)
Teronpi J, Misra DUK (2015) Experimental investigation of local scour around submerged vane. Int J Innov Res Adv Eng 2(7):21–24
Vaghefi M, Akbari M (2019) A procedure for setting up a 180-degree sharp bend flume including construction and examinations with hydraulic structures. Sci Iran Trans A 26(6):3165–3180. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2018.5033.1054
Vaghefi M, Akbari M, Fiouz AR (2016a) An experimental study of mean and turbulent flow in a 180 degree sharp open channel bend: secondary flow and bed shear stress. KSCE J Civ Eng 20:1582–1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-1560-0
Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M, Salimi S (2016b) The effect of circular bridge piers with different inclination angles toward downstream on scour. Sadhana 41:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0443-x
Vaghefi M, Motlagh MJTN, Hashemi SS, Moradi S (2018) Experimental study of bed topography variations due to placement of a triad series of vertical piers at different positions in a 180° bend. Arab J Geosci 11:102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3443-4
Yarahmadi MB, Bejestan MS (2016) Sediment management and flow patterns at river bend due to triangular vanes attached to the bank. J Hydro Environ Res 10:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2015.10.002
Zarei E, Vaghefi M, Hashemi SS (2019) Bed topography variations in bend by simultaneous installation of submerged vanes and single bridge pier. Arab J Geosci 12:178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4342-z
Acknowledgments
Not applicable
Funding
Any funding agency does not support this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CAC contributed to methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, data Collection, resources, formal analysis, software, investigation; MV contributed to supervision, conceptualization, methodology, project administration, formal analysis, validation, writing—reviewing, and editing; MA contributed to formal analysis, conceptualization, investigation, validation, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chooplou, C.A., Vaghefi, M. & Akbari, M. Effect of repositioned submerged vanes on local scour variations around a pier in a bend: experimental investigation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 8627–8640 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05031-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05031-3