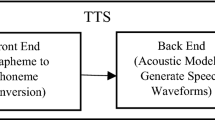
Abstract
Speech is the natural communication means, though not the typical input means afforded by computers. The interaction between humans and machines would have become easier, if speech were an alternative effective input means supplementing the keyboard and mouse. With advancement in techniques for signal processing and model building leading to the empowerment of computing devices with expanding list of abilities, significant progress has been made in speech recognition research, and various speech based applications have been developed. In such a backdrop, telephone speech technology have been receiving more attention in many new applications of spoken language processing. From the literature it has been found that the spectro-temporal features gives a significant performance improvement for telephone speech recognition in comparison to the conventionally used features for speech/speaker identification. Speech recognition systems can be characterized by many parameters. The commonly used method to measure the performance of a speech recognition system is the recognition accuracy. For obtaining proper accuracy it is necessary to design an efficient classifier for the recognition purpose which will lead to correct recognition results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurain C (2014) A Survey on Speech Recognition in Indian Languages. Proc Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol (IJCSIT) 5(5):6169–6175
Beigi H (2011) Fundamentals of speaker recognition. Springer, New York
Zuo G, Liu W, Ruan X (2003) Telephone Speech Recognition Using Simulated Data from Clean Database. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics, intelligent systems and signal processing, vol. 1, pp 49–53, Changsha, China
Venkateshwarlu RLK, Raviteja R, Rajeev R (2012) The performance evaluation of speech recognition by comparative approach. In: Karahoca A (ed) Advances in data mining knowledge discovery and applications. InTech. doi:10.5772/50640. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/advances-in-data-mining-knowledge-discovery-and-applications/the-performance-evaluation-of-speech-recognition-by-comparative-approach
Awasthy N, Saini JP, Chauhan DS (2008) Spectral analysis of speech: a new technique. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 2(7):946–955
Sarma M, Sarma KK (2014) Phoneme-based speech segmentation using hybrid soft computing framework, vol 550. Springer, New York
Anusuya MA, Katti SK (2009) Speech recognition by machine: a review. Proc Int J Comput Sci Inf Secur (IJCSIS) 6(3):181–205
Ganapathy S, Thomas S, Hermansky H (2010) Robust spectro-temporal features based on autoregressive models of Hilbert Envelopes. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), Dallas, TX, pp 4286–4289, ISBN 978-1-4244-4296-6. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2010.5495668
Boersma P (1993) Accurate Short-term analysis of the fundamental frequency and the harmonics-to-noise ratio of a sampled sound. Proc Inst Phon Sci 17(1193):97–110
Dehak N, Kenny P, Dehak R, Dumouchel P, Oullet P (2011) Front-end Factor Analysis for Speaker Verification. Proc IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(4):788–798
Mozer MC (1989) A focused back-propagation algorithm for temporal pattern recognition. Complex Syst 3(4):349–381
Yadav KS, Mukhedkar MM (2013) Review on speech recognition. Proc Int J Sci Eng (IJSE) 1(2):61–70
Gunes H, Pantic M (2010) Automatic, dimensional and continuous emotion recognition. Int J Synth Emot 1(1):68–99
Goswami GC (1982) Structure of Assamese, 1st edn. Department of Publication, Gauhati University, Gauhati
Sharma M, Sarma KK (2015) Soft-computational techniques and spectrotemporal features for telephonic speech recognition: an overview and review of current state of the art. In: Bhattacharyya S, Banerjee P, Majumdar D, Dutta P (eds) Handbook pf research on advanced hybrid intelligent techniques and applications, chapter- 006, Hersey, PA: Information Science Reference, pp 161–189
Sarma M, Sarma KK (2013) An ANN based approach to recognize initial phonemes of spoken words of Assamese language. J Appl Soft Comput 5(13):2281–2291
Acknowledgement
Funding was provided by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M., Sarma, K.K. Soft computation based spectral and temporal models of linguistically motivated Assamese telephonic conversation recognition. CSIT 5, 209–216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0145-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0145-5