Abstract
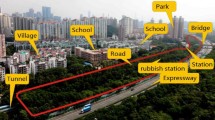
This paper investigates the behavior of deep excavations and damages on adjacent buildings based on an excavation in a thick sand layer in Vietnam. Firstly, measured horizontal displacements of diaphragm walls were used to calibrate soil stiffness parameters for finite element analysis (FEA). Then, the behavior of diaphragm walls, groundwater, ground surface deformation, and an adjacent building was analyzed. The analysis results and damages observed in the field were used to review the validity of the criteria for evaluating the damage potential of excavation to adjacent buildings. It can be concluded from the study that the damage potential of adjacent buildings as evaluated from FEA through the strain state chart proposed by Boscardin and Cording (1989) or the damage potential index (DPI) proposed by Schuster et al. (2009) is fairly accurate with field observations.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data and materials in this paper are available.
References
AIJ. Recommendations for design of building foundations, AIJ 2001
Alshibli, K.A., Alsaleh, M.I.: Characterizing surface roughness and shape of sands using digital microscopy. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 18(1), 36–45 (2004)
Altun, S., Göktepe, B., Sezer, A.: Relationships between shape characteristics and shear strength of sands. Soils Found. 51(5), 857–871 (2011)
Arai, K., Ohta, H., Kojima, K., WAKASUGI, M.: Application of back-analysis to several test embankments on soft clay deposits. Soils Found. 26(2), 60–72 (1986)
Bjerrum, L.: Allowable settlement of structures. In: Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Wiesbaden, Germany (1963)
Boscardin, M.D., Cording, E.J.: Building response to excavation-induced settlement. J. Geotech. Eng. 115(1), 1–21 (1989)
Burland, J.: "Behaviour of foundations and structures on soft ground." Proc. 9th ICSMFE, 1977, vol. 2, pp. 495–546 (1977)
Burland, J. B., Broms, B. B. and de Mello, V. F. 1978. "Behaviour of Foundations and Structures."
Clough, G.W.: Construction induced movements of in situ walls. In: Design and performance of earth retaining structures, pp. 439–470 (1990)
Cording, E., Long, J., Son, M., Laefer, D. and Ghahreman, B.. Assessment of excavation-induced building damage. Earth Retention Conference 3 (2010)
Finno, R.J., Calvello, M.: Supported excavations: observational method and inverse modeling. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 131(7), 826–836 (2005)
Gens, A., Ledesma, A., Alonso, E.: Estimation of parameters in geotechnical backanalysis—II. Application to a tunnel excavation problem. Comput. Geotech. 18(1), 29–46 (1996)
Halim, D., Wong, K.S.: Prediction of frame structure damage resulting from deep excavation. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 138(12), 1530–1536 (2011)
Hsieh, P.-G., Ou, C.-Y.: Shape of ground surface settlement profiles caused by excavation. Can. Geotech. J. 35(6), 1004–1017 (1998)
Hsiung, B.-C.B.: A case study on the behaviour of a deep excavation in sand. Comput. Geotech. 36(4), 665–675 (2009)
Hsiung, B.-C.B., Dao, S.-D.: Evaluation of constitutive soil models for predicting movements caused by a deep excavation in sands. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 19, 17325–17344 (2014)
Hsiung, B.-C.B., Yang, K.-H., Aila, W., Hung, C.: Three-dimensional effects of a deep excavation on wall deflections in loose to medium dense sands. Comput. Geotech. 80, 138–151 (2016)
Hung, N.K., Phienwej, N.: Practice and experience in deep excavations in soft soil of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 20(6), 2221–2234 (2016)
Huynh, Q.T., Lai V.Q., Tran, V.T., Nguyen, M.T.: Analyzing the settlement of adjacent buildings with shallow foundation based on the horizontal displacement of retaining wall. In: Geotechnics for Sustainable Infrastructure Development, pp. 313–320. Springer, Singapore (2020a)
Huynh, Q.T., Lai V.Q., Tran, V.T., Nguyen, M.T.: Back analysis on deep excavation in the thick sand layer by hardening soil small model. In: ICSCEA 2019, pp. 659–668. Springer, Singapore (2020b)
Khoiri, M., Ou, C.-Y.: Evaluation of deformation parameter for deep excavation in sand through case histories. Comput. Geotech. 47, 57–67 (2013)
Likitlersuang, S., Plengsiri, P., Mase, L.Z., Tanapalungkorn, W.: Influence of spatial variability of ground on seismic response analysis: a case study of Bangkok subsoils. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 79(1), 39–51 (2020)
Likitlersuang, S., Surarak, C., Wanatowski, D., Oh, E., Balasubramaniam, A.: Finite element analysis of a deep excavation: a case study from the Bangkok MRT. Soils Found. 53(5), 756–773 (2013)
Lim, A., Ou, C.-Y., Hsieh, P.-G.: Evaluation of clay constitutive models for analysis of deep excavation under undrained conditions. J. GeoEng. 5(1), 9–20 (2010)
Lin, H.-D., Mendy, S., Liao, H.-C., Dang, P.H., Hsieh, Y.-M., Chen, C.-C.: Responses of 3D excavation and adjacent buildings in sagging and hogging zones using decoupled analysis method. J. GeoEng. 11(2), 85–96 (2016)
Mana, A. I. and Clough, G. W.. "Prediction of movements for braced cuts in clay." Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 107(ASCE 16312 Proceeding) 1981
Mase, L.Z.: Liquefaction potential analysis along coastal area of Bengkulu Province due to the 2007 Mw 8.6 Bengkulu earthquake. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences. 49(6), 721–736 (2017)
Misliniyati, R., Mase, L.Z., Irsyam, M., Hendriawan, H., Sahadewa, A.: Seismic response validation of simulated soil models to vertical array record during a strong earthquake. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences. 51(6), 772–790 (2019)
Ou, C.-Y., Chiou, D.-C., Wu, T.-S.: Three-dimensional finite element analysis of deep excavations. J. Geotech. Eng. 122(5), 337–345 (1996)
Ou, C.-Y., Hsieh, P.-G., Chiou, D.-C.: Characteristics of ground surface settlement during excavation. Can. Geotech. J. 30(5), 758–767 (1993)
Ou, C. and Hsien, P. . Prediction of ground surface settlement induced by deep excavation, Geotechnical research report No. GT200008, Department of construction 2000
Plaxis 2D: Reference manual. Plaids BV, Amsterdam (2019)
Sabzi, Z., Fakher, A.: The performance of buildings adjacent to excavation supported by inclined struts. International Journal of Civil Engineering. 13(1), 1–13 (2015)
Sadrekarimi, A., Olson, S.M.: Critical state friction angle of sands. Géotechnique. 61(9), 771–783 (2011)
Sakurai, S., Akutagawa, S., Takeuchi, K., Shinji, M., Shimizu, N.: Back analysis for tunnel engineering as a modern observational method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 18(2–3), 185–196 (2003)
Sakurai, S., Takeuchi, K.: Back analysis of measured displacements of tunnels. Rock Mech. Rock. Eng. 16(3), 173–180 (1983)
Schanz, T., Vermeer, P., Bonnier, P.: The hardening soil model: formulation and verification. In: Beyond 2000 in computational geotechnics, pp. 281–296 (1999)
Schuster, M., Kung, G.T.-C., Juang, C.H., Hashash, Y.M.: Simplified model for evaluating damage potential of buildings adjacent to a braced excavation. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 135(12), 1823–1835 (2009)
Schweiger, H.. Influence of constitutive model and EC7 design approach in FEM analysis of deep excavations. Proceeding of ISSMGE International Seminar on Deep Excavations and Retaining Structures, Budapest (2009)
Shukor, F.: Comparison of back analysis and measured lateral displacement of cantilever diaphragm wall. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor Bahru (2009)
Skempton, A.W., MacDonald, D.H.: The allowable settlements of buildings. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 5(6), 727–768 (1956)
Son, M., Cording, E.J.: Estimation of building damage due to excavation-induced ground movements. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 131(2), 162–177 (2005)
Stroud, M.. "The standard penetration test: its application and interpretation." Penetration Testing in the UK: 29–49 (1989)
Tan, Y. and Chow, C. Design of retaining wall and support systems for deep basement construction–a Malaysian experience. Seminar on “Deep Excavation and Retaining Walls”, Jointly orgnaised by IEM-HKIE, Malaysia (2008)
Teo, P., Wong, K.: Application of the hardening soil model in deep excavation analysis. The IES Journal Part A: Civil & Structural Engineering. 5(3), 152–165 (2012)
Yong, C.C., Oh, E.: Modelling ground response for deep excavation in soft ground. Int. J. 11(26), 2633–2642 (2016)
Zhang, R., Goh, A., Zhang, W.: System reliability assessment on deep braced excavation adjacent to an existing upper slope in mountainous terrain: a case study. SN Applied Sciences. 1(8), 876 (2019)
Zhang, W., Goh, A.T., Zhang, Y.: Updating soil parameters using spreadsheet method for predicting wall deflections in braced excavations. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 33(6), 1489–1498 (2015)
Zhang, W., Li, Y., Goh, A., Zhang, R.: Numerical study of the performance of jet grout piles for braced excavations in soft clay. Comput. Geotech. 124, 103631 (2020)
Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Goh, A.T.: Multivariate adaptive regression splines approach to estimate lateral wall deflection profiles caused by braced excavations in clays. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 36(2), 1349–1363 (2018a)
Zhang, X., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Gao, Y.: Cause investigation of damages in existing building adjacent to foundation pit in construction. Eng. Fail. Anal. 83, 117–124 (2018b)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Hoa Binh Construction Group Joint Stock Company for the provision of data of the Madison Project. We would also like to express our gratitude to MSc. Viet Thai Tran, who contributed good ideas, insightful comments, and valuable experiences to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Quoc Thien Huynh acquired methodology and software and contributed to the investigation.
Van Qui Lai acquired methodology, supervision, and contributed to conceptualization and writing—original draft.
Suraparb Keawsawasvong provided resources and contributed to writing—review and editing, data curation.
Tirawat Boonyatee provided resources and contributed to writing—review and editing, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, Q.T., Lai, V.Q., Boonyatee, T. et al. Behavior of a Deep Excavation and Damages on Adjacent Buildings: a Case Study in Vietnam. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotech. 8, 361–389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-020-00142-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-020-00142-7