Abstract
Nowadays soaring energy price, increasing environmental concerns, and stringent legislations make energy saving very emergency and helpful both for enterprises and environment. To deal with these issues, this paper presents a generalized mathematical power prediction model of face milling process used in manufacturing. An attempt was made to develop a relatively precise and direct power consumption model to help researchers make power optimization much easier and more practical than before. First, an infinitesimal cutting force model was proposed based on theoretical and experimental foundations. Secondly, relationship between power consumption and cutting force components was revealed, and power consumption based on infinitesimal cutting forces during metal removal process was developed. Finally, the proposed model was experimentally verified by comparing predicted and measured power consumption. Both average and instantaneous values of power consumption were used to analyze prediction error of the model. This proposed model can be used to evaluate and optimize cutting power consumption once cutting parameters were decided based on minimal energy demand. Results showed that the mean errors of maximum power and mean power were 0.076% and 0.208%, respectively. Otherwise, this proposed model will drive the field of power consumption simulation development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
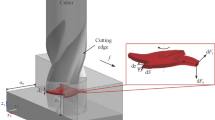
- dA:
-
Cutting area of infinitesimal cutting edge (mm2)
- db :
-
Width of cutting edge element (mm)
- d z :
-
Thickness of infinitesimal cutting edge (mm)
- dF c :
-
Cutting force component normal to the tool rake (N)
- dF t :
-
Cutting force component tangential to the elementary cutting edge (N)
- dF n :
-
Radial cutting force component (N)
- F v :
-
Cutting force component along cutting speed vc (N)
- f z :
-
Feed per tooth of the milling parameters (mm/tooth)
- Ktc, Knc, Kcc :
-
Cutting force coefficients (N/mm2)
- Kte, Kne, Kce :
-
Edge force coefficients (N/mm)
- P a-f :
-
Additional power loss of feed drive system in cutting state (W)
- P a-n :
-
Additional power loss of main drive system in cutting state (W)
- P c :
-
Total cutting power consumption of experiment (W)
- P c-idle :
-
Spindle motor’s power consumption of the auxiliary components in cutting state (W)
- P idle :
-
Spindle motor’s power consumption of the auxiliary components in idling state (W)
- P servo :
-
Feed motion power consumption in cutting state (W)
- P spindle :
-
Total spindle rotational power in cutting state (W)
- P remove :
-
Total power consumption of material removing process (W)
- P u :
-
Unload power of servo motor in feed motion system in stand-by state (W)
- r :
-
The radius of face miller (mm)
- t 0 :
-
Chip thickness (mm)
- vc :
-
Cutting speed (m/min)
- vf :
-
Feeding speed (m/min)
- η :
-
Additional load loss coefficient of spindle system
- ϕ(t):
-
The instantaneous cutting angle (°)
- ϕ st :
-
Cutter entry angle (°)
- ϕ ex :
-
Cutter exit angle (°)
References
Campatelli, G., Scippa, A., Lorenzini, L., and Sato, R., “Optimal Workpiece Orientation to Reduce the Energy Consumption of a Milling Process,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 5–13, 2015.
Zhao, F. and Sharma, A., “Environmentally Friendly Machining Machining Process Environmentally Friendly Machining,” Handbook of Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, pp. 1127–1154, 2015.
Liu, F., Xie, J., and Liu, S., “A Method for Predicting the Energy Consumption of the Main Driving System of a Machine Tool in a Machining Process,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 105, pp. 171–177, 2015.
Velchev, S., Kolev, I., Ivanov, K., and Gechevski, S., “Empirical Models for Specific Energy Consumption and Optimization of Cutting Parameters for Minimizing Energy Consumption during Turning,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 80, pp. 139–149, 2014.
Jang, D., Jung, J., and Seok, J., “Modeling and Parameter Optimization for Cutting Energy Reduction in MQL Milling Process,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 5–12, 2016.
Yoon, H.-S., Lee, J.-Y., Kim, M.-S., and Ahn, S.-H., “Empirical Power-Consumption Model for Material Removal in Three-Axis Milling,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 78, pp. 54–62, 2014.
Al-Hazza, M. H. F., Adesta, E. Y. T., Ali, A. M., Agusman, D., and Suprianto, M., “Energy Cost Modeling for High Speed Hard Turning,” Journal of Applied Sciences, Vol. 11, No. 14, pp. 2578–2584, 2011.
Li, W. and Kara, S., “An Empirical Model for Predicting Energy Consumption of Manufacturing Processes: A Case of Turning Process,” Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, Vol. 225, No. 9, pp. 1636–1646, 2011.
Li, L., Yan, J., and Xing, Z., “Energy Requirements Evaluation of Milling Machines Based on Thermal Equilibrium and Empirical Modelling,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 52, pp. 113–121, 2013.
Liu, N., Zhang, Y., and Lu, W., “A Hybrid Approach to Energy Consumption Modelling Based on Cutting Power: A Milling Case,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol. 104, pp. 264–272, 2015.
Liu, X.-W., Cheng, K., Webb, D., and Luo, X.-C., “Prediction of Cutting Force Distribution and Its Influence on Dimensional Accuracy in Peripheral Milling,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 42, No. 7, pp. 791–800, 2002.
Ehmann, K., Kapoor, S., DeVor, R., and Lazoglu, I., “Machining Process Modeling: A Review,” Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Vol. 119, pp. 655–663, 1997.
Wei, Z., Wang, M., Zhu, J., and Gu, L., “Cutting Force Prediction in Ball End Milling of Sculptured Surface with Z-Level Contouring Tool Path,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 428–432, 2011.
Abou-El-Hossein, K., Kadirgama, K., Hamdi, M., and Benyounis, K., “Prediction of Cutting Force in End-Milling Operation of Modified AISI P20 Tool Steel,” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 182, No. 1, pp. 241–247, 2007.
Sun, Y., Ren, F., Guo, D., and Jia, Z., “Estimation and Experimental Validation of Cutting Forces in Ball-End Milling of Sculptured Surfaces,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 49, No. 15, pp. 1238–1244, 2009.
Gradišek, J., Kalveram, M., and Weinert, K., “Mechanistic Identification of Specific Force coefficients for a General end Mill,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 44, No. 4, pp. 401–414, 2004.
Fu, H.-J., DeVor, R., and Kapoor, S., “A Mechanistic Model for the Prediction of the Force System in Face Milling Operations,” Journal of Engineering for Industry, Vol. 106, No. 1, pp. 81–88, 1984.
Korkut, I. and Donertas, M., “The Influence of Feed Rate and Cutting Speed on the Cutting Forces, Surface Roughness and Tool-Chip Contact Length during Face Milling,” Materials & Design, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 308–312, 2007.
Baek, D. K., Ko, T. J., and Kim, H. S., “Optimization of Feedrate in a Face Milling Operation Using a Surface Roughness Model,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 451–462, 2001.
Altintas, Y., “Manufacturing Automation: Metal Cutting Mechanics, Machine Tool Vibrations, and CNC Design,” Cambridge University Press, pp. 8–47, 2000.
Budak, E., Altinta, Y., and Armarego, E., “Prediction of Milling Force Coefficients from Orthogonal Cutting Data,” Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Vol. 118, No. 2, pp. 216–224, 1996.
Lamikiz, A., de Lacalle, L. L., Sanchez, J., and Salgado, M., “Cutting Force Estimation in Sculptured Surface Milling,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 44, No. 14, pp. 1511–1526, 2004.
Bouzakis, K.-D., Aichouh, P., and Efstathiou, K., “Determination of the Chip Geometry, Cutting Force and Roughness in free Form Surfaces Finishing Milling, with Ball End Tools,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 43, No. 5, pp. 499–514, 2003.
Karpuschewski, B., Binh, N. T., and Bello, J., “An Emperical Cutting-Force Model in High-Speed-Milling Process with Spherical Cutter,” Manufacturing Engineering/ Vyrobne Inzinierstvo, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 5–8, 2007.
Lee, P. and Altintas, Y., “Prediction of Ball-End Milling Forces from Orthogonal Cutting Data,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 36, No. 9, pp. 1059–1072, 1996.
Shirase, K. and Altintas, Y., “Cutting Force and Dimensional Surface Error Generation in Peripheral Milling with Variable Pitch Helical End Mills,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 567–584, 1996.
Cheng, K., “Machining Dynamics: Fundamentals, Applications and Practices,” Springer Science & Business Media, pp. 21–30, 2008.
Hu, T., “Energy Consumption Characteristics of Feed Drive System in CNC Machine Tools,” Chongqing University, pp. 17–30, 2012.
Hu, S., Liu, F., He, Y., and Peng, B., “Characteristics of Additional Load Losses of Spindle System of Machine Tools,” Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, Vol. 4, No. 7, pp. 1221–1233, 2010.
Luan, X., Zhang, S., and Cai, G., “Optimal Cutting Parameters to Reduce Power Consumption in Face Milling of a Cast Iron Alloy for Environmental Sustainability,” Sustainable Design and Manufacturing, pp. 135–148, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, X., Zhang, S. & Li, G. Modified power prediction model based on infinitesimal cutting force during face milling process. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 5, 71–80 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-018-0008-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-018-0008-7