Abstract
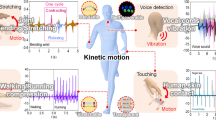
The exploration of smart electronic textiles is a common goal to improve people’s quality of life. However, current smart e-textiles still face challenges such as being prone to failure under humid or cold conditions, lack of washing durability and chemical fragility. Herein, a multifunctional strain sensor with a negative resistance change was developed based on the excellent elasticity of knitted fabrics. A reduced graphene oxide (rGO) conductive fabric was first obtained by electrostatic self-assembly of chitosan (CS). Then a strain sensor was prepared using a dip-coating process to adsorb nanoscale silica dioxide and poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS). A broad working range of 60%, a fast response time (22 ms) and stable cycling durability over 4000 cycles were simultaneously achieved using the prepared sensor. Furthermore, the sensor showed excellent superhydrophobicity, photothermal effects and UV protection, as graphene, silica and PDMS acted in synergy. This multifunctional sensor could be mounted on human joints to perform tasks, including activity monitoring, medical rehabilitation evaluation and gesture recognition, due to its superior electromechanical capabilities. Based on its multiple superior properties, this sensor could be used as winter sportswear for athletes to track their actions without being impacted by water and as a warmer to ensure the wearer's comfort.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang XP, Ren ZL, Fu YF, Liu YF, Zou R, Ji GP, Ning HM, Li YQ, Wen J, Qi HJ, Xu CH, Fu SY, Qiu JH, Hu N. Highly compressible and sensitive pressure sensor under large strain based on 3D porous reduced graphene oxide fiber fabrics in wide compression strains. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:37051.
Guo LH, Li ZK, Hu WW, Liu TP, Zheng YB, Yuan MM, Dai YJ, Ning RZ, Zhu YJ, Tao KY, Zhang M, Du T, Zhang L, Su C, Haick H, Wu WW. A flexible dual-structured MXene for ultra-sensitive and ultra-wide monitoring of anatomical and physiological movements. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:26867.
Dai ZY, Ding S, Lei M, Li SB, Xu Y, Zhou YN, Zhou BP. A superhydrophobic and anti-corrosion strain sensor for robust underwater applications. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:15282.
Pu XJ, Guo HY, Tang Q, Chen J, Feng L, Liu GL, Wang X, Xi Y, Hu CG, Wang ZL. Rotation sensing and gesture control of a robot joint via triboelectric quantization sensor. Nano Energy 2018;54:453.
Jian MQ, Wang CY, Wang Q, Wang H, Xia KL, Yin Z, Zhang MC, Liang XP, Zhang YY. Advanced carbon materials for flexible and wearable sensors. Sci China Mater 2017;60:1026.
Li XB, He LZ, Li YF, Chao MY, Li MK, Wan PB, Zhang LQ. Healable, degradable, and conductive MXene nanocomposite hydrogel for multifunctional epidermal sensors. ACS Nano 2021;15:7765.
Liu XH, Miao JL, Fan Q, Zhang WX, Zuo XW, Tian MW, Zhu SF, Zhang XJ, Qu LJ. Smart textile based on 3D stretchable silver nanowires/MXene conductive networks for personal healthcare and thermal management. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:56607.
Huang JY, Li DW, Zhao M, Ke HZ, Mensah A, Lv PF, Tian XJ, Wei QF. Flexible electrically conductive biomass-based aerogels for piezoresistive pressure/strain sensors. Chem Eng J 2019;373:1357.
Huang JY, Zhao M, Cai YB, Zimniewska M, Li DW, Wei QF. A dual-mode wearable sensor based on bacterial cellulose reinforced hydrogels for highly sensitive strain/pressure sensing. Adv Electron Mater 2020;6:1900934.
Guan FY, Han ZL, Jin MT, Wu ZT, Chen Y, Chen SY, Wang HP. Durable and flexible bio-assembled RGO-BC/BC bilayer electrodes for pressure sensing. Adv Fiber Mater 2021;3:128.
Li YP, Tan SJ, Yang LY, Li LY, Fang F, Sun QZ. Optical microfiber neuron for finger motion perception. Adv Fiber Mater 2022;4:226.
Wang HM, Wang HM, Wang YL, Su XY, Wang CY, Zhang MG, Jian MQ, Xia KL, Liang XP, Lu HJ, Li S, Zhang YY. Laser writing of janus graphene/kevlar textile for intelligent protective clothing. ACS Nano 2020;14:3219.
Peng X, Dong K, Ye CY, Jiang Y, Zhai SY, Cheng RW, Liu D, Gao XP, Wang J, Wang ZL. A breathable, biodegradable, antibacterial, and self-powered electronic skin based on all-nanofiber triboelectric nanogenerators. Sci Adv 2020;6:eaba9624.
Wang ZW, Chen J, Cong Y, Zhang H, Xu T, Nie L, Fu J. Ultrastretchable strain sensors and arrays with high sensitivity and linearity based on super tough conductive hydrogels. Chem Mater 2018;30:8062.
Li LY, Liu YF, Song CY, Sheng SF, Yang LY, Yan ZJ, Hu DJJ, Sun QZ. Wearable alignment-free microfiber-based sensor chip for precise vital signs monitoring and cardiovascular assessment. Adv Fiber Mater 2022;4:475.
Liu ZK, Li ZH, Zhai H, Jin L, Chen KL, Yi YPQ, Gao Y, Xu LL, Zheng Y, Yao SR, Liu ZC, Li G, Song QW, Yue PF, Xie SQ, Li Y, Zheng ZJ. A highly sensitive stretchable strain sensor based on multi-functionalized fabric for respiration monitoring and identification. Chem Eng J 2021;426:130869.
Xu H, Jiang XY, Han XS, Cai HZ, Gao F. Cooking inspired tough, adhesive, and low-temperature tolerant gluten-based organohydrogels for high performance strain sensors. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:25104.
Wu C, Deng CC, Liu LB, Han J, Chen JQ, Yin SY, Wei SJ. An Efficient application mapping approach for the co-optimization of reliability, energy, and performance in reconfigurable NoC architectures. IEEE Trans Comput Des Integr Circuits Syst. 2015;34:1264.
Kazemi KK, Zarifi T, Mohseni MJ, Narang R, Golovin K, Zarifi MH. Smart superhydrophobic textiles utilizing a long-range antenna sensor for hazardous aqueous droplet detection plus prevention. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:34877.
Dong K, Peng X, Wang ZL. Fiber/fabric-based piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for flexible/stretchable and wearable electronics and artificial intelligence. Adv Mater 2020;32:1902549.
Niu B, Yang S, Tian X, Hua T. Highly sensitive and stretchable fiber strain sensors empowered by synergetic conductive network of silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Appl Mater Today 2021;25:101221.
Seyedin SY, Razal JM, Innis PC, Jeiranikhameneh A, Beirne S, Wallace GG. Knitted strain sensor textiles of highly conductive all-polymeric fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015;7:21150.
Lv JC, Liu Z, Zhang L, Li KK, Zhang SH, Xu H, Mao ZP, Zhang HF, Chen JF, Pan GB. Multifunctional polypyrrole and rose-like silver flower-decorated E-textile with outstanding pressure/strain sensing and energy storage performance. Chem Eng J 2022;427:130823.
Feng JD, Wang XY, Lv ZH, Qu JG, Lu XM, Wei QF, Wang QQ. Multifunctional wearable strain sensor made with an elastic interwoven fabric for patients with motor dysfunction. Adv Mater Technol 2020;5:2000560.
Lu DX, Liao SQ, Wei QF, Xiao XL, Wang QQ. Comparative study of different carbon materials for the preparation of knitted fabric sensors. Cellulose 2022;29:7431.
Park C, Kim T, Samuel EP, Kim Y, An S, Yoon SS. Superhydrophobic antibacterial wearable metallized fabric as supercapacitor, multifunctional sensors, and heater. J Power Sources 2021;506:230142.
Liu LX, Chen W, Zhang HB, Wang QW, Guan FL, Yu ZZ. Flexible and multifunctional silk textiles with biomimetic leaf-like MXene/silver nanowire nanostructures for electromagnetic interference shielding, humidity monitoring, and self-derived hydrophobicity. Adv Funct Mater 2019;29:1905197.
Zhao J, Wang XF, Xu YQ, He PW, Si Y, Liu LF, Yu JY, Ding B. Multifunctional, waterproof, and breathable nanofibrous textiles based on fluorine-free, all-water-based coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020;12:15911.
Wang CY, Xia KL, Wang HM, Liang XP, Yin Z, Zhang YY. Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv Mater 2019;31:1801072.
Liu LL, Niu ZQ, Zhang L, Zhou WY, Chen XD, Xie SS. Nanostructured graphene composite papers for highly flexible and foldable supercapacitors. Adv Mater 2014;26:4855.
Yang Z, Pang Y, Han XL, Yang YF, Ling J, Jian MQ, Zhang YY, Yang YF, Ren TL. Graphene textile strain sensor with negative resistance variation for human motion detection. ACS Nano 2018;12:9134.
Zheng YJ, Li YL, Zhou YJ, Dai K, Zheng GQ, Zhang B, Liu CT, Shen CY. High-performance wearable strain sensor based on graphene/cotton fabric with high durability and low detection limit. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020;12:1474.
Pakdel E, Xie WJ, Wang JF, Kashi S, Sharp J, Zhang Q, Varley RJ, Sun L, Wang XG. Superhydrophobic natural melanin-coated cotton with excellent UV protection and personal thermal management functionality. Chem Eng J 2022;433:133688.
Cheng DH, Bai X, Pan JJ, Wu JH, Ran JH, Cai GM, Wang X. In situ hydrothermal growth of Cu NPs on knitted fabrics through polydopamine templates for heating and sensing. Chem Eng J 2020;382:123036.
Ni YM, Huang JY, Li SH, Wang XQ, Liu LX, Wang MY, Chen Z, Li X, Lai YK. Underwater, multifunctional superhydrophobic sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:4740.
Asadi MM, Bashir T, Persson NK. Electrostatic grafting of graphene onto polyamide 6,6 yarns for use as conductive elements in smart textile applications. New J Chem 2020;44:7591.
Ling YZ, Li XY, Zhou SW, Wang XY, Sun RC. Multifunctional cellulosic paper based on quaternized chitosan and gold nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide via electrostatic self-assembly. J Mater Chem A 2015;3:7422.
Kim SJ, Song W, Yi Y, Min B, Mondal S, An KS, Choi CG. High durability and waterproofing rGO/SWCNT-fabric-based multifunctional sensors for human-motion detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2018;10:3921.
Nandgaonkar AG, Wang QQ, Fu K, Krause WE, Wei QF, Gorga R, Lucia LA. A one-pot biosynthesis of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/bacterial cellulose (BC) nanocomposites. Green Chem 2014;16:3195.
Zhao HT, Tian MW, Hao YN, Qu LJ, Zhu SF, Chen SJ. Fast and facile graphene oxide grafting on hydrophobic polyamide fabric via electrophoretic deposition route. J Mater Sci 2018;53:9504.
Zhang L, Yu YN, Zheng S, Zhong LL, Xue JQ. Preparation and properties of conductive bacterial cellulose-based graphene oxide-silver nanoparticles antibacterial dressing. Carbohydr Polym 2021;257:117671.
Chen GY, Ai YL, Mugaanire IT, Ma WJ, Hsiao BJS, Hou K, Zhu MF. A simple inorganic hybrids strategy for graphene fibers fabrication with excellent electrochemical performance. J Power Sources 2020;450:227637.
Yang K, Cheng HN, Wang B, Tan YS, Ye T, Yang YQ, Wang CX. Highly durable and stretchable Ti3C2Tx/PPy-fabric-based strain sensor for human-motion detection. Adv Mater Technol 2022;7:2100675.
Maleki-Ghaleh H, Hossein SM, Fallah A, Zarrabi A, Afghah F, Koc B, Dalir AE, Omidi Y, Barar J, Akbari-Fakhrabadi A, Beygi-Khosrowshahi Y, Adibkia K. Effect of zinc-doped hydroxyapatite/graphene nanocomposite on the physicochemical properties and osteogenesis differentiation of 3D-printed polycaprolactone scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Chem Eng J 2021;426:131321.
Cheng DS, Bai X, Pan JJ, Ran JH, Wu JH, Bi SG, Cai GM, Wang X. Immobilizing reduced graphene oxide on polydopamine-templated PET fabrics for UV protection, electrical conduction and application as wearable sensors. Mater Chem Phys 2020;241:122371.
Asadi MM, Bashir T, Persson NK. The role and importance of surface modification of polyester fabrics by chitosan and hexadecylpyridinium chloride for the electrical and electro-thermal performance of graphene-modified smart textiles. New J Chem 2019;43:6643.
Chen JY, Yuan LH, Shi C, Wu CQ, Long ZW, Qiao H, Wang KL, Fan QH. Nature-inspired hierarchical protrusion structure construction for washable and wear-resistant superhydrophobic textiles with self-cleaning ability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:18142.
Xu LL, Liu ZK, Chen X, Sun RJ, Hu ZR, Zheng ZJ, Ye TT, Li Y. Deformation-resilient embroidered near field communication antenna and energy harvesters for wearable applications. Adv Intell Syst 2019;1:1900056.
Xu LL, Liu ZK, Zhai H, Chen X, Sun RJ, Lyu S, Fan YY, Yi YPE, Chen ZD, Jin L, Zhang J, Li Y, Ye TT. Moisture-resilient graphene-dyed wool fabric for strain sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020;12:13265.
Kan CW, Au CH. Effect of biopolishing and UV absorber treatment on the UV protection properties of cotton knitted fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 2014;101:451.
Subbiah DK, Mani GK, Babu KJ, Das A, Balaguru RJB. Nanostructured ZnO on cotton fabrics—a novel flexible gas sensor & UV filter. J Clean Prod 2018;194:372.
Emam HE, Abdelhameed M. Anti-UV radiation textiles designed by embracing with nano-MIL (Ti, In)-metal organic framework. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017;9:28034.
Chiolerio A, Quadrelli MB. Smart fluid systems: the advent of autonomous liquid robotics. Adv Sci 2017;4:1700036.
Vasios N, Gross AJ, Soifer S, Overvelde J, Bertoldi K. Harnessing ciscous flow to simplify the actuation of fluidic soft robots. Soft Robot 2020;7:1.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Innovation Team and Talents Cultivation Program of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. Z YYCXTD-D-202206), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (No. 20212BAB214016), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP52007A), the International Science and Technology Center (No. BZ2018032), the Jiangsu Province Advanced Textile Engineering Technology Centre Funding Project (XJFZ/2021/4) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51603090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 6858 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 6790 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 7754 KB)
Supplementary file4 (AVI 5614 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 11508 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, D., Liao, S., Chu, Y. et al. Highly Durable and Fast Response Fabric Strain Sensor for Movement Monitoring Under Extreme Conditions. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 223–234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00211-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00211-1