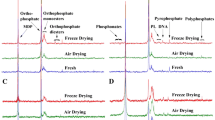
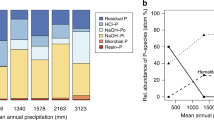
Abstract
The most commonly used differentiation of soil phosphorus (P) is between inorganic and organic forms, despite the fact that this is only the beginning of soil P speciation. Forms of inorganic and organic soil P include a large range of specific P compounds, and spectroscopic techniques can offer the best potential for determining the speciation of soil organic P. The focus of this chapter is to summarise the relative merits of three spectroscopic techniques: solution and solid state 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES). We aim to provide current and potential end-users of these techniques the ability to compare these methods on the basis of four criteria: sample preparation, sensitivity, resolution and quantitation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA (1990) 31P-NMR identification of phosphorus compounds in neutral extracts of Mountain Ash (Eucalyptus regnans F. Muell.) soils. Soil Biol Biochem 22:419–421
Adams MA, Byrne LT (1989) 31P-NMR analysis of phosphorus compounds in extracts of surface soils from selected karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor F. Muell.) forests. Soil Biol Biochem 21:523–528
Ajiboye B, Akinremi OO, Hu Y, Flaten DN (2007a) Phosphorus speciation of sequential extracts of organic amendments using nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopies. J Environ Qual 36:1563–1576
Ajiboye B, Akinremi OO, Jurgensen A (2007b) Experimental validation of quantitative XANES analysis for phosphorus speciation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1288–1291
Ajiboye B, Akinremi OO, Hu Y, Jurgensen A (2008) XANES speciation of phosphorus in organically amended and fertilized Vertisol and Mollisol. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:1256–1262
Al Deen TS, Hibbert DB, Hook JM, Wells RJ (2002) Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry – II. Purity of phosphorus-based agrochemicals glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)-glycine) and profenofos (O-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl) O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate) measured by 1H and 31P QNMR spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 474:125–135
Anderson G (1967) Nucleic acids, derivatives, and organic phosphates. In: McLaren AD, Peterson GH (eds) Soil biochemistry. Edward Arnold, London, pp 67–90
Anderson G (1980) Assessing organic phosphorus in soils. In: Khasawneh FE, Sample EC, Kamprath EJ (eds) Role of phosphorus in agriculture. ASA, Madison, pp 411–428
Baer E, Stancer HC, Korman IA (1953) Migration during hydrolysis of esters of glycerophosphoric acid. III. Cephalin and glycerylphosphorylethanolamine. J Biol Chem 200:251–255
Beauchemin S, Hesterberg D, Beauchemin M (2002) Principle component analysis approach for modeling sulfur K-XANES spectra of humic acids. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:83–91
Beauchemin S, Hesterberg D, Chou J, Beauchemin M, Simard RR, Sayers DE (2003) Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using X-ray near-edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. J Environ Qual 32:1809–1819
Bedrock CN, Cheshire MV, Chudek JA, Goodman BA, Shand CA (1994) Use of 31P-NMR to study the forms of phosphorus in peat soils. Sci Total Environ 152:1–8
Benitez-Nelson CR, O’Neill L, Kolowith LC, Pellechia P, Thunell R (2004) Phosphonates and particulate organic phosphorus cycling in an anoxic marine basin. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1593–1604
Berg AS, Joern BC (2006) Sorption dynamics of organic and inorganic phosphorus compounds in soil. J Environ Qual 35:1855–1862
Borie F, Rubio R (2003) Total and organic phosphorus in Chilean volcanic soils. Gayana Bot 60:69–78
Borie F, Zunino H, Martãnez L (1989) Macromolecule-P associations and inositol phosphates in some Chilean volcanic soils of temperate regions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 20:1881–1894
Bowman RA, Moir JO (1993) Basic EDTA as an extractant for soil organic phosphorus. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1516–1518
Brandes JA, Ingall E, Paterson D (2007) Characterization of minerals and organic phosphorus species in marine sediments using soft X-ray fluorescence spectromicroscopy. Mar Chem 103:250–265
Briceño M, Escudey M, Galindo G, Borchardt D, Chang AC (2006) Comparison of extraction procedures used in determination of phosphorus species by 31P-NMR in Chilean volcanic soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 37:1553–1569
Bünemann EK, Smernik RJ, Marschner P, McNeill AM (2008) Microbial synthesis of organic and condensed forms of phosphorus in acid and calcareous soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:932–946
Cade-Menun B (2005a) Using phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to characterise organic phosphorus in environmental samples. In: Turner BL, Frossard E, Baldwin DS (eds) Organic phosphorus in the environment. CABI, Wallingford, pp 21–44
Cade-Menun BJ (2005b) Characterizing phosphorus in environmental and agricultural samples by P-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Talanta 66:359–371
Cade-Menun BJ, Preston CM (1996) A comparison of soil extraction procedures for 31P NMR spectroscopy. Soil Sci 161:770–785
Cade-Menun BJ, Liu CW, Nunlist R, McColl JG (2002) Soil and litter phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: extractants, metals, and phosphorus relaxation times. J Environ Qual 31:457–465
Changani KK, Ala-Korpela M, Fuller BJ, Mierisova S, Bryant DJ, Taylor-Robinson SD, Davidson BR, Bell JD (1999) Incorporation of metabolite prior knowledge for data analysis: biochemical implications of dynamic 31P NMR ex vivo pig liver studies. NMR Biomed 12:197–204
Condron LM, Frossard E, Newman RH, Tekely P, Morel J-L (1997) Use of 31P NMR in the study of soils and the environment. In: Nanny MA, Minear RA, Leenheer JA (eds) Nuclear magnetic resonance in environmental chemistry. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 247–271
Condron LM, Turner BL, Cade-Menun BJ (2005) Chemistry and dynamics of soil organic phosphorus. In: Sims JT, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment. ASA, CSSA and SSSA, Madison, pp 87–122
Conte P, Šmejkalová D, Piccolo A, Spaccini R (2008) Evaluation of the factors affecting direct polarization solid state 31P-NMR spectroscopy of bulk soils. Eur J Soil Sci 59:584–591
Corbett RJT (1993) How to perform automated curve fitting to in vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopic data. Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 1:65–76
Costello AJR, Glonek T, Myers TC (1976) 31P nuclear magnetic resonance-pH titrations of myo-inositol hexaphosphate. Carbohydr Res 46:159–171
Crouse DA, Sierzputowska-Gracz H, Mikkelsen RL (2000) Optimization of sample pH and temperature from phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of poultry manure extracts. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:229–240
Dai K, David MB, Vance GF, Krzyszowska AJ (1996) Characterization of phosphorus in a spruce-fir spodosol by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1943–1950
Dalal RC (1977) Soil organic phosphorus. Adv Agron 29:83–117
Derome AE (1987) Modern NMR techniques for chemistry research. Pergamon, Singapore
Doolette AL, Smernik RJ, Dougherty WJ (2009) Spiking improved solution phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance identification of soil phosphorus compounds. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:919–927
Dougherty WJ, Smernik RJ, Chittleborough DJ (2005) Application of spin counting to the solid-state 31P NMR analysis of pasture soils with varying phosphorus content. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:1–13
Dougherty WJ, Smernik RJ, Bünemann EK, Chittleborough DJ (2007) On the use of HF pre-treatment of soils for 31P NMR analyses. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1111–1118
Escudey M, Galindo G, Forster JE, Briceño M, Diaz P, Chang A (2001) Chemical forms of phosphorus of volcanic ash-derived soils in Chile. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 32:601–616
Folch J (1942) The nature of the glycerophosphoric acid present in phosphatides. J Biol Chem 146:31–33
Frossard E, Tekely P, Grimal JY (1994) Characterization of phosphate species in urban sewage sludges by high-resolution solid-state 31P NMR. Eur J Soil Sci 45:403–408
Frossard E, Skrabal P, Sinaj S, Bangerter F, Traore O (2002) Forms and exchangeability of inorganic phosphate in composted solid organic wastes. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 62:103–113
Fyfe CA (1983) Solid state NMR for chemists. CFC, Guelph
Guggenberger G, Christensen BT, Rubæk G, Zech W (1996) Land-use and fertilization effects on P forms in two European soils: resin extraction and 31P-NMR analysis. Eur J Soil Sci 47:605–614
Gungor K, Jurgensen A, Karthikeyan KG (2007) Determination of phosphorus speciation in dairy manure using XRD and XANES spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 36:1856–1863
Hawkes GE, Powlson DS, Randall EW, Tate KR (1984) A P-31 nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the phosphorus species in alkali extracts of soils from long-term field experiments. J Soil Sci 35:35–45
He Z, Ohno T, Cade-Menun BJ, Erich MS, Honeycutt CW (2006) Spectral and chemical characterization of phosphates associated with humic substances. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1741–1751
He Z, Cade-Menun B, Toor G, Fortuna A, Honeycutt C, Sims J (2007a) Comparison of phosphorus forms in wet and dried animal manures by solution phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and enzymatic hydrolysis. J Environ Qual 36:1086–1095
He Z, Honeycutt C, Xing B, McDowell R, Pellechia P, Zhang T (2007b) Solid-state Fourier transform infrared and P-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectral features of phosphate compounds. Soil Sci 172:501–515
He Z, Honeycutt CW, Zhang T, Pellechia PJ, Caliebe WA (2007c) Distinction of metal species of phytate by solid-state spectroscopic techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:940–943
He Z, Honeycutt CW, Griffin TS, Cade-Menun BJ, Pellechia PJ, Dou Z (2009) Phosphorus forms in conventional and organic dairy manure identified by solution and solid state 31P NMR spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 38:1909–1918
Hesterberg D, Zhou W, Hutchinson KJ, Beauchemin S, Sayers DE (1999) XAFS study of adsorbed and mineral forms of phosphate. J Synchrotron Radiat 6:636–638
Hinedi ZR, Chang AC (1989) Solubility and phosphorus-31 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance of phosphorus in sludge-amended soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1057–1061
Hunger S, Cho H, Sims JT, Sparks DL (2004) Direct speciation of phosphorus in alum-amended poultry litter: solid-state 31P NMR investigation. Environ Sci Technol 38:674–681
Khare N, Hesterberg D, Beauchemin S, Wang S-L (2004) XANES determination of adsorbed phosphate distribution between ferrihydrite and boehmite in mixtures. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:460–469
Koopmans GF, Chardon WJ, McDowell RW (2007) Phosphorus movement and speciation in a sandy soil profile after long-term animal manure applications. J Environ Qual 36:305–315
Kruse J, Leinweber P (2008) Phosphorus in sequentially extracted fen peat soils: a K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy study. J Plant Nutr 171:613–620
Kruse J, Leinweber P, Eckhardt K-U, Godlinski F, Hu Y, Zuin L (2009) Phosphorus L2, 3-edge XANES: overview of reference compounds. J Synchrotron Radiat 16:247–259
Lombi E, Susini J (2009) Synchrotron-based techniques for plant and soil science: opportunities challenges and future perspectives. Plant Soil 320:1–35
Lombi E, Scheckel KG, Armstrong RD, Forrester S, Cutler JN, Paterson D (2006) Speciation and distribution of phosphorus in a fertilized soil: a synchrotron-based investigation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:2038–2048
Makarov MI, Malysheva TI, Haumaier L, Alt HG, Zech W (1997) The forms of phosphorus in humic and fulvic acids of a toposequence of alpine soils in the northern Caucasus. Geoderma 80:61–73
Makarov MI, Haumaier L, Zech W (2002a) The nature and origins of diester phosphates in soils: a 31P-NMR study. Biol Fertil Soils 35:136–146
Makarov MI, Haumaier L, Zech W (2002b) Nature of soil organic phosphorus: an assessment of peak assignments in the diester region of 31P NMR spectra. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1467–1477
Maniara G, Rajamoorthi K, Rajan S, Stockton GW (1998) Method performance and validation for quantitative analysis by 1H and 31P NMR spectroscopy. Applications to analytical standards and agricultural chemicals. Anal Chem 70:4921–4928
McBeath TM, Smernik RJ, Lombi E, McLaughlin MJ (2006) Hydrolysis of pyrophosphate in a highly calcareous soil: a solid-state phosphorus-31 NMR study. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:856–862
McDowell RW, Stewart I (2005a) Peak assignments for phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in pH range 5–13 and their application in environmental samples. Chem Ecol 21:211–226
McDowell RW, Stewart I (2005b) An improved technique for the determination of organic phosphorus in sediments and soils by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem Ecol 21:11–22
McDowell RW, Stewart I (2006) The phosphorus composition of contrasting soils in pastoral, native and forest management in Otago, New Zealand: sequential extraction and 31P NMR. Geoderma 130:176–189
McDowell RW, Brookes PC, Mahieu N, Poulton PR, Johnston AE, Sharpley AN (2002a) The effect of soil acidity on potentially mobile phosphorus in a grassland soil. J Agric Sci 139:27–36
McDowell RW, Condron LM, Mahieu N, Brookes PC, Poulton PR, Sharpley AN (2002b) Analysis of potentially mobile phosphorus in arable soils using solid state nuclear magnetic resonance. J Environ Qual 31:450–456
McDowell RW, Condron LM, Mahieu N (2003a) Analysis of phosphorus in sequentially extracted grassland soils using solid state NMR. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 34:1623–1636
McDowell RW, Mahieu N, Brookes PC, Poulton PR (2003b) Mechanisms of phosphorus solubilisation in a limed soil as a function of pH. Chemosphere 51:685–692
McDowell RW, Stewart I, Cade-Menun BJ (2006) An examination of spin-lattice relaxation times for analysis of soil and manure extracts by liquid state phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 35:293–302
McDowell RW, Cade-Menun B, Stewart I (2007) Organic phosphorus speciation and pedogenesis: analysis by solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur J Soil Sci 58:1348–1357
Metz K, Dunphy L (1996) Absolute quantitation of tissue phospholipids using 31P NMR spectroscopy. J Lipid Res 37:2251–2265
Murphy PNC, Bell A, Turner BL (2009) Phosphorus speciation in temperate basaltic grassland soils by solution P-31 NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Soil Sci 60:638–651
Neal C, Neal M, Wickham H (2000) Phosphate measurement in natural waters: two examples of analytical problems associated with silica interference using phosphomolybdic acid methodologies. Sci Total Environ 251–252:511–522
Newman RH, Condron LM (1995) Separating subspectra from cross-polarization magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectra by proton spin relaxation editing. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 4:259–266
Newman RH, Tate KR (1980) Soil phosphorus characterization by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 11:835–842
Peak D, Sims JT, Sparks DL (2002) Solid-state speciation of natural and alum-amended poultry litter using XANES spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36:4253–4261
Preston CM (1996) Applications of NMR to soil organic matter analysis: history and prospects. Soil Sci 161:144–166
Puppato A, DuPré DB, Stolowich N, Yappert MC (2007) Effect of temperature and pH on 31P nuclear magnetic resonances of phospholipids in cholate micelles. Chem Phys Lipids 150:176–185
Šárka M, Mika A-K (2001) MR spectroscopy quantitation: a review of frequency domain methods. NMR Biomed 14:247–259
Sato S, Solomon D, Hyland C, Ketterings QM, Lehmann J (2005) Phosphorus speciation in manure and manure-amended soils using XANES spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 39:7485–7491
Shand C, Cheshire M, Bedrock C, Chapman P, Fraser A, Chudek J (1999) Solid-phase 31P NMR spectra of peat and mineral soils, humic acids and soil solution components: influence of iron and manganese. Plant Soil 214:153–163
Shober AL, Hesterberg DL, Sims JT, Gardner S (2006) Characterization of phosphorus species in biosolids and manures using XANES spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 35:1983–1993
Smernik RJ, Baldock JA (2005) Does solid-state 15N NMR spectroscopy detect all soil organic nitrogen? Biogeochemistry 75:507–528
Smernik RJ, Dougherty WJ (2007) Identification of phytate in phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra – the need for spiking. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1045–1050
Smernik RJ, Oades JM (2000a) The use of spin counting for determining quantitation in solid state 13C NMR spectra of natural organic matter 1. Model systems and the effects of paramagnetic impurities. Geoderma 96:101–129
Smernik RJ, Oades JM (2000b) The use of spin counting for determining quantition in solid state 13C NMR spectra of natural organic matter 2. HF-treated soil fractions. Geoderma 96:159–171
Tate KR, Newman RH (1982) Phosphorus fractions of a climosequence of soils in New Zealand tussock grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 14:191–196
Tiessen H, Moir JO (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 75–86
Toor GS, Peak JD, Sims JT (2005) Phosphorus speciation in broiler litter and turkey manure produced from modified diets. J Environ Qual 34:687–697
Turner B (2008) Soil organic phosphorus in tropical forests: an assessment of the NaOH-EDTA extraction procedure for quantitative analysis by solution 31P NMR. Eur J Soil Sci 59:453–466
Turner GL, Smith KA, Kirkpatrick RJ, Oldfieldt E (1986) Structure and cation effects on phosphorus-31 NMR chemical shifts and chemical-shift anisotropies of orthophosphates. J Magn Reson 70:408–415
Turner BL, Mahieu N, Condron LM (2003a) Quantification of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in alkaline soil extracts by solution 31P NMR spectroscopy and spectral deconvolution. Soil Sci 168:469–478
Turner BL, Mahieu N, Condron LM (2003b) Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectral assignments of phosphorus compounds in soil NaOH-EDTA extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:497–510
Turner BL, Mahieu N, Condron LM (2003c) The phosphorus composition of temperate pasture soils determined by NaOH-EDTA extraction and solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. Org Geochem 34:1199–1210
Turner BL, Cade-Menun BJ, Condron LM, Newman S (2005) Extraction of soil organic phosphorus. Talanta 66:294–306
Turner BL, Newman S, Reddy KR (2006) Overestimation of organic phosphorus in wetland soils by alkaline extraction and molybdate colorimetry. Environ Sci Technol 40:3349–3354
Veeman WS (1997) Nuclear magnetic resonance, a simple introduction to the principles and applications. Geoderma 80:225–242
Williams RJP, Giles RGF, Posner AM (1981) Solid state phosphorus N.M.R. spectroscopy of minerals and soils. J Chem Soc Chem Comm:1051–1052
Yoder CH, Schaeffer CD (1987) Introduction to multinuclear NMR. Benjamin Cummings, Menlo Park
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Doolette, A.L., Smernik, R.J. (2011). Soil Organic Phosphorus Speciation Using Spectroscopic Techniques. In: Bünemann, E., Oberson, A., Frossard, E. (eds) Phosphorus in Action. Soil Biology, vol 26. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15271-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15271-9_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15270-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15271-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)