Abstract
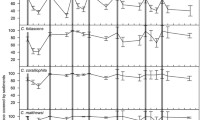
The biology of Corbicula fluminea, the Asiatic clam, in the Vermilion River, Louisiana, as affected by sediment, dissolved oxygen (DO) levels, and sewage treatment plant (STP) effluents was investigated. A point source of high DO water to the Vermilion River established a gradient of DO that decreased as the river moved towards the Gulf of Mexico. Lowering DO levels were exacerbated by municipal sewage treatment plant discharges in the 20 km reach studied. Low dissolved oxygen was associated with reduced Corbicula density in the river and 30-day in-stream growth studies (weight and length) demonstrated that low DO inhibited growth. Generally, if DO was < 1.0 mg l−1 in sediment pore water and/or < 3.0 mg l−1 at the sediment-water interface, growth was significantly impaired (p < 0.05). Corbicula experienced substantial mortality near the STP discharges (up to 70% in 30 days) and laboratory toxicity tests with Ceriodaphnia dubia, a sensitive cladoceran, also strongly suggested discharges were chronically toxic at 6.25–25.0% effluent. Respiration experiments along with environmental measurements of DO, temperature, and STP discharge chemistry support a hypothesis that clam populations are adversely affected by the suite of environmental conditions present in the Vermilion River. Further, growth studies were consistent with observed population densities in situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belanger, S. E., J. L. Farris, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1985. Sediment preference of the freshwater Asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea. Nautilus 99: 66–73.
Belanger, S. E., J. L. Farris, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1986a. Growth of Asiatic clams, Corbicula sp., during and after zinc exposure in field located and laboratory artificial streams. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 15: 427–434.
Belanger, S. E., D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1986b. The uptake of chrysotile asbestos fibers alters growth and reproduction of Asiatic clams. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 43: 43–52.
Belanger, S. E., J. L. Farris & D. S. Cherry, 1987. Comparison of Ceriodaphnia 7-day chronic tests with the 30-day Corbicula functional test at USEPA quality criteria levels. Published Abstract, p. 249. The Eighth Meeting of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, November 1987, Pensacola, Florida.
Belanger, S. E., J. L. Farris & D. S. Cherry, 1989. Effect of diet, water hardness and population source on acute and chronic toxicity of copper to Ceriodaphnia dubia. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 18: 601–611.
Belanger, S. E., 1989. Acute and chronic toxicity relationships for five cladocerans. Published Abstract, p. 244. The Tenth Meeting of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, October 1989, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Belanger, S. E., J. L. Farris, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1990. Validation of Corbicula growth reductions induced by copper in artificial stream and natural rivers. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 47: 904–914.
Belanger, S. E. & D. S. Cherry, 1990. Interacting effects of pH acclimation, pH, and heavy metals on acute and chronic toxicity to Ceriodaphnia dubia. J. Crust. Biol. 10: 225–235.
Belanger, S. E., D. S. Cherry, J. L. Farris, K. G. Sappington & J. Cairns, Jr., In review. Biocidal control of Asiatic clams by monochloramine, ammonia, chlorine, bromine and copper. J. am. Wat. Wks. Ass.
Britton, J. C. & B. Morton, 1982. A Dissection Guide, Field and Laboratory Manual for the Introduced Bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Malacol. Rev. Suppl. 3. p. 81.
Byrne, R. A., R. F. McMahon & T. Dodd, 1988. Temperature and relative humidity effects on aerial exposure tolerance in the freshwater bivalve, Corbicula fluminea. Biol. Bull. 175: 253–260.
Cairns, J., Jr. & W. H. van der Schalie, 1980. Biological monitoring, Part I: Early warning systems. Wat. Res. 14: 1179–1196.
Cameron, G. N., J. M. Symons, S. R. Spencer & J. Y. Ma, 1989a. Minimizing THM formation during control of the Asiatic clam: a comparison of biocides. J. am. Wat. Ws. Ass. 81: 53–61.
Cameron, G. N., J. M. Symons, D. Bushek & R. Kulkarni, 1989b. Effect of temperature and pH on the toxicity of monochloramine to the Asiatic clam. J. am. Wat. Ws. Ass. 81: 62–71.
Cherry, D. S., R. L. Roy, R. A. Leichleitner, P. A. Dunhardt, G. T. Peters & J. Cairns, Jr., 1986. Corbicula fouling and control measures at the Celco Plant, Virginia. Am. Malacol. Bull. Spec. Ed. 2: 69–82.
Cherry, D. S., J. L. Farris & S. E. Belanger, 1989. Use of ecological, biochemical and toxicological procedures for identifying and quantifying the extent of stressful constituents in power plant effluent-Final Report. American Electric Company, Columbus, Ohio, 389 pp.
Counts, C. L. III, 1986. The zoogeography and history of the invasion of the United States by Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae). Am. Malacol. Bull., Spec. Ed. 2: 7–40.
Doherty, F. G., D. S. Cherry, J. L. Farris & J. Cairns, Jr., 1986. Control of the freshwater fouling bivalve Corbicula fluminea by halogenation. Arch. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 15: 535–542.
Doherty, F. G., D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1987. Valve closure responses of the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea exposed to cadmium and zinc. Hydrobiol. 153: 15–167.
Doherty, F. G. & D. S. Cherry, 1988. Tolerance of the Asiatic clam Corbicula spp. to lethal levels of toxic stressors — a review. Envir. Pollut. 51: 269–313.
Doherty, F. G., 1990. The Asiatic clam, Corbicula spp., as a biological monitor in freshwater environments. Envir. Monit. Assess. 15: 143–181.
Dudgeon, D., 1980. A comparative study of the Corbiculidae of southern China. p. 37–60, In, Morton, B. (Ed.). The Malacofauna of Hong Kong and southern China, Hong Kong University Press. Hong Kong.
Farris, J. L., J. H. VanHassel, S. E. Belanger, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1988. Validation of cellulolytic activity versus macroinvertebrate colonization as biomonitoring tools for power plant effluent. Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 7: 701–713.
Farris, J. L., S. E. Belanger, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, Jr., 1989. Cellulolytic activity as a novel approach to assess long-term zinc stress to Corbicula. Wat. Res. 23: 1275–1283.
Finney, D. J., 1971. Statistical Methods in Biological Assay. Third Edition. Cambridge University Press, London, England. 333 pp.
Foe, C. & A. Knight, 1987. Assessment of the biological impact of point source discharges employing Asiatic clams. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 16: 39–51.
Habel, M. L., 1970. Oxygen consumption, temperature tolerance and filtration rate of the introduced Asiatic clam, Corbicula manilensis, from the Tennessee River. M.S. Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama.
Hayashi, Y. S., O. Matsushima, H. Katayama & K. Yamada, 1986. Activities of the three ammonia-forming enzymes in the tissues if the brackish water bivalve, Corbicula japonica. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 83: 721–724.
Heath, A. G., 1987. Water Pollution and Fish Physiology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Herreid, C. F., 1980. Review: hypoxia in invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 67A: 311–320.
Hollander, M. & D. A. Wolfe, 1973. Nonparametric Statistical Methods. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Mattice, J. S. & L. L. Dye, 1977. Thermal tolerance of the adult Asiatic clam, in, Esch, G. W. and R. W. McFarlane (eds), Thermal Energy II, United States Energy and Development Administration Symposium Series, Washington, D.C. 1976: 130–135.
McLeod, M. J., 1986. Electrophoretic variation in North American Corbicula. Am. Malacol. Bull., Spec. Ed. 2: 125–132.
McMahon, R. F., 1979. Response to temperature and hypoxia in the oxygen consumption of the introduced Asiatic freshwater clam, Corbicula fluminea (Muller). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 63A: 383–388.
McMahon, R. F., 1983. Ecology of the invasive pest bivalve Corbicula. p. 505–562, In Russel-Hunter, W. D. (Ed.). The Mollusca: Ecology, Vol. 6. Academic Press, Inc. New York.
Morgan, E. L., 1989. Freshwater bivalve toxicity testing using automated biomonitoring. Published Abstract. p. 153. The Tenth Meeting of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, October 1989, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Neiheisel, T. W., W. B. Horning, B. M. Austern, D. F. Bishop, S. C. Reed & J. F. Estenik, 1988. Toxicity reduction at municipal wastewater treatment plants. J. Wat. Pollut.Cont. Fed. 60: 57–67.
Pittinger, C. A., V. C. Hand, J. A. Masters & L. F. Davidson, 1988. Interstitial water sampling in ecotoxicological testing: partitioning of a cationic surfactant. In, Adams, W. J., G. A. Chapman, and W. G. Landis (Eds.)., Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment: 10th Volume, ASTM STP 971, pp. 138–148. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA.
Rodgers, J. W., 1986. Alternative guidelines for statistical analysis and interpretation of chronic bioassay data. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Bureau of Water Resources Management, Madison, Wisconsin.
Sappington, K. G., 1987. Toxicological, physiological, and behavioral responses of the Asiatic clam, Corbicula sp., to biocidal and copper perturbations. M.S. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Virginia.
Statistical Analysis System (SAS), 1985. SAS User's Guide: Statistics. Version 5.0 edition. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. 1983. Methods for chemical analyses of water and wastes. Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio. EPA-600/4–79–020.
Weber, C. I., W. H. Peltier, T. J. Norberg-King, W. B. Horning, II, F. A. Kessler, J. R. Menkedick, T. W. Neiheisel, P. A. Lewis, D. J. Klemm, Q. H. Pickering, E. L. Robinson, J. M. Lazorchak, L. J. Wymer, & R. W. Freyberg, 1989. Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater organisms. Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio. EPA/600/4–89/001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belanger, S.E. The effect of dissolved oxygen, sediment, and sewage treatment plant discharges upon growth, survival and density of Asiatic clams. Hydrobiologia 218, 113–126 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006784
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006784