Abstract
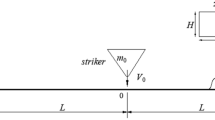
The Charpy impact test is modelled as a mass on a spring which is loaded via a contact stiffness. The strain energy release rate G is evaluated for this model for the case of slow crack growth rate initiation. The solution involves the kinetic energy and is shown to be harmonic in nature. Correction factors are then deduced for tests in which G c is to be evaluated via load, energy and displacement and these are applied to a wide range of experimental data. It is concluded that the displacement measurement method gives the least dynamic error and that loads are, by a large margin, the worst.
Résumé
On modélise l'essai de résilience Charpy par une masse sous un ressort, chargée par contact avec un élément d'une certaine raideur. Ce modèle conduit à l'évaluation du taux de relaxation de l'énergie de déformation G dans le cas d'un amorçage à faible vitesse de propagation de fissure. La solution met en oeuvre l'énergie cinétique; on montre qu'elle a une forme harmonique par essence. On déduit les coefficients correctifs pour les essais où Gc est évalué à partir de la charge, de l'énergie et des déplacements, et on les applique à une large gamme de données expérimentales. On conclut que la méthode de mesure des déplacements donne la plus faible erreur dynamique, et que celle basée sur les charges est dans une large mesure la moins précise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Kalthoff, W. Bohme, S. Winkler and W. Klemm, in Proceedings 5th International Conference on Fracture, Cannes, 1 Pergamon (1985) 363–373.
J.G. Williams, Fracture Mechanics of Polymers, Ellis Horwood (1984) Chapter 8.
D. Ireland, in Proceedings, International Conference on Dynamic Fracture Toughness, Welding Institute, London (1976).
J.G. Williams International Journal of Fracture 33 (1987), in publication.
W. Bohme and J.F. Kalthoff, Journal Physique, Collogue C5, supplement No. 8, 46 (1985).
J.G. Williams and M.W. Birch, in Proceedings, 4th International Conference on Fracture, Waterloo, 1 Pergamon (1977) 501–528.
J.G. Williams and J.M. Hodgkinson, Proceedings Royal Society London A375 (1981) 231–248.
J.M. Hodgkinson and J.G. Williams, Proceedings ASTM Conference on Impact Testing of Polymers, Houston (1985) STP 936.
J.G. Williams and G.C. Adams, paper presented at Plastics and Rubber Institute Conference on Impact Testing, Guildford (1985).
J.M. Greig and Skiplorne, paper presented at Plastics and Rubber Institute Conference on Impact Testing, Guildford (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, J.G., Adams, G.C. The analysis of instrumented impact tests using a mass-spring model. Int J Fract 33, 209–222 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00013171
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00013171