Abstract
The beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) is the dominant tree in Middle Europe under many different ecological conditions. But like other tree species, it is suffering in the last ten years increasingly by air pollutants including heavy metals which have been deposited and accumulated for decades in many forest soils. Increasingly mobilized by acidification processes, these metals may have toxic effects on trees.
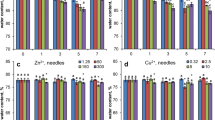
In autecological studies (dose-response-experiments) effects of root-applied Pb and Cd on various growth parameters, on uptake of mineral nutrients and on transpiration of young beech trees were evaluated, and ‘critical’ concentrations (threshold levels) could be established. Significant leaf area reduction was found with 6 ppm Pb (0.3 ppm Cd) in the leaves (DW), but biomass reduction only with 18 ppm Pb (3.6 ppm Cd). Root elongation rates of seedlings were significantly reduced with 44 ppm plant-available Pb in the soil by about 30%, but only with 24 ppm Pb when combined with 2 ppm Cd, exhibiting synergistic effects. After treatments with 20 ppm Pb and 1 ppm Cd in sand culture, a considerable decrease in the contents of K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, and Zn in roots and leaves of saplings was coincident with high (roots) and moderate (leaves) accumulation of Pb and Cd. A 20% reduction of transpiration rates was measured in ten-year-old beech trees after three months of exposure to a forest soil containing 2.5 ppm plant-available Cd.
The data indicate that present-day concentrations mainly of Pb, but not yet of Cd, in acidified European forest soils are sufficiently high to affect germination, growth and mineral nutrition of natural rejuvenation of beech.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrend, R., Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1989. Effect of cadmium on transpiration of young beech trees (Fagus sylvatica L.). Proc. 14th Int. JUFRO Meeting on Air pollution and forest decline, ed. J. B., Bucher, Birmensdorf, (Switzerland) pp. 381–383.
Bertels, C., Rüther, P., Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1989. Die Entwicklung des Wurzelsystems von Buchenkeimlingen bei Cadmium- und kombinierter Blei/Cadmiumbelastung. Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. für Ökologie 18: 367–371.
Breckle, S.-W. 1991. Plant roots, growth under stress: heavy metals. in Waisel, Y., Kafkafi, Y. & Eshel, A.: Plant Roots: The hidden Half. Kluwer Publ. pp. 351–373.
Breckle, S.-W., Hagemeyer, J., Heppel, T. & Lohrmann, D. 1990. Untersuchung des Einflusses von Schwermetallen auf die Kambiumaktivität mitteleuropäischer Waldbäume (Buche, Fichte). Forschungsberichte MURL NRW Düsseldorf zum Forschungsprogramm Luftverunreinigungen und Waldschäden 18: 11.1–11.14.
Breckle, S.-W. & Kahle, H. (Hrsg.) 1985. Schwermetalle und saure Depositionen. Bielefelder Ökologische Beiträge, Band 1: 191 pp.
Breckle, S.-W. & Kahle, H. (Hrsg.) 1989. Komplexschäden an Buchen-Ursachenforschung zum Baumsterben. Bielefelder Ökologische Beiträge, Band 5: 239 pp.
Bredemeier, M., Matzner, E. & Ulrich, B. 1990. Internal and external proton load to forest soils in Northern Germany. J. Environmental Quality 19 (3): 469–477.
BMELF: Bundesminist. f. Ernährung, Landwirtschaft u. Forsten (1991). Bericht über den Zustand des Waldes 1991. Bonn, 36 pp.
Brümmer, G. & Herms, U. 1985. Einflußgrößen der Schwermetall-Löslichkeit, -Bindung und-Verfügbarkeit in Böden. Bielefelder Ökologische Beiträge 1: 117–139.
Buschmann, B., Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1991. Zum Einfluß von Cadmium auf Mineralstoffhaushalt und Vegetationszeit von Buchenjungwuchs auf verschiedenen Substraten. Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. für Ökologie (Osnabrück): 19 (3): 209–213.
Glavac, V. 1987. Ist die Abnahme der Ca-, Mg-, K- und Zn-Gehalte in Blättern immissionsgeschädigter Altbuchen die Folge vergrößerter Blattauswaschung oder verminderter Mineralstoffversorgung? Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. für Ökologie (Giessen) 16: 253–266.
Hagemeyer, J. & Breckle, S.-W. 1991. Abschlußbericht des Forschungsvorhabens Untersuchung des Einflusses von Schwermetallen (insbes. Cd,Zn) auf die Kambiumaktivität mitteleuropäischer Waldbäume(Buche,Fichte). Forschungs-berichte MURL NRW Düsseldorf zum Forschungsprogramm Lufverunreinigungen und Waldschäden NN: 142 pp.
Hagemeyer, J., Kahle, H., Breckle, S.-W. & Waisel, Y. 1986. Cadmium in Fagus sylvatica L. trees and seedlings: Leaching, uptake and interconnection with transpiration. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 29: 347–359.
Jentschke, G., Fritz, E. & Godbold, D. L. 1991. Distribution of lead in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal Norway spruce seedlings. Physiologia Plant. 81: 417–422.
Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1986. Blei- und Cadmiumbelastung in Buchenwäldern. Verhandl. d. Ges. für Ökologie 14: 265–267.
Kahle, H. 1988. Wirkungen von Blei und Cadmium auf Wachstum und Mineralstoffhaushalt von Jungbuchen (Fagus sylvatica L.) in Sandkultur. Diss. Bot. 127, 226 pp.
Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1989. Single and combined effects of lead and cadmium on young beech trees (Fagus sylvatica L.). Proc. 14th Int. JUFRO Meeting on Air pollution and forest decline, ed. J. B., Bucher, Birmensdorf (Switzerland) pp. 442–444.
Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1990. Abschlußbericht des Forschungsvorhabens Untersuchungen zum Mineralstoff-und Wasserhaushalt sowie zur Regenerationsfähigkeit schwermetallbelasteter Jungbuchen. Forschungsberichte MURL NRW Düsseldorf zum Forschungsprogramm Luftverunreinigungen und Waldschäden 12: 84 pp.
König, N., Baccini, P. & Ulrich, B. 1986. Der Einfluß der natürlichen organischen Substanzen auf die Metallverteilung zwischen Boden und Bodenlösung in einem sauren Waldboden. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. BodenK. 149: 68–82.
Lamersdorf, N. 1989. The behaviour of Pb and Cd in the intensive rooting zone of acid spruce forest soils. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry 18: 239–247.
Mayer, R. 1981. Natürliche und anthropogene Komponenten des Schwermetallhaushalts von Waldökosystemen. Göttinger Bodenkundliche Ber. 70: 292 pp.
Neite, H. & Wittig, R. 1989. Blei- und Zinkgehalte von Böden und Pflanzen in Buchenwäldern NRW's. Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. f. Ökologie (Essen) 18: 425–429.
Noack, G. & Breekle, S.-W. 1989. Der Einfluß von Blei auf die Wurzelentwicklung von Buchenkeimlingen im Rhizotron. Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. für Ökologie 17: 563–566.
Rebele, F. 1988. Waldschäden in Mitteleuropa. AFZ 51–53: 1412–1147.
Rehfuess, K. E. 1987. Perceptions on Forest Diseases in Central Europe. Forestry (Oxford) 60: 1–11.
Röder, U. & Breckle, S.-W. 1989. Der Einfluß von Blei und Cadmium auf das Wachstum und den Kationengehalt von Buchenkeimlingen auf Waldböden. Verhandl. d. Gesellsch. für Ökologie 17: 557–562.
Schlote, F.-W. 1989. Blei als Teilursache von Waldschäden. In: Ulrich, B. (ed.): International Congress of Forest Decline Research, Friedrichshafen, Lake Constance (FRG), Poster. vol. 1: 261–262.
Schütt, P. & Cowling, E. B. 1985. Waldsterben, a general decline of forests in central Europe: symptoms, development and possible causes. Plant Disease 69: 548–558.
Ulrich, B. 1986. Die Rolle der Bodenversauerung beim Waldsterben: Langfristige Konsequenzen und forstliche Möglichkeiten. Forstwiss. Centralbl. 105: 421–435.
Ulrich, B., Pirouzpanah, D. & Murach, D. 1984. Beziehungen zwischen Bodenversauerung und Wurzelentwicklung von Fichten mit unterschiedlich starken Schadsymptomen. Forstarchiv 55: 127–134.
Walter, H. & Straka, H. 1970. Arealkunde. Floristischhistorische Geobotanik. 2. Aufl. Fischer/Stgt. 478 pp.
Weisser, F., Kahle, H. & Breckle, S.-W. 1992. Wurzelwachstum der Buche in Wurzelkästen mit Pb-Kontaminierten Bodenhorizonten. (in prep.)
Wittig, R. 1986. Acidification phenomena in beech (Fagus sylvatica) forests of Europe. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 31: 317–323.
Wittig, R. & Neite, H. 1989. Distribution of Pb in the soils of Fagus sylvatica forests in Europe. In: Öztürk, M. A. (ed.): Plants and pollutants in developed and developing countries. Izmir/Turkey: 199–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The data published here are part of a doctoral and of various diploma theses: Mrs. Christiane Bertels, Barbara Buschmann, Martina Hücker, Gritli Noack, Ute Röder, Swantje von Oy and Mr. Rüdiger Ahrend, Peter Rüther and Frank Weisser.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breckle, S.W., Kahle, H. Effects of toxic heavy metals (Cd, Pb) on growth and mineral nutrition of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Vegetatio 101, 43–53 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00031914
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00031914