Abstract
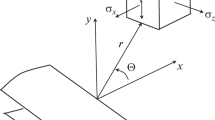
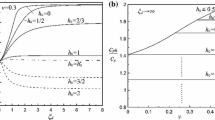
This paper deals with the general problem of crack extension in a combined stress field where a crack can grow in any arbitrary direction with reference to its original position. In a situation, when both of the stress-intensity factors,k 1,k 2 are present along the crack front, the crack may spread in any direction in a plane normal to the crack edge depending on the loading conditions. Preliminary results indicate that the direction of crack growth and fracture toughness for the mixed problem of Mode I and Mode II are governed by the critical value of the strain-energy-density factor,S cr. The basic assumption is that crack initiation occurs when the interior minimum ofS reaches a critical value designatedS cr. The strain-energy-density factorS represents the strength of the elastic energy field in the vicinity of the crack tip which is singular of the order of 1/r where the radial distancer is measured from the crack front. In the special case of Mode I crack extensionS cr is related tok 1c alone asS cr = (κ − 1)k 21 /8μ. In general,S takes the quadratic forma 1 1 k 1 + 2a 1 2 k 1 k 2 +a 2 2 k 2 whose critical value is assumed to be a material constant. The analytical predictions are in good agreement with experimental data on the problem of an inclined crack in plexiglass and aluminum alloy specimens. The result of this investigation provides a convenient procedure for determining the critical crack size that a structure will tolerate under mixed mode conditions for a given applied stress.
Résumé
L'article a trait au problème général de l'extension d'une fissure dans un champ de contraintes combinées de façon telle qu'une fissure peut s'étendre dans toute direction arbitraire par rapport à sa position d'origine. Dans une situation où les deux facteurs d'intensité d'entaillek 1 etk 2 sont présents le long du front de la fissure, celle-ci peut s'étendre dans toute direction située dans un plan normal à ce bord de la fissure, en fonction des conditions de charge.
Des résultats préliminaires indiquent que la direction d'accroissement de la fissure, et la ténacité à la rupture dans un problème mixte où se retrouvent à la fois le Mode I et le Mode II, sont régies par la valeur critiqueS cr du facteur de densité d'énergie de déformation.
L'hypothèse de base est que l'amorçage de la fissure survient lorsqueS passe par une valeur critiqueS cr. Le facteur de densité d'énergie de déformationS représente la force du champ d'énergie élastique au voisinage de l'extrémité de l'entaille, lequel est une fonction singulière de 1/r, oùr représente la distance radiale depuis le front de fissure.
Dans le cas particulier du Mode I d'extension de fissure,S cr ne dépend que dek 1c suivant:
S cr = (κ − 1)k 21 /8μ
En général,S prend la forme quadratique
a 1 1 k 1 + 2a 1 2 k 1 k 2 +a 2 2 k 2
dont la valeur critique est supposée être une constante du matériau.
Les prédictions analytiques sont en bon accord avec les données expérimentales pour le problème de la fissure inclinée dans des éprouvettes de plexiglass et d'alliage d'aluminium.
Le résultat de cette recherche fournit une procédure commode pour la détermination de la dimension critique d'une fissure qu'une structure peut tolérer sous des conditions de modes mixtes d'extension de fissure, en présence d'une contrainte appliquée donnée.
Zusammenfassung
Man behandelt das allgemeine Problem der Rißausdehnung in einem zusammengesetzten Spannungsfeld wo ein Riß sich in irgend eine beliebige Richtung ausdehnen kann bezüglich auf seine Anfangsposition. Im Fall wo beide Spannungsintensitätsfaktorenk 1 andk 2 an der Rißspitze vorhanden sind kann sich der Riß in einer beliebigen Richtung, in einer normal zum Rißrand liegenden Ebene ausdehnen, abhängig von den Belastungsbedingungen. Die vorläufigen Ergebnisse zeigen daß die Richtung der Rißausdehnung und die Bruchzähigkeit für das gemischte Problem des ersten und zweiten Modes durch den kritischen Wert des Faktors der VerformungsenergiedichteS cr regiert werden. Die Grundhypothese ist daß die Rißeinleitung stattfindet wenn das innere Minimum vonS einen kritischen Wert erreicht bezeichnet durchS cr. Der Faktor der Verformungsenergiedichte stellt die Stärke des elastischen Energiefeldes in der Nähe der Rißspitze dar welches eine Besonderheit der Ordnung 1/r hat wo der Radialabstand von der Front des Risses ausgemessen wird. Im Sonderfall des Modes 1 ist die RißausdehnungS cr mitk 1c allein verbunden daS cr = (κ − 1)k 21 /8μ. Im allgemeinen nimmtS die quadratische Forma 1 1 k 1 + 2a 1 2 k 1 k 2 +a 2 2 k 2 an, deren kritischen Wert als eine Unveränderliche des Materials angenommen wird. Die analytische Voraussagungen sind in guter Übereinstimmung mit den Versuchergebnissen des Problems eines schrägen Risses in Proben aus Plexiglas und Aluminiumlegierungen. Die Ergebnisse dieser Untersuchung ergeben ein gutes Verfahren zur Bestimmung der kritischen Rißgröße die ein Bauelement unter gemischten Moden Bedingungen zulassen kann unter einer gegebenen Spannung.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.A. Griffith, The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids,Phil. Trans. Royal Society, Vol. A221 (1921) 163.
A. A. Griffith, The theory of rupture,Proc. 1st Int. Congr. Applied Mech., Delft (1924) 55–63.
J.E. Srawley, M.H. Jones and W.F. Brown, Determination of plane strain fracture toughness,Materials Research Standard, 7 (1967) 262–266.
F. Erdogan and G.C. Sih, On the crack extension in plates under plane loading and transverse shear,J. of Basic Engrg., 85 (1963) 519–527.
B. Cotterell, Notes on the paths and stability of cracks,Int. J. of Fracture Mech., 2 (1966) 526–533.
L.P. Pook, The effect of crack angle on fracture toughness,J. of Engrg. Fracture Mech., 3 (1966) 205–218.
T.T. Wang, T.K. Kwei and H.M. Zupko, Tensile strength of butt-joined epoxy-aluminum plates,Int. J. of Fracture Mech., 6 (1970) 127–137.
G.C. Sih, P.C. Paris and F. Erdogan, Crack-tip stress-intensity factors for plane extension and plate bending ploblems,Int. J. of Fracture Mech., 29 (1962) 306–312.
J.G. Williams and P.D. Ewing, Fracture under complex stress—the angle crack problem,Int. J. of Fracture Mech., 8 (1972) 441–446.
G. C. Sih and M. E. Kipp, Discussion on “Fracture under complex stress—the angle crack problem”,Int. J. of Fracture (in press).
G.R. Irwin,Fracture mechanics, Structural Mechanics, Pergamon Press, London, England (1960) 560–574.
G.C. Sih and H. Liebowitz, Mathematical theories of brittle fracture,Mathematical Fundamental of Fracture, Academic Press, New York (1968) 67–190.
M.L. Williams, On the stress distribution at the base of a stationary crack,J. of Applied Mechanics, 24 (1957) 109–114.
G. C. Sih,Application of the strain-energy-density theory to fundamental problems in fracture mechanics, presented at the 10th Annual Meeting of the Society of Engineering Science, Raleigh, North Carolina, November 1973.
E. Hoek and Z. T. Bieniawski,Fracture propagation mechanics in hard rock, Technical Report—Rock Mech. Div., South African Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (1965).
F. A. McClintock and J. B. Walsh, Friction on Griffith cracks in rocks under pressure,Proceedings of the 4th U.S. National Congress of Applied Mechanics (1962) 1015–1021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sih, G.C. Strain-energy-density factor applied to mixed mode crack problems. Int J Fract 10, 305–321 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035493
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035493