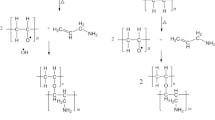
An improved cell compatibility of polymers is determined by interactions with the cell surface, which are influenced by the chemical surface properties of the polymers. Of special interest are methods to change the surface properties by generating new functional groups for a better cell adhesion without affecting the bulk properties of the polymer. The study describes the surface modifications of a new flexible copolymer comprising polyvinylchloride by either wet chemical treatment or plasma treatment. In the first case the immobilization of different diols to the activated surface changes the hydrophilicity of the surface. Furthermore, for the first time the surface of the copolymer is modified by SO2-plasma treatment to generate oxidized sulfur spezies at the surface. All modifications are characterized by X-ray-photoelectron-spectroscopy (XPS), ATR-FTIR-spectroscopy and the contact angle. The correlation between the chemical surface properties and the fibronectin adhesion indicates the surface/biological system interactions. The SO2-plasma treated surface shows the highest value of fibronectin adsorption compared to the other surface modifications. This correlates to the results of human endothelial cell culture experiments. On the SO2-plasma modified surface of the copolymer the cell proliferation is better than on surfaces modified by immobilization of different diols.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. D. RATNER, “The synthesis, characterisation, applications of polymers, Vol. 7, Specialty polymers and polymer processing” (Pergamon Press, 1989) 201–248.
W. MÖHL, Adv. Mater. 2 (1991) 9–10.
A. S. HOFFMANN, in “Advances in polymer science 57, Polymers in medicine” (Springer-Verlag, 1984) pp. 141–157
E. ENGVALL, and P. PERLMANN, Immunohistochemistry 8 (1971) 871–875.
R. SOWODA and J. C. MC GOWAN (eds) “Calculation of HLB values, “Physikalische Chemie”, (Carl Hanser Verlag, München, 1992) pp. 109–113.
J. GIGA, J. J. VERBIST, P. JOSSEAUX, A. R. MESSMAKER Surf. Interface Anal 7 (1985) 163–167.
A. G. WREN, R. W. PHILLIPS and C. V. TOLENTINO, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 70 (1979) 544–571.
M. JOZEFOWICZ, J. Membrane Sci. 22 (1985) 269–282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klee, D., Villari, R.V., Höcker, H. et al. Surface modification of a new flexible polymer with improved cell adhesion. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 5, 592–595 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120336