Summary
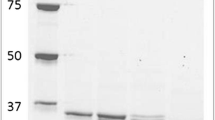
A fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (E.C.4.1.2.13) from Staphylococcus carnosus DSM 20501 was purified for the first time. The enzymatic activity was insensitive to high levels of EDTA indicating that the enzyme is a class I aldolase. This enzyme exhibits good stability at high temperatures and extreme stability over a wide pH range. The K m for fructose 1,6-bisphosphate as substrate was 0.022 mm. The S. carnosus aldolase is a monomeric enzyme with a molecular mass of about 33 kDa. It exhibits a relatively broad pH optimum between pH 6.5 and 9.0. Furthermore, the aldolase accepts other aldehydes in place of its natural substrate, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, allowing the synthesis of various sugar phosphates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama A, Bednarski M, Kim MJ, Simon ES, Waldmann H, Whitesides GM (1988) Enzymes in organic synthesis. Chemtech 18:627–633
Bednarski MD, Simon ES, Bischofberger S, Fessner WD, Kim MJ, Lees W, Saito T, Waldmann H, Whitesides GM (1989) Rabbit muscle aldolase as a catalyst in organic synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 111:627–635
Blostein R, Rutter WJ (1963) Comparative studies of liver and muscle aldolase. J Biol Chem 238:3280–3285
Boehringer Mannheim (1989) Firmenschrift über “Methoden der biochemischen Analytik und Lebensmittelanalytik”
Bossow-Berke B (1989) Kontinuierliche bioorganische Synthese am Beispiel der C-C Verknüpfung mit Aldolase. Dissertation, University of Bonn
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
DFG Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (1987) Starterkulturen und Enzyme für die Lebensmitteltechnik. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim
Durrwachter JR, Sweers HM, Nozaki K, Wong CH (1986) Enzymatic aldol reaction/isomerization as a route to unusual sugars. Tetrahedron Lett 27:1261–1264
Effenberger F, Straub A (1987) A novel convenient preparation of dihydroxyacetonphosphate and its use in enzymatic aldol reactions. Tetrahedron Lett 28:1641–1645
Götz F, Fischer S, Schleifer KH (1980) Purification and characterization of an unusually heat-stable and acid/base-stable class I F-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem 108:295–301
Hanes CS, Isherwood FA (1949) Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature 164:1107–1112
Horecker BL, Tsolas O, Lai CY (1972) Aldolases. In: Boyer PD (ed.) The enzymes, vol 7, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 213–258
Jaenicke R (1984) Proteinfaltung und Proteinassoziation. Angew Chem 96:385–402
Lämmli UK (1979) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lebherz HG, Rutter WJ (1973) A class I (schiff'base) fructose-disphosphate aldolase of procaryotic origin. J Biol Chem 248:1650–1659
Merril CR, Dunau ML, Goldman D (1981) A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 110:201–207
Meyerhof O, Lohmann K, Schuster Ph (1936) Über die Aldolase, ein Kohlenstoff-verknüpfendes Ferment. Biochem Z 286:319–335
Schleifer HK, Fischer U (1982) Description of a new species of the genus Staphylococcus: Staphylococcus carnosus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:153–156
Whitesides GM, Wong CH (1985) Enzyme in der organischen Synthese. Angew Chem 97:617–639
Wong CH, Whitesides GM (1983) Synthesis of sugars by aldolase-catalyzed condensation reactions. J Org Chem 48:3199–3205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: M. R. Kula
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brockamp, H.P., Kula, M.R. Purification and characterization of a class I fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Staphylococcus carnosus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34, 287–291 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170044
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170044