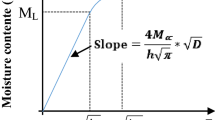
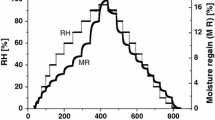
Summary
Water vapour diffusion characteristics and adsorption isotherms were determined for cell-lumen and cell-wall treated wood polymer composites (WPC). The diffusion coefficients of the cell-lumen WPC were lower than untreated wood and the cell-wall WPC coefficients were lower than cell-lumen. Using the Hailwood and Horrobin sorption model, it was found that the unimolecular layer is formed at lower moisture contents in WPC than in wood. The amount of free dissolved water was reduced only in the cell-wall WPC. The polymer reduces the water vapour accessibility in both types of WPC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ellwood, E. L.; Gilmore, R. C.; Stamm, A. J. 1972: Dimensional stabilization of wood with vinyl monomers. Wood Sci. 4 (3): 137–141
Hailwood, A. J.; Horrobin, S. 1946: Absorption of water by polymers: analysis in terms of a simple model. Trans. Faraday Soc. 42B: 84–92 (General Discussions 42B: 93–102)
Hartley, I. D.; Schneider, M. H. 1989: Modelling direct current resistivity of wood polymer composites. Wood Fiber Sci. 21 (4): 411–419
Langmuir, I. 1918: The adsorption of gases on plain surfaces of glass, mica, and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40: 1361–1405
Langwig, J. E.; Meyer, J. A.; Davidson, R. W. 1969: New monomers used in making wood plastics. For. Prod. J. 19(11): 57–61
Meyer, J. A. 1977: Wood polymer composites and their industrial applications. In: Goldstein, I. S. (ed.) Wood Technology. Chemical aspects. ACS Symposium Series 43. Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society, 301–325pp
Meyer, J. A. 1984: Wood polymer materials. In: Rowell, R. M. (ed.) The chemistry of solid wood. Advances in chemistry series 207. Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society, 257–289pp
Schneider, M. H.; Brebner, K. I.; Hartley, I. D. 1991: Swelling of a cell-lumen filled and a cell wall bulked wood polymer composite in water. Wood Fiber Sci. 23(2): 165–172
Schneider, M. H.; Phillips, J. G.; Brebner, K. I.; Tingley, D. A. 1989: Toughness of polymer impregnated sugar maple at two moisture contents. For Prod. J. 39 (6): 11–14
Schneider, M. H.; Phillips, J. G.; Tingley, D. A.; Brebner, K. I. 1990. Mechanical properties of polymer impregnated maple. For. Prod. J. 40(1): 37–41
Siau, J. F. 1984: Transport processes in wood. Berlin: Springer-Verlag
Skaar, C. 1988: Wood water relations. Berlin: Springer-Verlag
Spalt, H. A. 1958: The fundamentals of water vapor sorption by wood. For. Prod. J. 8: 288–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartley, I.D., Schneider, M.H. Water vapour diffusion and adsorption characteristics of sugar maple (Acer saccharum, Marsh.) wood polymer composites. Wood Sci.Technol. 27, 421–427 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193864
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193864