Abstract
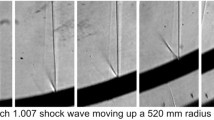
The signal speed, namely the local sound speed plus the flow velocity, behind the reflected shocks produced by the interaction of weak shock waves (M i < 1.4) with rigid inclined surfaces has been measured for several shock strengths close to the point of transition from regular to Mach reflection. The signal speed was measured using piezo-electric transducers, and with a multiple schlieren system to photograph acoustic signals created by a spark discharge behind a small aperture in the reflecting surfaces. Both methods yielded results with equal values within experimental error. The theoretical signal speeds behind regularly reflected shocks were calculated using a non-stationary model, and these agreed with the measured results at large angles of incidence. As the angle of incidence was reduced, for the same incident shock Mach number, so as to approach the point of transition from regular to Mach reflection, the measured values of the signal speed deviated significantly from the theoretical predictions. It was found, within experimental uncertainty, that transition from regular to Mach reflection occurred at the experimentally observed sonic point, namely, when the signal speed was equal to the speed of the reflection point along the reflecting surface. This sonic condition did not coincide with the theoretical value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Dor, G.; Takayama, K.; Kawauchi, T. 1980: The transition from regular to Mach reflection and from Mach to regular reflection in truly non-stationary flows. J. Fluid Mech. 100, 147–160
Dewey, J. M.; Walker, D. K. 1975: A multiply pulsed double-pass laser schlieren system for recording the movement of shocks and particle tracers within a shock tube. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 3454–3458
Dewey, J. M.; McMillin, D. J. 1985: Observation and analysis of the Mach reflection of weak uniform plane shock waves. 2. Analysis. J. Fluid Mech. 152, 67–81
Henderson, L. F.; Lozzi, A. 1975: Experiments on transition of Mach reflection. J. Fluid Mech. 68, 139–155
Henderson, L. F.; Siegenthaler, A. 1980: Experiments on the diffraction of weak blast waves: the von Neumann paradox. Proc. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. A 369, 537–555
Hornung, H. G.; Oertel, H.; Sandeman, J. 1979: Transition to Mach reflection in steady and pseudosteady flow with and without relaxation. J. Fluid Mech. 90, 541–560
Takayama, K.; Gotah, J.; Ben-Dor, G. 1981: Regular to Mach reflection transition in truly non-stationary flows. Influence of surface roughness. AIAA J. 19, 1238–1240
Neumann, J. von 1963: Collected works, vol. 6, p. 239. New York: Pergamon Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lock, G.D., Dewey, J.M. An experimental investigation of the sonic criterion for transition from regular to Mach reflection of weak shock waves. Experiments in Fluids 7, 289–292 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198446
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198446