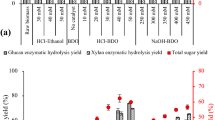
Summary
Enzymatic hydrolysates of hemicellulose from steam-pretreated aspenwood were more fermentable than the acid hydrolysate after rotoevaporation or ethyl acetate extraction treatments to remove acetic acid and sugar- and lignin-degradation products prior to fermentation by Pichia stipitis CBS 5776. Total xylose and xylobiose utilization from 5.0% (w/v) ethyl acetate extracted enzymatic hydrolysate was observed with an ethanol yield of 0.47 g ethanol/g total available substrate and an ethanol production rate of 0.20 g·l-1 per hour in 72 h batch fermentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando S, Arai I, Kiyoto K, Hanai S (1986) Identification of aromatic monomers in steam-exploded poplar and their influences on ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Technol 64:567–570
Beck MJ (1986a) Factors affecting efficiency of biomass fermentation to ethanol. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 17:617–627
Beck MJ (1986b) Effect of intermittent feeding of cellulose hydrolysate to hemicellulose hydrolysate on ethanol yield by Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol Lett 8:513–516
Biely P, Kratky Z, Vrsanska M, Urmanicova D (1980) Induction and inducers of endo-1,4-β-xylanase in the yeast Cryptococcus albidus. Eur J Biochem 108:323–329
Biely P, MacKenzie CR, Puls J, Schneider H (186) Cooperatively of esterases and xylanases in the enzymatic degradation of acetyl cylan. Bio/technology 4:731–733
Brownell HH, Saddler JN (1987) Steam pretreatment of lignocellulosic material for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:228–235
Burtscher E, Bobleter O, Schwald W, Concin R, Binder H (1987) Chromatographic analysis of biomass reaction products produced by hydrothermolysis of poplar wood. J Chromatogr 390:401–412
Clark TA, Mackie KL (1984) Fermentation inhibitors in wood hydrolysates derived from the softwood pinus radiata. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 34b:101–110
duPreez JC, Bosch M, Prior BA (1986) The fermentation of hexose and pentose sugars by Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:228–233
Lee H, Biely P, Latta RK, Barbosa MFS, Schneider H (1986) Utilization of xylan by yeasts and its conversion to ethanol by Pichia stipitis strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:320–324
Liu H-S, Hsu H-W, Sayler GS (1988) Bioconversion of d-xylose and pretreated oak sawdust to ethanol using Clostridium thermosaccharolyticum by batch and continuous upflow reactors. Biotechnol Prog 4:40–46
Nishikawa NK, Sutcliffe R, Saddler JN (1988) The influence of lignin degradation products on xylose fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:549–552
Parekh SR, Parekh RS, Wayman M (1987) Fermentation of wood-derived acid hydrolysates in a batch bioreactor and in a continuous dynamic immobilized cell bioreactor by Pichia stipitis R. Process Biochem 22:85–91
Puls J, Poutanen K, Viikari L (1985) The effect of steaming pretreatment on the biotechnical utilization of wood components. In: Egneus H, Ellegard A (eds) Bioenergy 84, vol. III, Biomass conversion. Elsevier, London, pp 173–180
Schwald W, Saddler JN (1988) A comparison of methods for quantitating the fermentation of wood derived sugars to solvents. Enzyme Microb Technol 10:37–41
Schwald W, Chan M, Brownell HH, Saddler JN (1988) Influence of hemicellulose and lignin on the enzymatic hydrolysis of wood. In: Aubert JP, Beguin P, Millet J (eds) FEMS Symposium no. 43, Biochemistry and genetics of cellulose degradation, Paris Sept. 7–9, 1987. Academic Press, New York, pp 303–314
Skoog K, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1988) Xylose fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 10:66–80
Sutcliffe R, Saddler JN (1986) The role of lignin in the adsorption of cellulases during enzymatic treatment of lignocellulosic material. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 17:749–762
Tan LUL, Yu EKC, Louis-Seize GW, Saddler JN (1987) Inexpensive, rapid procedure for bulk purification of cellulase-free β-1,4-D-xylanase of high specific activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 30:96–100
Tran AV, Chambers RP (1986) Ethanol fermentation of red oak prehydrolysate by the yeast Pichia stipitis CBS 5776. Enzyme Microb Technol 8:439–444
Watson NE, Prior BA, Lategan PM (1984) Factors in acid treated bagasse inhibiting ethanol production from d-xylose by Pachysolen tannophilus. Enzyme Microb Technol 6:451–456
Zyl C van, Prior BA, duPreez JC (1988) Production of ethanol from sugar cane bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate by Pichia stipitis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 17:357–369
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, J.J., Deschatelets, L. & Nishikawa, N.K. Comparative fermentability of enzymatic and acid hydrolysates of steam-pretreated aspenwood hemicellulose by Pichia stipitis CBS 5776. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 592–596 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270801
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270801