Summary
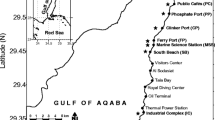
Reef flats in the vicinity of tin dredging and smelting activities around the Laem Pan Wah peninsula, Phuket, and been quantitatively surveyed. the diversity of corals on all intertidal reefs was low (≏10 genera), the dominant genera being Porites, Montipora, Acropora and Platygyra. Two basic types of reef can be discerned, one dominated by Porites lutea and faviid species and the other by Montipora ramosa and Acropora aspera, reef type apparently being governed by the degree of exposure to water movement. Other natural factors affecting coral cover included freshwater run off, considerable sedimentation, and aerial exposure for 2–3 h each day. Heavy metal concentrations in invertebrate species such as the oyster Saccostrea, the bivalve Isognomon, and in the alga Padina reflected elevated metal levels at all sites when compared with controls (Figs. 8 and 9). In particular, levels of metals were considerably elevated in molluscs taken from the reef below the tin smelter. Interestingly, dead coral cover on this reef, although high, was not significantly different from values observed on reefs several kilometres away from the smelter, which were not apparently under the influence of such increased metal loads (Fig. 2).
No elevation in metal concentrations in coral tissue or skeleton was evident at any site. It would appear, then, that these intertidal coral species are not obviously affected by the levels of metals discharged at the smelter site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banner AH (1974) Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii—urban pollution and a coral reef ecosystem. Proc 2nd Int Symp Coral Reefs 2:578–583
Barnard LA, Macintyre IG, Pierce JW (1974) Possible environmental index in tropical reef corals. Nature 252:219–220
Boyden CR (1974) Trace element content and body size in molluscs. Naturc 251:311–314
Brooks RR, Presley BJ, Kaplan IR (1967) APDC-MIBK Extraction system for the determination of trace elements in saline waters by atomic-absorption spectrophotometry. Talanta 14:809–816
Brown BE (1976) Observations on the tolerance of the isopod Asellus meridianus Rac, to copper and lead. Water Res 10:555–559
Brown BE (1978) Lead detoxification by a copper tolerant isopod. Nature 276:388–390
Brown BE, Holley MC Coral assemblages of intertidal reef flats at Ko Phuket, Thailand. Res Bull Phuket Mar Biol Cent (in press)
Bryan GW (1971) The effects of heavy metals (other than mercury) on marine and estuarine organisms. Proc R Soc Lond (B) 177:389–410
Bryan GW (1976) Heavy metal contamination in the sea. In: Johnstone R (ed) Marine pollution. Academic Press, London New York, pp 185–302
Bryan GW (1980) Recent trends in research on heavy metal contamination in the sea. Helgoland Wiss Meer 33:6–25
Bryan GW, Hummerstone LG (1971) Adaptations of the polychaete Nereis diversicolor to estuarine sediments containing high concentrations of heavy metals. 1. General observations and adaptation to copper. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 51:845–863
Bryan GW, Hummerstone LG (1973a) Adaptation of the polychaete Nereis diversicolor to estuarine sediments containing high concentrations of zinc and cadmium. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 53:839–857
Bryan HW, Hummerstone LG (1973b) Brown seaweed as an indicator of heavy metals in estuaries in south-west England. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 53:705–720
Bryan GW, Langston WJ, Hummerstone LG (1980) The use of biological indicators of heavy metal contamination in estuaries. Mar Biol Assoc UK. Occ Publ no 1
Butterworth J, Lester P, Nickless G (1972) Distribution of heavy metals in the Severn estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 3:72–74
Ditlev H (1978) Zonation of corals (Scleractinia: Coelenterata) on intertidal reef flats at Ko Phuket, Eastern Indian Ocean. Mar Biol 47:29–39
Dodge RE, Rimas Vaisnys J (1977) Coral populations and growth patterns; responses to sedimentation and turbidity associated with dredging. J Mar Res 35:715–730
George SG (1980) Correlation of metal accumulation in mussels with the mechanisms of uptake, metabolism and detoxification. Biochemical and ultrastructural studies. VIth Int Conf Chem Medit Rovinj, Yugoslavia, June 1980. Thalassia Jugosl 16:347–365 (extended abstract)
Georghiou L, Ford G (1981) Arab silver from the Red Sea mud. N Sci 89:470–472
Goreau TJ (1977a) Coral skeletal chemistry: physiological and environmental regulation of stable isotopes and trace metals in Montastrea annularis. Proc R Soc Lond (B) 196:291–315
Groot AJ de, Goeij JJM, Zegers C (1971) Contents and behaviour of mercury as compared with other heavy metals in sediments from the rivers Rhine and Ems. Geol Mijnbouw 50:393–398
Hubbard JAEB, Pocock YP (1972) Sediment rejection by recent scleractinian corals, a key to palaeoenvironmental reconstruction. Geol Rundsch 61:598–626
Jones MB (1975) Synergistic effects of salinity, temperature and heavy metals on mortality and osmoregulation in marine and estuarine isopods (Crustacea). Mar Biol 30:13–20
Livingston HO, Thompson G (1971) Trace element concentrations in some modern corals. Limnol Oceanogr 16:786–796
Lobel P (1978) A rapid digestion procedure for use in metal analysis. Mar Poll Bull 9:22–23
Loya Y (1972) Community structure and species diversity of hermatypic corals at Eilat, Red Sea Mar Biol 13:100–123
Loya Y, Rinkevich B (1980) Effects of oil pollution on coral reef communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 3:167–180
Milliman JD (1974) Marine carbonates. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Preston A, Jeffries DF (1969) Aquatic aspects in chronic and acute contamination situations. In: Environmental contamination by radioactive materials. IAEA, Vienna, pp 183–211
Reeve MR, Grice GT, Gibson VR, Walter MA, Darcy K, Ikeda T (1976) A controlled environmental experiment (CEPEX) and its usefulness in the study of larger marine zooplankton under toxic stress. In: Lockwood APM (ed) Effects of pollutants on aquatic organisms. Society for experimental biology seminar series 2, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 145–164
Smith S (1977) Kaneohe Bay: a preliminary report on the responses of a coral reef/estuary ecosystem to relaxation of sewage stress. Proc 3rd Int Symp Coral Reefs 2:578–583
St. John BE (1973) Trace elements in corals of the Coral Sea; their relationship to oceanographic factors. In: Fraser R (ed) Oceanography of the South Pacific 1972. New Zealand National Commission for UNESCO, Wellington, pp 149–158
St. John BE (1974) Heavy metals in the skeletal carbonate of scleractinian corals. Proc 2nd Int Symp Coral Reefs 2:461–469
Veeh HH, Turekian KK (1978) Cobalt, silver and uranium concentrations of reef building corals in the Pacific Ocean. Limmol Oceanogr 13:304–308
Wright DA (1977) The effect of calcium on cadmium uptake in the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. J Exp Biol 67:163–173
Wright DA (1978) Heavy metal accumulation by aquatic invertebrates. Appl Biol 3:331–394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, B.E., Holley, M.C. Metal levels associated with tin dredging and smelting and their effect upon intertidal reef flats at ko phuket, Thailand. Coral Reefs 1, 131–137 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301695
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301695