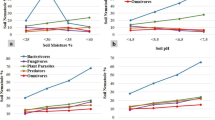
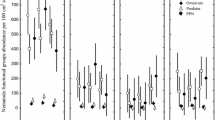
Summary
Nematode assemblages constitute a potential instrument for assessing the quality of submersed, temporarily submersed, and terrestrial soils and for the development of an ecological typology and biomonitoring system. Interpretation of physical or pollution-induced disturbances has hitherto mainly been based on changes in diversity, dominance patterns or percentage of dorylaimids (Adenophorea). The maturity index, based on the nematode fauna, is proposed as a gauge of the condition of the soil ecosystem. Values on a coloniser/persister scale are given for nematodes that occur in The Netherlands. The possibilities of the use of this index are demonstrated by a retrospective interpretation of some literature data. The use of nematodes in environmental studies is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrássy I (1959) Taxonomische Übersicht der Dorylaimen (Nematoda). I. Acta Zool Acad Sci Hung 5 (3-4):191–240
Boag B, Alphey TJW (1988) Influence of interspecific competition on the population dynamics of migratory plant-parasitic nematodes with r and K survival strategies. Rev Nematol 11:321–326
Bongers T (1985) Dutch forest nematodes. Nematologica 31:356–357
Bongers T (1988) De Nematoden van Nederland. Natuurhistorische Bibliotheek van de KNNV, nr. 46. Pirola, Schoorl
Bongers T, Goede RGM de, Kappers FI, Manger R (1989) Ecologische typologie van de Nederlandse bodem op basis van de vrij levende nematodenfauna. RIVM-rapport nr. 718602002
Bongers T, Yeates GW (1988) Report on a workshop: Nematodes in natural systems; the use of nematodes in environmental studies. Pedobiologia 32:88
Boström S (1989) The taxonomic position of some teratocephalid nematodes — a scanning electron microscope study. Rev Nematol 12:181–190
Esbroek MLP van (1988) Voorkomen en successie van nematoden tijdens landfarming en rijping van havenslib. RIVM-rapport nr. 718602001
Heip C, Vincx M, Vranken G (1985) The ecology of marine nematodes. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 23:399–489
Highler LWG (1985) Onderwaterbodems en de betekenis ervan voor het aquatisch ecosysteem. In: Bergen VWJ van den, Kerkhoff MAT, Wegman RCC (eds) Onderwaterbodems, Rol en Lot. Proc. Symp. 28–29 May 1985, Rotterdam, pp 14–25
Jacobs LJ (1987) Inleiding tot de biologische kwaliteitsbeoordeling van onderwaterbodems in Nederland door middel van de Nematofauna. Rapport Vg. Nematologie i.o.v DBW/RIZA Lelystad.
Johnson SR, Ferris JM, Ferris VR (1974) Nematode Community Structure of Forest Woodlots: III. Ordinations of taxonomic groups and biomass. J Nematol 6:118–126
Kappers FI, Esbroek MLP van (1988) Ecological recovery of decontaminated soil. Proc. Sec. Intern. TNO/BMFT Conf. on Contaminated Soil. Hamburg, 11–15 April 1988
Kroes HW (1983) Achtergronden van milieuhygienische normstelling voor oppervlaktewater H2O 16:281–284
Lambshead PJD, Platt HM, Shaw KM (1983) The detection of differences among assemblages of marine benthic species based on an assessment of dominance and diversity. J Nat Hist 17:859–874
Lee DL (1961) Two new species of cryptobiotic (anabiotic) freshwater nematodes, Actinolaimus hintoni sp. nov. and Dorylaimus keilini sp. nov. (Dorylaimidae). Parasitology 51:237–240
Maggenti AR, Luc M, Raski DJ, Fortuner R, Geraert E (1987) A reappraisal of Tylenchina (Nemata). 2. Classification of the suborder Tylenchina (Nemata: Diplogasteria). Rev Nematol 10:135–142
Parry GD (1981) The meanings of r-and K-selection. Oecologia 48:260–264
Pitcher RS, McNamara DG (1972) The toxicity of low concentrations of silver and cupric ions to three species of plant-parasitic nematodes. Nematologica 18:385–390
Platt HM, Shaw KM, Lambshead PJD (1984) Nematode species abundance patterns and their use in the detection of environmental perturbations. Hydrobiologia 118:59–66
Platt HM, Warwick RM (1980) The significance of Free-living Nematodes to the littoral Ecosystem. Systematic Association Special Volume No 17(b), The Shore Environment, Vol 2; Ecosystems, pp 729–759
Platt HM, Warwick RM (1983) Freeliving marine nematodes. Part I: British Enoplids. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series) No. 28, Cambridge University Press
Platt HM, Warwick RM (1988) Freeliving marine nematodes. Part II: British Chromadorids Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series) No. 38, E.J. Brill, Leiden
Por FD, Masry D (1968) Survival of a nematode and an oligochaete species in the anaerobic benthal Lake Tiberias. Oikos 19:388–391
Samoiloff MR (1987) Nematodes as Indicators of Toxic Environmental Contaminants. In: Veech JA, Dickson DW (eds) Vistas on Nematology. E.O. Painter Printing Co. De Leon Springs, Florida, pp 433–439
Schiemer F, Duncan A (1974) The oxygen consumption of a freshwater benthic nematode Tobrilus gracilis (Bastian). Oecologia 15:121–126
Schiemer F (1983) Comparative aspects of food dependence and energetics of free living nematodes. Oikos 41:32–42
Siddiqi MR (1986) Tylenchida, Parasites of Plants and Insects. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, London
Sohlenius B (1985) Influence of climatic conditions on nematode coexistence: a laboratory experiment with a coniferous forest soil. Oikos 44:430–438
Sturhan D (1989) Nematodes as potential indicators of heavy metals. In: Wal AF van der, Goede RGM de (eds) Nematodes in natural systems, a status report of a workshop. Meded. 199, Nematology Dept. Agric. Univ. Wageningen, p 41
Tamis W (1986) Nematoden in een Ammoniumdepositiegradient in een Grovedennenbos. Hydrobiologisch Adviesburo Klink bv Wageningen. Rapporten en Mededelingen 23
Tietjen JH, Lee JJ (1984) The use of Free-Living Nematodes as a Bioassay for Estuarine sediments. Mar Env Res 11:233–251
Urk G van, Kerkum FCM (1988) Bottom fauna of polluted Rhine sediments. In: Wolf K, Brink WJ van den, Colon FJ (eds) Contaminated Soil '88. Kluwer Acad. Publ., pp 1405–1407
Wasilevska L (1971) Nematodes of the dunes in the Kampinos Forest. II. Community structure based on numbers of individuals, state of biomass and respiratory metabolism. Ekol Polska XIX 38:651–688
Wasilevska L (1974) Rola wskaznikowa wszystkozernej grupy nicieni glebowych. Wiad Ekol XX:385–390
Wharton DA (1986) A functional biology of Nematodes. Croom Helm, London & Sydney
Woombs M, Laybourn-Parry J (1984) Feeding biology of Diplogasteritus nudicapitatus and Rhabditis curvicaudata (Nematoda) related to food concentrations and temperature, in sewage treatment plants. Oecologia 64:163–167
Zullini A (1976) Nematodes as indicators of river pollution. Nematol Medit 4:13–22
Zullini A, Peretti E (1986) Lead pollution and moss-inhabiting nematodes of an industrial area. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 27:403–410
Zullini A, Ricci C (1980) Bdelloid rotifers and nematodes in a small Italian stream. Freshwater Biol 10:67–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bongers, T. The maturity index: an ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia 83, 14–19 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324627
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324627