Abstract
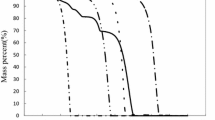
Traces of H4 phases in soils, sediments and mineral standards were determined by thermal analysis at successively higher temperature steps. Mercury was liberated at each step, concentrated on Au, then determined by flameless atomic absorption. Some Hq determinations were made by liberating the element by continuous heating at the rate of 20 and 100°C min−1. Soil samples were collected from the vicinity of a Hg mine, a Cu deposit and fault zones. Sediment samples were collected near a H9 roasting plant, a chlor-alkali plant and a Cu smelter. The results show that, for all the samples, most of the Hg is liberated during the 200°C temperature step. Some samples show thermal release characteristics similar to those of a. cinnabar-quartz mixture. Other samples show characteristics possibly related to sorbed elemental Hg. The results show that stepwise compared to continuous heating gives more resolution and thus may prove to be easier in estimating traces of Hg phases in soils and sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aftabi, A. and Azzaria, L.M.: 1983, J. Geochem. Explor., 19, 447.
Armstrong, J.E.: 1949. Fort St. James map-area, Cassiar and Coast Districts, British Columbia. Geol. Sur. Can., Memoir 252, 210 p.
Armstrong, R.C.: 1975, The dispersion of mercury and other metals related to mineral deposits in the Canadian Cordillera. Ph.D. thesis, Queen's Univ. (Kingston, Ontario).
Azzaria, L.M.: 1967, A method of determining traces of mercury in geologic materials. Geol. Surv. Can., Paper 66-54: 13–26.
Azzaria, L.M.: 1973, Mercury in soil and air as a guide to mineralization in four areas of Québec. Ministère des Richesses Naturelles du Québec, Publication Spéciale S-136, 35 p.
Azzaria, L.M.: 1977, Mercury sediment survey, Saint Lawrence River near Cornwall, Ontario. Report for the St. Regis Band Council, 10 p.
Azzaria, L.M. and Webber, G.R.: 1969, Can. Min. Metall. Bull., 62, 521.
Azzaria, L.M. and Fréchette, G.: 1987, Natural and industrial sources of trace elements, Rouyn-Noranda-Val d'Or mining area, Québec, Canada. In The Practical Applications of Trace Elements and Isotopes to Environmental Biooeochemistry and Mineral Resources Evaluation, Theophrastus Publications, pp 3–26.
Bureau d'étude sur les substances toxiques: 1979, Etude des sédiments de la région de Rouyn-Noranda. Service de protection de l'environnement du Québec, Rapport sectoriel E-8, 189 p.
Canadian British Consultants, Atlantic Industrial Research Institute, Dearborn Environmental Consulting Services, and Azzaria, L.M.: 1981, Mercury reduction in sediments. Report for Environment Canada, 93 p.
Lindberg, S.E.: 1986, Mercury vapor in the atmosphere: three case studies on emission, deposition, and plant uptake. in Toxic Metals in the Atmosphere, Wiley, pp 535–560.
McCarthy, J.H., Vaughan, W.W., Learned, R.E., and Mueschke, J.L.: 1969, Mercury in soil, gas and air — a potential tool in mineral exploration. U.S. Geol. Surv. Circular 609, 16 p.
Schroeder, W.H., Hamilton, M.C., and Stobart, S.R.: 1985, Reviews in Anal. Chem., 8, 179.
Watling, R.J. Davis, G.R., and Meyer, W.T.: 1973, Trace identification of mercury compounds as a guide to sulphide mineralization at Keel, Eire. In Geochemical Exploration 1972, Inst. Min. Metall., pp 59–69.
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Dong, Y., and Peng, S.: 1989, J. Geochem. Explor., 33, 73.
Zonghua, W. and Yangfen, J.: 1981, J. Geochem. Explor., 15, 77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzaria, L.M., Aftabi, A. Stepwise thermal analysis technique for estimating mercury phases in soils and sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 56, 203–217 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342272