Abstract
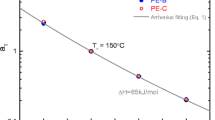
We report experimental data for a linear low density grade of polyethylene at elevated temperatures using a newly designed Multi-Pass Rheometer. This rheometer is capable of measuring oscillatory viscoelastic data and steady shear capillary measurements on the same test fluid within an enclosed environment. Data presented in this paper show that at low pressures there is reasonable self-consistency between the Multi-Pass data and separate oscillatory data obtained by using a Rheometrics Mechanical Spectrometer and steady shear data obtained from a Rosand capillary rheometer. In addition, we report experimental data on the pressure dependence for both viscoelastic and steady shear data over the range of 1–230 bar. The steady shear results appear to be consistent with previously published data. The apparent viscosity and the viscoelastic data both show a linear increase of about 20% over the pressure range tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed R, Liang RF, Mackley MR (1995) The experimental observation and numerical prediction of planar entry flow and die swell for molten polyethylene. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 59:2–3, 129–153
Baker FS, Thomas M (1993) The effect of hydrostatic pressure on the flow properties of various polymers. Makromol Chem Macromol Symp 68:13–24
Brydson JA (1981) Flow properties of polymer melts, 2nd Edition. George Godwin Limited in association with The Plastic and Rubber Institute, London
Christmann L, Knappe W (1974) Viskositätsmessungen an Kunststoffschmelzen mit verschiedenen Molekulargewichten. Coll Pol Sci 252:705–711
Choi SY (1968) Determination of melt viscosity as a function of hydrostatic pressure in an extrusion rheometer. J Pol Sci A2 6:2043–2049
Cogswell FN (1981) Polymer melt theology. A guide for industrial practice. John Wiley & Sons in association with The Plastics and Rubber Institute
Cogswell FN, McGowan JC (1972) The effects of pressure and temperature upon the viscosities of liquids with special reference to polymeric liquids. British Polymer Journal 4:183–198
Gouldhomme A, Crochet MJ (1993) Numerical prediction of extrudate swell of a high-density polyethylene: further results. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 34:281–287
Kadijk SE, van den Brule BHAA (1994) On the pressure dependence of the viscosity of molten polymers. Polymer Eng and Sci 34:1535–1546
Karl VH (1979) Über die Druckabhängig-keit der viskoelastischen und physikalisch-chemischen Eigenschaften von Polymeren. Ang Makromol Chem 79:11–19
Laun HM (1978) Description of the nonlinear shear behaviour of a low density polyethylene melt by means of an experimentally determined strain dependent memory function. Rheol Acta 17:1–15
Lord HA (1977) Flow of polymers with pressure dependent viscosity in injection molding dies. National Symp plastic molds designs, design, Newark NJ 16/1–16/9, vol 16:1–9
Mackley MR, Marshall RTM, Smeulders JBAF (1994) Multi-pass rheometry. In: Gallegos C (ed) Proc 4th Eur Rheol Conference Seville. Steinkopf, Darmstadt 502–505
Mackley MR, Marshall RTM, Smeulders JBAF (1995) The multi-pass rheometer. J Rheology 39:6 1293–1309
Meissner J (1975) Basic parameters, melt theology, processing and end-use properties of three similar low density polyethylene samples. Pure and Applied Chem 42:551–612
Smits HJE, van den Ende D, Beukema GJ, Altena EG, Spitteler PHJ (1992) An automated dynamic viscometer with air bearing and inductive pressure transducers for angular displacement detection. Rheol Acta 31:471–480
Utraki LA (1983) Pressure dependence of Newtonian viscosity. Pol Eng and Science 23:446–451
Utraki LA (1985) A method of computation of the pressure effect on melt viscosity. Pol Eng and Science 25:655–668
Wagner MH (1979) Zur Netwerktheorie von Polymer-Schmelzen. Rheol Acta 18:33–50
Westover RF (1961) Effect of hydrostatic pressure on polyethylene melt theology. Soc Plastics Engrs Trans 1:14–20 Transactions
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. J. Meissner on the occasion of his retirement from the chair of Polymer Physics at the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH) Zürich, Switzerland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackley, M.R., Spitteler, P.H. Experimental observations on the pressure-dependent polymer melt rheology of linear low density polyethylene, using a multi-pass rheometer. Rheol Acta 35, 202–209 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396047
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396047