Summary
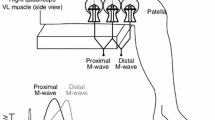
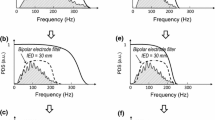
A surface electrode array has been used to investigate the relationship between muscle fibre conduction velocity and the frequency spectrum during sustained isometric contractions of the biceps brachii. Measurement of muscle fibre conduction velocity was made directly, using the zero-crossing time delay method with two pairs of bipolar electrodes. It was found that the average conduction velocity during an intense (12 kg) sustained contraction decreased by about 20% at the end of the contracting period. Except for peak frequency, changes in the spectral parameters decreased in a similar manner. These results indicate that, during fatiguing contraction, spectral modifications are partly due to reduction in the action potential conduction velocity along the muscle fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal G, Gottlieb G (1975) An analysis of the electromyogram by fourier simulation and experimental techniques. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 22: 225–229
Bigland-Ritchie B, Donovan E, Roussos C (1981) Conduction velocity and EMG power spectrum changes in fatigue of sustained maximal efforts. J Appl Physiol 51: 1300–1305
Buchthal F, Guld C, Rosenfalk P (1955) Propagation velocity in electrically activated muscle fibres in man. Acta Physiol Scand 34: 75–89
Emerson N, Zahalak G (1981) Longitudinal electrode arrays for electromyography. Med Biol Eng Comput 19: 504–506
Kadefors R, Kaiser E, Petersen I (1968) Dynamic spectrum analysis of myo-potentials and with special reference to muscle fatigue. Electromyography 8: 39–74
Kogi K, Hakamada T (1962) Slowing of surface electromyogram and muscle strength in muscle fatigue. Rep Inst Sci Labour 60: 27–41
Lindström L, Magnusson R, Petersen I (1970) Muscular fatigue and action potential conduction velocity changes studied with frequency analysis of EMG signals. Electromyography 4: 341–353
Lindström L, Kadefors R, Petersen I (1977) An electromyographic index for localized muscle fatigue. J Appl Physiol 43: 750–754
Lynn P, Bettles N, Hughes A, Johnson S (1978) Influences of electrode geometry on bipolar recordings of the surface electromyogram. Med Biol Eng Comput 16: 651–660
Lynn P (1979) Direct on-line estimation of muscle fibre conduction velocity by surface electromyography. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 26: 564–571
Masuda T, Miyano H, Sadoyama T (1982) The measurement of muscle fiber conduction velocity using a gradient threshold zero-crossing method. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 10: 673–678
Milner-Brown H, Stein R (1975) The relation between the surface electromyogram and muscle force. J Physiol 246: 549–569
Miyano H, Sadoyama T (1979) Theoretical analysis of surface EMG in voluntary isometric contraction. Eur J Appl Physiol 40: 155–164
Mortimer J, Magnusson R, Petersen I (1970) Conduction velocity in ischemic muscle effort on EMG frequency spectrum. Am J Physiol 219: 1324–1329
Naeiji M, Zorn H (1982) Relation between EMG power spectrum shifts and muscle fibre action potential conduction velocity changes during local muscular fatigue in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 50: 23–33
Nishizono H, Saito Y, Miyashita M (1979) The estimation of conduction velocity in human skeletal muscle in situ with surface electrodes. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 46: 659–664
Person R, Libkind M (1970) Simulation of electromyograms showing interference patterns. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 28: 625–632
Petrofsky J, Lind A (1980) Frequency analysis of surface electromyogram during sustained isometric contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol 43: 173–182
Sadoyama T, Miyano H (1981) Frequency analysis of surface EMG to evaluation of muscle fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 47: 239–246
Sameshima M, Katada A, Suzuki H, Ozaki H, Suhara K (1977) Propagation of impulse to the skin and its spatial distribution. Jap Med Electron 15: 556–557
Stulen F, DeLuca C (1981) Frequency parameters of the myoelectric signal as a measure of muscle conduction velocity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 28: 515–523
Viitasalo J, Komi P (1977) Signal characteristics of EMG during fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 37: 111–121
Zipp P (1978) Effect of electrode parameters on the bandwidth of surface e.m.g. power density spectrum. Med Biol Eng Comput 16: 537–541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadoyama, T., Masuda, T. & Miyano, H. Relationships between muscle fibre conduction velocity and frequency parameters of surface EMG during sustained contraction. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 247–256 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455188
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455188