Abstract
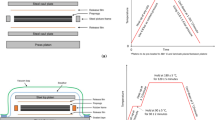
A brief review is given of techniques which have been employed in attempts to determine the mechanical properties of composite materials under tensile impact loading. The difficulties encountered in the design of a satisfactory tensile impact testing machine for composite materials are discussed and a new method, using a modified version of the standard tensile split Hopkinson's pressure bar (SHPB), is described. Dynamic stress-strain curves for unidirectionally-reinforced carbon/epoxy composite, in which failure occurs in less than 30 μsec at a mean strain rate of about 400 sec−1, are presented and their validity is established. An extension of the technique to allow the testing of wovenroving reinforced glass/epoxy composites is described and dynamic stress-strain curves obtained for which the times to failure approach 100 μsec and the average strain rate is of the order of 1000 sec−. Comparative stress-strain curves at low and intermediate rates of strain are obtained and the effect of strain rate, over about 7 orders of magnitude, on the tensile modulus, and strength, fracture strain and energy absorbed in fracturing is determined. The limitations of the technique are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Dorey, “Fracture behaviour of carbon fibre composites subjected to impact loads”, AGARD Conference Proceedings 163 on Failure modes of composite materials with organic matrices and their consequences in design. AGARD-CP-163, 1974.
A. E. Arménakas and C. A. Sciammarella, Exp. Mech. 13 (1973) 433.
A. Rotem and J. M. Lifshitz, in Proceedings of the 26th Annual Technical Conference, SPI Reinforced Plastics/Composites Division (Society of Plastics Industry, New York, 1971) Paper 10-G.
G. Marom, S. Fischer, F. R. Tuler and H. D. Wagner, J. Mater. Sci. 13 (1978) 1419.
D. F. Adams and A. K. Miller, ibid. 11 (1976) 1697.
M. G. Phillips, “Fracture and fatigue of hybrid composites”, in Fibre Composite Hybrid Materials, edited by N. L. Hancox (Applied Science Publishers, Barking, Essex, 1981) Chap. 4.
D. F. Adams, ASTM STP 617 (1977) p. 409.
R. L. Sierakowski, G. E. Nevill, C. A. Ross and E. R. Jones, J. Comp. Mater. 5 (1971) 362.
L. J. Griffiths and D. J. Martin, J. Phys. D. Appl Phys. 7 (1974) 2329.
T. Parry and J. Harding, Colloque International du CNRS No. 139, Plastic behaviour of anisotropic solids, Grenoble, June 1981 (OUEL Report No. 1365/81).
J. Harding, in Proceedings of the Conference on Mechanical Properties at High Rates of Strain, Oxford, April 1979, edited by J. Harding, Conf. Ser. No. 47 (Institute of Physics, Bristol and London, 1979) p. 318.
E. McAbee and M. Chmura, in Proceedings of the 16th Annual Technical Conference, SPI Reinforced Plastics Division, Chicago (Society of Plastics Industry, New York, 1961) Paper 13-D.
B. Revsin and S. R. Bodner, Israel J. Tech. 7 (1969) 485.
T. Fujii and M. Miki, in Proceedings of the Symposium on Mechanical Behaviour of Materials, Kyoto, Japan, 1973, p. 83.
I. M. Daniel, R. H. La Bedz and T. Liber, Exper. Mech. 21 (1981) 71.
K. Kawata, A. Hondo, S. Hashimoto, N. Takeda and H. L. Chung, in Proceedings of the Japan — US Conference on Composite Materials, Tokyo, January 1981, edited by K. Kawata and T. Akasaka (Japan Society for Composite Materials, Tokyo, 1981) p. 2.
J. Harding and L. M. Welsh, presented at the 4th International Conference on Composite Materials, Tokyo, October 1982 (Japan Society for Composite Materials).
P. D. Ewins, RAE Technical Report No. 71217 (1971).
“Grafil test methods”, Courtaulds Ltd., Carbon Fibres Unit, PO Box 16, Coventry, 1977.
J. Harding, E. O. Wood and J. D. Campbell, J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2 (1960) 88.
R. H. Cooper and J. D. Campbell, ibid. 9 (1967) 278.
E. Pink and J. D. Campbell, J. Mater. Sci. 9 (1974) 658.
D. F. Adams, ibid. 10 (1975) 1591.
R. R. Dixon, 35th SPE Conference, USA (1977) p. 344.
B. Harris and A. R. Bunsell, Composites 6 (1975) 197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harding, J., Welsh, L.M. A tensile testing technique for fibre-reinforced composites at impact rates of strain. J Mater Sci 18, 1810–1826 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542078
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542078