Abstract
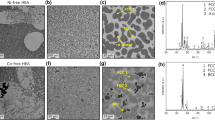
The main modes of isothermal oxidation of Fe-Cr-Al, Ni-Cr-Al, and Co-Cr-Al Alloys, containing 10–15 % or 26–30 % Cr and 0.9–1.3 % or 4.3–5.7% Al, in oxygen at 1000 and 1200° C are summarized. Where protectiveα-Al 2 O 3 scales always predominate, their ease of formation is in the order Fe-Cr-Al > Ni-Cr-Al > Co-Cr-Al. However, where catastrophic breakaway is possible, Ni-Cr-Al gives the most reliably protective scales, whereas Co-Cr-Al produces the most generally distributed breakaway or initially nonprotective scales, and Fe-Cr-Al the most locally catastrophic breakaway. The oxidation behavior is discussed in terms of the pertinent alloy and oxide parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. H. Stott, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester (1970).
M. G. Hobby, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Manchester (1968).
B. Chattopadhyay and G. C. Wood,Oxidation of Metals 2, 373 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stott, F.H., Wood, G.C. & Hobby, M.G. A comparison of the oxidation behavior of Fe-Cr-Al, Ni-Cr-Al, and Co-Cr-Al alloys. Oxid Met 3, 103–113 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603481
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603481