Summary
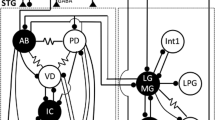
In the stomatogastric nervous system of the Cape lobster,Jasus lalandii, all the neurons comprising the pyloric central pattern generator are cellular oscillators. This was shown by isolating in situ pyloric neurons from all other elements in the pyloric network. These neuronal oscillators are conditional and require modulatory inputs from anterior centers in order to express their oscillatory capabilities.
-
1.
Pyloric neurons were isolated from their counterparts in the network by photoinactivation of most of their presynaptic neurons (Miller and Selverston 1979, 1982a), and completed by pharmacological blockade of the remaining presynaptic influences. Under these conditions, all pyloric neurons display spontaneous bursting and underlying oscillations of their membrane potential.
-
2.
Both period and amplitude of oscillation in all isolated pyloric neurons vary when their membrane potential is modified by current injection. Furthermore, in isolated constrictor neurons (LP, PY and IC) the duration of the rhythmic regenerative depolarizations is also dependent on membrane potential.
-
3.
After isolation in situ, each type of pyloric neuron manifests a particular oscillatory behavior. The isolated interneuron AB has the fastest oscillation period with the shortest depolarizing phase. These oscillations closely resemble AB oscillations in the intact network. At the other extreme are the constrictor neurons (LP, PY and IC) which, when isolated, display spontaneous oscillations rather different from their oscillations in the intact network. Oscillations of isolated pyloric constrictor neurons are rhythmical plateaus whose duration and frequency are fairly irregular.
-
4.
When axonal conduction is blocked in the single input nerve to the stomatogastric ganglion, none of the isolated pyloric neurons is able to oscillate whether at rest or when their membrane potential is modified by current injection. Under these conditions, electrical stimulation of the input nerve on the ganglionic side of the block restores oscillations in isolated pyloric neurons.
-
5.
In conclusion, the pyloric network can be considered as a set of conditional oscillatory neurons, one of which, the interneuron AB, has a pacemaker function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB :
-
anterior burster neuron
- BPP :
-
bursting pacemaker potential
- CPG :
-
central pattern generator
- PD :
-
dilator motor neuron
- STG :
-
stomatogastric ganglion
- VD :
-
ventricular dilator
References
Anderson WW, Kushner PD (1987) The pyloric pacemakers of the crayfish stomatogastric ganglion are conditional burster neurons. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. A model for the study of central nervous systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 139–145
Bidaut M (1980) Pharmacological dissection of pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion using picrotoxin. J Neurophysiol 44:1089–1101
Cardi P, Nagy F, Moulins M (in press) Variation discontinue de la fréquence d'oscillation dans un système d'oscillateurs neuronaux couplés. J Physiol (Paris)
Cazalets JR (1987) Contrôle de l'activité du réseau neuronique pylorique du homard par des afférences modulatrices suppressives: étude pharmacologique et électrophysiologique. Thèse de doctorat, Université de Bordeaux I
Cazalets JR, Nagy F, Moulins M (1987) Suppressive control of a rhythmic central pattern generator by an identified modulatory neuron in Crustacea. Neurosci Lett 81:267–272
Delcomyn F (1980) Neural basis of rhythmic behavior in animals. Science 210:492–498
Delmar M, Jalife J, Michaels DC (1986) Effects of changes in excitability and intercellular coupling on synchronization in the rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol (Lond) 370:127–150
Dickinson PS, Nagy F (1983) Control of a central pattern generator by an identified modulatory interneurone in Crustacea. II. Induction and modification of plateau properties in pyloric neurones. J Exp Biol 105:59–82
Eisen JS, Marder E (1984) A mechanism for production of phase shifts in a pattern generator. J Neurophysiol 51:1375–1393
Flamm RE, Harris-Warrick RM (1986) Aminergic modulation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. II. Target neurons of dopamine, octopamine, and serotonin within the pyloric circuit. J Neurophysiol 55:866–881
Frazier WT, Kandel ER, Kupfermann I, Waziri R, Coggeshall RE (1967) Morphological and functional properties of identified neurons in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica. J Neurophysiol 30:1288–1351
Getting PA (1987) Understanding central pattern generators: insights gained from the study of invertebrate systems. In: Grillner S, Stein PSG, Stuart DG, Forssberg H, Herman RM (eds) Neurobiology of vertebrate locomotion. Wenner-Gren Int Symp Series 45. MacMillan, pp 231–244
Getting PA (in press) Comparative analysis of invertebrate central pattern generators. In: Cohen AH, Rossignol S, Grillner S (eds) Neural control of rhythmic movements. Wiley, New York
Graubard K, Raper JA, Hartline DK (1983) Graded synaptic transmission between identified spiking neurons. J Neurophysiol 50:508–521
Harris-Warrick RM, Flamm RE (1987) Multiple mechanisms of bursting in a conditional bursting neuron. J Neurosci 7:2113–2128
Harris-Warrick RM, Johnson BR (in press) Potassium channel blockade induces rhythmic activity in a conditional burster neuron. Brain Res
Hooper SL, Marder E (1987) Modulation of the lobster pyloric rhythm by the peptide proctolin. J Neurosci 7:2097–2112
Marder E (1976) Cholinergic motor neurones in the stomatogastric system of the lobster. J Physiol (Lond) 257:63–86
Marder E, Eisen JS (1984a) Transmitter identification of pyloric neurons: electrically coupled neurons use different transmitters. J Neurophysiol 51:1345–1361
Marder E, Eisen JS (1984b) Electrically coupled pacemaker neurons respond differently to same physiological inputs and neurotransmitters. J Neurophysiol 51:1362–1374
Maynard DM (1972) Simpler networks. Ann NY Acad Sci 193:59–72
Maynard DM, Selverston AI (1975) Organization of the stomatogastric ganglion of the spiny lobster. IV. The pyloric system. J Comp Physiol 100:161–182
Meyrand P, Moulins M (1986) Myogenic oscillatory activity in the pyloric rhythmic motor system of Crustacea. J Comp Physiol A 158:489–503
Miller JP (1987) Pyloric mechanisms. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. A model for the study of central nervous systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 109–136
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1979) Rapid killing of single neurons by irradiation of intracellularly injected dye. Science 206:702–704
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1982a) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. II. Oscillatory properties of pyloric neurons. J Neurophysiol 48:1378–1391
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1982b) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. IV. Network properties of pyloric system. J Neurophysiol 48:1416–1432
Moulins M, Cournil I (1982) All-or-none control of the bursting properties of the pacemaker neurons of the lobster pyloric pattern generator. J Neurobiol 13:447–458
Moulins M, Nagy F (1981) Participation of an unpaired motor neurone in the bilaterally organized oesophageal rhythm in the lobstersJasus lalandii andPalinurus vulgaris. J Exp Biol 90:205–230
Moulins M, Nagy F (1983) Control of integration by extrinsic inputs in the crustacean pyloric circuit. J Physiol (Paris) 78:755–764
Moulins M, Nagy F (1985) Extrinsic inputs and flexibility in the motor output of the lobster pyloric neural network. In: Selverston AI (ed) Model neural networks and behavior. Plenum, New York London, pp 49–68
Mulloney B (1987) Neural circuits. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. A model for the study of central nervous systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 57–75
Nagy F (1981) Etude de l'expression d'activités motrices rythmiques organisées par des générateurs paucineuroniques du système nerveux stomatogastrique des crustacés décapodes. Thèse de doctorat d'état, Université de Bordeaux I
Nagy F, Dickinson PS (1983) Control of a central pattern generator by an identified modulatory interneurone in Crustacea. I. Modulation of the pyloric motor output. J Exp Biol 105:33–58
Nagy F, Miller JP (1987) Pyloric pattern generation inPanulirus interruptus is terminated by blockade of activity through the stomatogastric nerve. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. A model for the study of central nervous systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 136–139
Nagy F, Moulins M (1987) Extrinsic inputs. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. A model for the study of central nervous systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 205–242
Nusbaum MP, Marder E (1987) A newly identified modulatory proctolin-containing neuron (MP neuron) in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crabCancer borealis. Neurosci Abstr 13:1257
Prince DA (1983) Mechanisms of epileptogenesis in brain-slice model systems. In: Ward Jr AA, Penry JK, Purpura D (eds) Epilepsy. Raven Press, New York, pp 29–52
Robertson RM, Moulins M (1981) Oscillatory command input to the motor pattern generators of the crustacean stomatogastric ganglion. I. The pyloric rhythm. J Comp Physiol 143:453–463
Russell DF, Hartline DK (1978) Bursting neural networks: a reexamination. Science 200:453–456
Russell DF, Hartline DK (1982) Slow active potentials and bursting motor patterns in pyloric network of the lobster,Panulirus interruptus. J Neurophysiol 48:914–937
Selverston AI, Miller JP (1980) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. I. Pyloric system. J Neurophysiol 44:1102–1121
Selverston AI, Moulins M (1985) Oscillatory neural networks. Annu Rev Physiol 47:29–48
Selverston AI, Russell DF, Miller JP, King DG (1976) The stomatogastric nervous system: structure and function of a small neural network. Prog Neurobiol 7:215–290
Tazaki K, Cooke IM (1979) Spontaneous electrical activity and interaction of large and small cells in the cardiac ganglion of the crab,Portunus sanguinolentus. J Neurophysiol 42:975–999
Tazaki K, Cooke IM (1983) Separation of neuronal sites of driver potential and impulse generation by ligaturing in the cardiac ganglion of the lobster,Homarus americanus. J Comp Physiol 151:329–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, T., Nagy, F. & Moulins, M. The pyloric central pattern generator in Crustacea: a set of conditional neuronal oscillators. J. Comp. Physiol. 163, 715–727 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604049
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604049