Abstract
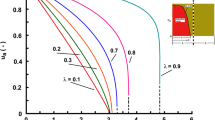
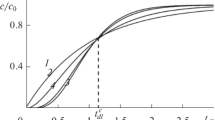
Under some constraints, solutes undergoing nonlinear adsorption migrate according to a traveling wave. Analytical traveling wave solutions were used to obtain an approximation for the solute front shape,c(z, t), for the situation of equilibrium nonlinear adsorption and first-order degradation. This approximation describes numerically obtained fronts and breakthrough curves well. It is shown to describe fronts more accurately than a solution based on linearized adsorption. The latter solution accounts neither for the relatively steep downstream solute front nor for the deceleration in time of the nonlinear front.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
parameter
- c :
-
concentration [mol/m3]
- c *0 :
-
depth-dependent local maximum concentration [mol/m3]
- δc; c 0;c i :
-
concentration difference, feed, and initial resident concentrations, respectively [mol/m3]
- D :
-
pore scale diffusion/dispersion coefficient [m2/yr]
- f :
-
adsorption isotherm
- f′:
-
derivative off toc
- f″:
-
second derivative off toc
- G * :
-
parameter
- K :
-
nonlinear adsorption coefficient [mol/m3)1−n]
- l :
-
column length [m]
- L d :
-
dispersivity [m]
- m :
-
parameter
- n :
-
Freundlich sorption parameter
- P :
-
function ofc *0
- δ q :
-
change inq [mol/m3]
- q :
-
adsorbed amount (volumetric basis) [mol/m3]
- q′:
-
derivative ofq toc
- R :
-
nonlinear retardation factor
- \(\tilde R\) :
-
retardation factor for concentrationc
- R l :
-
linear retardation factor
- 〈R(z *)〉:
-
depth-dependent average retardation factor, for front at depthz *
- s :
-
adsorbed amount (mass basis) [mol/kg]
- t :
-
time [years]
- u :
-
parameter
- v :
-
flow velocity [m]
- z * :
-
downstream front depth [m]
- z :
-
depth [m]
- η :
-
transformed coordinate [m]
- η * :
-
reference point value ofη [m]
- Μ :
-
first-order decay parameter [y−1]
- ρ :
-
dry bulk density [kg/m3]
- θ :
-
volumetric water fraction
- ζ :
-
parameter
References
Bolt, G. H., 1982, Movement of solutes in soil: Principles of adsorption/exchange chromatography, in G. H. Bolt (ed.),Soil Chemistry B, Physico-Chemical Models, Elsevier, New York, 1982, pp. 285–348.
Bond, W. J. and Philips, I. R., 1990, Approximate solutions for cation transport during unsteady, unsaturated soil water flow,Water Resour. Res. 26, 2195–2205.
Calvet, R., Tercé, M. and Arvieu, J. C., 1980, Adsorption des pesticides par les sols et leurs constituants. III. Caractéristiques générales de l'adsorption des pesticides,Ann. Agronomiques 31, 239–257.
Cameron, D. A. and Klute, A., 1977, Convective-dispersive solute transport with a combined equilibrium and kinetic adsorption model,Water Resour. Res. 13, 183–188.
Cederberg, G. A., Street, R. L. and Lecky, J. O., 1985, A groundwater mass transport and equilibrium chemistry model for multicomponent systems,Water Resour. Res. 12, 1095–1104.
Christensen, T. H., 1980, Cadmium sorption onto two mineral soils, Report, Dept. Sanit. Eng., Tech. Univ. of Denmark, Lingby.
Coats, K. H. and Smith, B. D., 1964, Dead-end pore volume and dispersion in porous media,Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 4, 73–84.
Deans, H. H., 1963, A mathematical model for dispersion in the direction of flow in porous media,Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 3(1), 49–52.
De Haan, F. A. M., van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. and van Riemsdijk, W. H., 1987, The role of soil chemistry and soil physics in protecting soil quality; Variability of sorption and transport of cadmium as an example,Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 35, 347–359.
De Smedt, F. and Wierenga, P. J., 1979, A generalized solution for solute flow in soils with mobile and immobile water,Water Resour. Res. 15, 1137–1141.
Friesel, P., Milde, G. and Steiner, B., 1984, Interactions of halogenated hydrocarbons with soils,Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 319, 160–164.
Frissel, M. J., Poelstra, P. and Reiniger, P., 1970, Chromatographic transport through soils: III A simulation model for the evaluation of the apparent diffusion coefficient in undisturbed soils with titriated water,Plant and Soil 33, 161–176.
Lake, L. W. and Helfferich, F., 1978, Cation exchange in chemical flooding, 2, The effect of dispersion, cation exchange, and polymer/surfactant adsorption on chemical flood environment,Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 18, 435–444.
Lexmond, Th. M., 1980, The effect of soil pH on copper toxicity to forage maize grown under field conditions,Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 28, 164–183.
Nkedi-Kizza, P., Biggar, J. W., Selim, H. M., van Genuchten, M. Th., Wierenga, P. J., Davidson, J. M. and Nielsen, D. R., 1984, On the equivalence of two conceptual models for describing ion exchange during transport through an aggregated oxisol,Water Resour. Res. 20, 1123–1130.
Reiniger, P. and Bolt, G. H., 1972, Theory of chromatography and its application to cation exchange in soils,Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 20, 301–313.
Selim, H. M., Davidson, J. M. and Mansell, R. S., 1976, Evaluation of a two-site adsorption-desorption model for describing solute transport in soils,Proc. 1976 Summer Computer Simulation Conference, July 12–14, Washington D.C., pp. 444–448.
Valocchi, A. J., 1985, Validity of the local equilibrium assumption for modeling sorbing solute transport through homogeneous soils,Water Resour. Res. 21, 808–820.
Van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., 1990, Analytical traveling wave solutions for transport with nonlinear and nonequilibrium adsorption,Water Resour. Res. 26, 2563–2578 (Correction, 1991,Water Resour. Res. 27, 983).
Van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. and Boesten, J. J. T. I., 1991, Effects of soil heterogeneity on pesticide leaching to ground water,Water Resour. Res. 27, 3051–3063.
Van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. and van Riemsdijk, W. H., 1987, Transport of reactive solute in spatially variable soil systems,Water Resour. Res. 23, 2059–2069.
Van Duijn, C. J. and Knabner, P., 1990, Traveling waves in the transport of reactive solutes through porous media: Adsorption and binary exchange, Part 2, Report 205, Schwertpunkt programm der Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Univ. Augsburg, Inst. Mathematik.
Van Genuchten, M. Th., 1981, Analytical solutions for chemical transport with simultaneous adsorption, zero-order production and first-order decay,J. Hydrol. 49, 213–233.
Van Genuchten, M. Th. and Alves, W. J., 1982, Analytical solutions of the one-dimensional convectivedispersive transport equation, USDA Tech. Bull. 1661. U.S. Dep. of Agric, Washington, D.C.
Van Genuchten, M. Th. and Wierenga, P. J., 1974, Simulation of one-dimensional solute transfer in porous media, Bull. 628, NMSU Agric. Exp. Stn., New Mexico State University, Las Cruces.
Van Genuchten, M. Th. and Wierenga, P. J., 1976, Mass transfer studies in sorbing porous media, I, Analytical solutions,Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 473–480.
Van Riemsdijk, W. H., Koopal, L. K. and de Wit, J. C. M., 1987, Heterogeneity and electrolyte adsorption: Intrinsic and electrostatic effects,Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 35, 241–257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosma, W.J.P., Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. Analytical approximation for nonlinear adsorbing solute transport and first-order degradation. Transp Porous Med 11, 33–43 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614633
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614633